Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
Display Method:
, Available online ,
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-024
Abstract:
, Available online ,
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-015
Abstract:
, Available online ,
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-026
Abstract:
, Available online ,
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-025
Abstract:
, Available online ,
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-020
Abstract:
, Available online ,
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-018
Abstract:
2025, 55(4): 707-746.
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-021
Abstract:
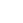
Non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials are a class of architected functional materials that exhibit negative or zero Poisson’s ratio effect at the macroscopic scale through configuration design. Their distinctive capabilities in controlling transverse deformation, maintaining dimensional stability, and enhancing energy absorption confer significant potential for applications in aerospace, marine engineering, transportation, wearable protective equipment, and biomedicine. In recent years, continuous advancements in microstructural design, advanced material fabrication techniques, and multi-material integration methods have driven significant progress in non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials, particularly in configuration diversity, mechanical response tunability, and multifunctional integration. Guided by the dominant mechanisms that activate transverse deformation, this paper systematically surveys the typical design strategies of non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials. For negative Poisson’s ratio architectures, the discussion is organized around re-entrant geometries, rotating systems (rotating rigid-body/truss and chiral/anti-chiral configurations), kirigami/origami schemes, elastic instability-induced mechanisms, and rigid-body linkages. Zero Poisson’s ratio architectures are categorized into geometric paradigms, including rectangular/parallelogram-like, semi-re-entrant, positive/negative Poisson’s ratio unit combinations, and rigid-flexible composites. Focusing on performance requirements in cushioning and energy absorption, enhancement strategies include multi-plateau response designs, graded structural architectures, multi-material coupling, and the incorporation of smart materials. At the level of structural integration, technical pathways such as modular assembly, sandwich structure, and intrinsically three-dimensional architectures are reviewed. Finally, by synthesizing recent research progress on non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials in terms of design and fabrication, performance regulation, and system integration, the current core technical bottlenecks are identified, the key directions for breakthroughs are clarified, and future development pathways for multiscale manufacturing, multifield response integration, and engineering applications are proposed.
Non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials are a class of architected functional materials that exhibit negative or zero Poisson’s ratio effect at the macroscopic scale through configuration design. Their distinctive capabilities in controlling transverse deformation, maintaining dimensional stability, and enhancing energy absorption confer significant potential for applications in aerospace, marine engineering, transportation, wearable protective equipment, and biomedicine. In recent years, continuous advancements in microstructural design, advanced material fabrication techniques, and multi-material integration methods have driven significant progress in non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials, particularly in configuration diversity, mechanical response tunability, and multifunctional integration. Guided by the dominant mechanisms that activate transverse deformation, this paper systematically surveys the typical design strategies of non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials. For negative Poisson’s ratio architectures, the discussion is organized around re-entrant geometries, rotating systems (rotating rigid-body/truss and chiral/anti-chiral configurations), kirigami/origami schemes, elastic instability-induced mechanisms, and rigid-body linkages. Zero Poisson’s ratio architectures are categorized into geometric paradigms, including rectangular/parallelogram-like, semi-re-entrant, positive/negative Poisson’s ratio unit combinations, and rigid-flexible composites. Focusing on performance requirements in cushioning and energy absorption, enhancement strategies include multi-plateau response designs, graded structural architectures, multi-material coupling, and the incorporation of smart materials. At the level of structural integration, technical pathways such as modular assembly, sandwich structure, and intrinsically three-dimensional architectures are reviewed. Finally, by synthesizing recent research progress on non-positive Poisson’s ratio mechanical metamaterials in terms of design and fabrication, performance regulation, and system integration, the current core technical bottlenecks are identified, the key directions for breakthroughs are clarified, and future development pathways for multiscale manufacturing, multifield response integration, and engineering applications are proposed.
2025, 55(4): 747-818.
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-005
Abstract:
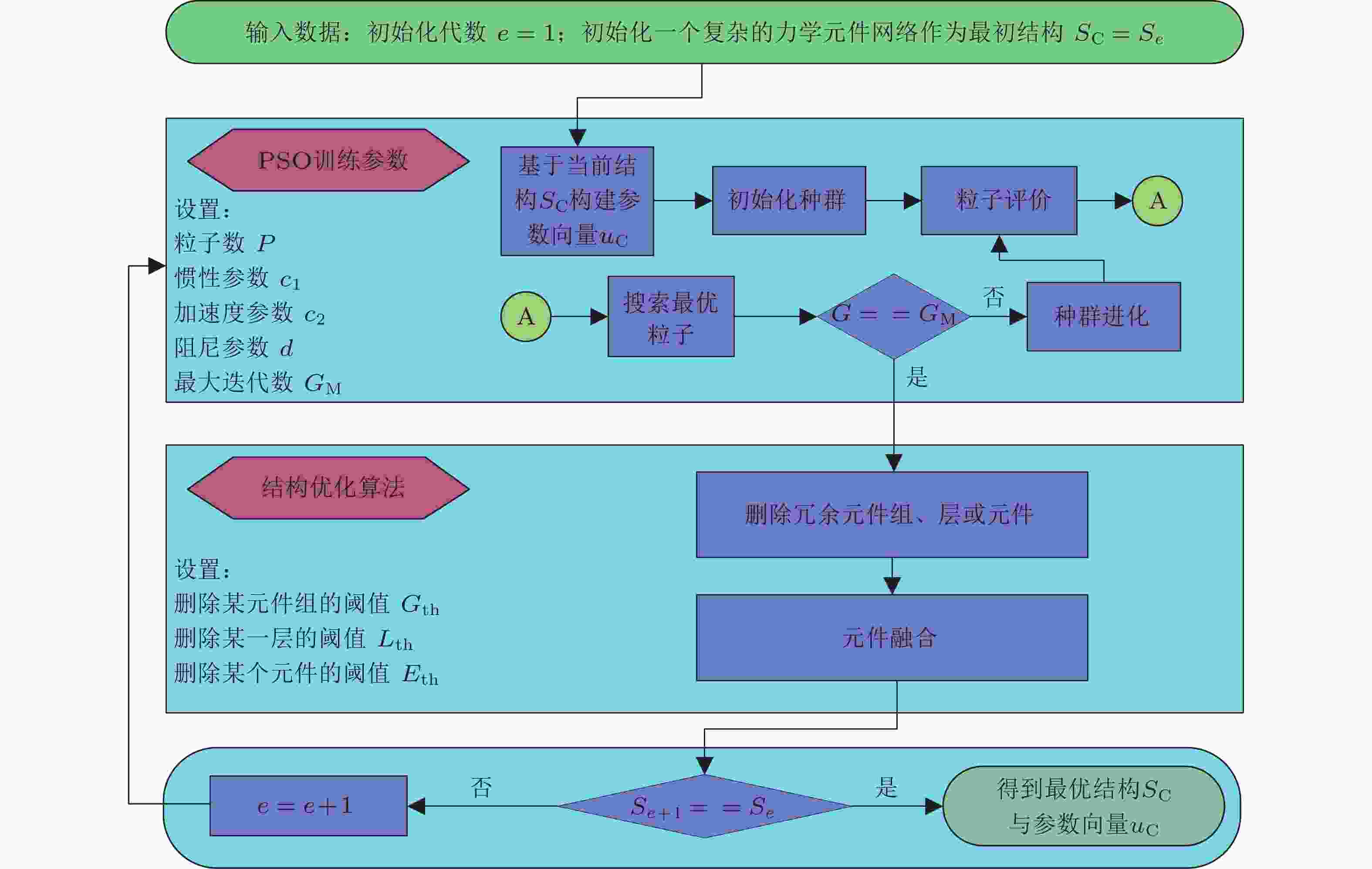
Dynamics and control is a discipline that studies the dynamic mechanisms of systems and their control strategies, and plays an important role in modern engineering and scientific research. The complexity caused by geometric nonlinearity, the non-smoothness of contact forces, and the uncertainty of environmental interferences and multi-physics problems poses significant challenges to dynamic modeling, prediction and intelligent control. The rapid development of data-driven methods has provided new ideas and new research paradigms for addressing these challenges. Recent researches have shown that data-driven methods can not only solve some problems that traditional dynamics methods cannot address but also significantly enhance the ability to predict dynamical behavior and design advanced structures. These methods lay the foundation for intelligent research in dynamics and control and demonstrate great potential and scientific value in the modeling, analysis, and regulation and control of complex systems. This paper briefly reviews the research progress of data-driven methods in areas such as robot motion control, transonic aeroelastic modeling and analysis, dynamics design, stochastic dynamics, neurodynamics, fault diagnosis and remaining useful life prediction of machinery. It also discusses the challenges and trends in these fields.
Dynamics and control is a discipline that studies the dynamic mechanisms of systems and their control strategies, and plays an important role in modern engineering and scientific research. The complexity caused by geometric nonlinearity, the non-smoothness of contact forces, and the uncertainty of environmental interferences and multi-physics problems poses significant challenges to dynamic modeling, prediction and intelligent control. The rapid development of data-driven methods has provided new ideas and new research paradigms for addressing these challenges. Recent researches have shown that data-driven methods can not only solve some problems that traditional dynamics methods cannot address but also significantly enhance the ability to predict dynamical behavior and design advanced structures. These methods lay the foundation for intelligent research in dynamics and control and demonstrate great potential and scientific value in the modeling, analysis, and regulation and control of complex systems. This paper briefly reviews the research progress of data-driven methods in areas such as robot motion control, transonic aeroelastic modeling and analysis, dynamics design, stochastic dynamics, neurodynamics, fault diagnosis and remaining useful life prediction of machinery. It also discusses the challenges and trends in these fields.
2025, 55(4): 819-853.
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-012
Abstract:
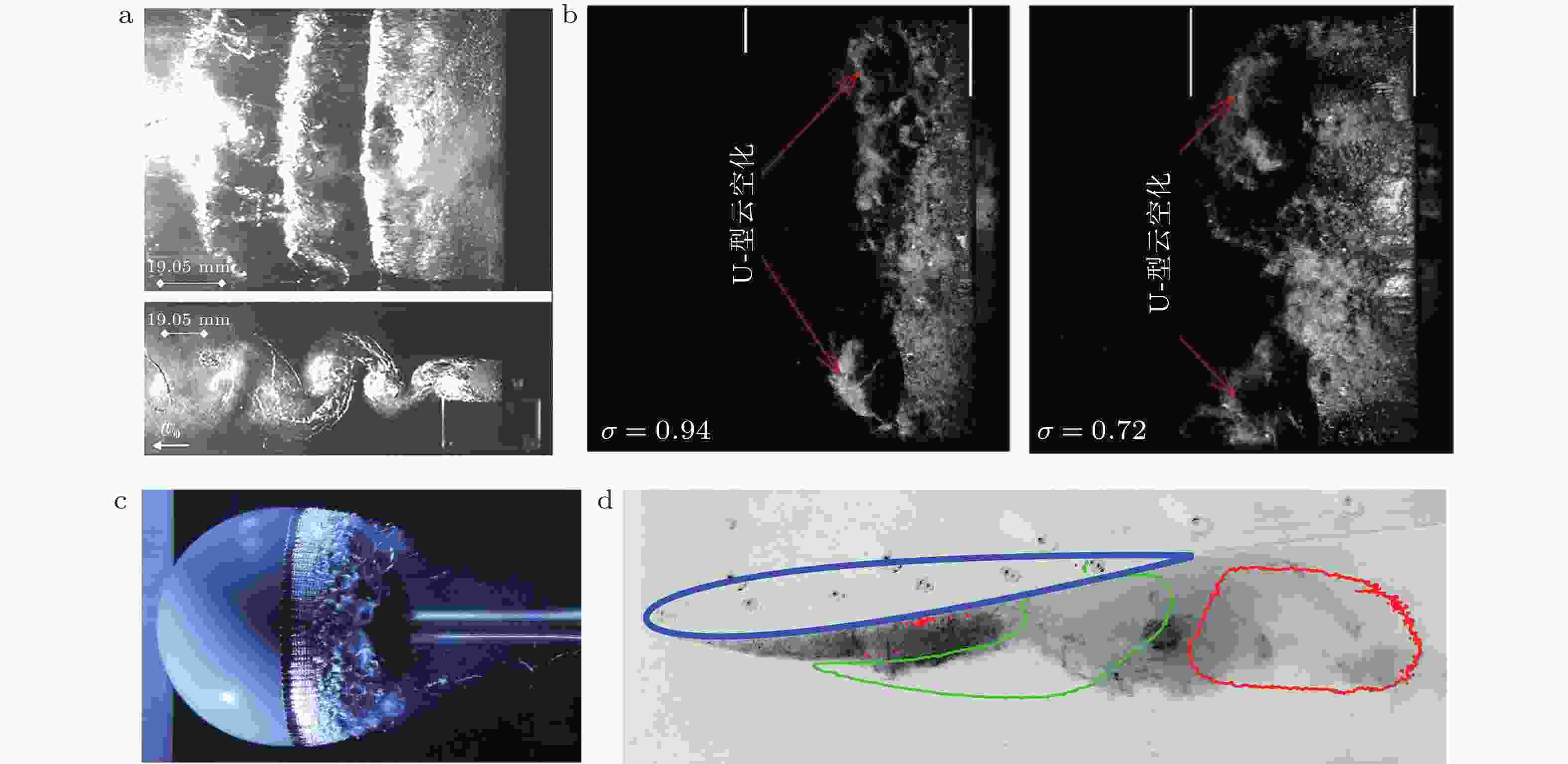
Hydrodynamic cavitation is a prevalent physical phenomenon in ship propulsion and underwater vehicles. To accurate prediction of cavitation noise prediction and cavitation erosion forecasting, this paper reviews key advances over the past two decades: nuclei and inception mechanisms of cavitation, pressure fluctuations and acoustic propagation across cloud cavitating regions, interaction between cavitation and turbulence, transient impact dynamics during cavity collapse and shock wave generation. Current research status and limitations are discussed through perspectives including phase transition model, multiphase flow simulation methodology, and cavitation-turbulence interactions. A concise overview is presented on multi-scale simulation methodologies for cavitating flows, summarizing recent insights into mixed-phase medium characteristics within cavitating zones and spatiotemporal evolution features of cavity fields derived from meso-scale simulations. For future development in multi-scale modeling and engineering forecasting of cavitating flows, the paper identifies two critical theoretical challenges requiring quantitative characterization: (1) fundamental modeling of vapor-water mixture properties in cavitating regions; and (2) precise representation of spatiotemporal dynamics of cavitating flows.
Hydrodynamic cavitation is a prevalent physical phenomenon in ship propulsion and underwater vehicles. To accurate prediction of cavitation noise prediction and cavitation erosion forecasting, this paper reviews key advances over the past two decades: nuclei and inception mechanisms of cavitation, pressure fluctuations and acoustic propagation across cloud cavitating regions, interaction between cavitation and turbulence, transient impact dynamics during cavity collapse and shock wave generation. Current research status and limitations are discussed through perspectives including phase transition model, multiphase flow simulation methodology, and cavitation-turbulence interactions. A concise overview is presented on multi-scale simulation methodologies for cavitating flows, summarizing recent insights into mixed-phase medium characteristics within cavitating zones and spatiotemporal evolution features of cavity fields derived from meso-scale simulations. For future development in multi-scale modeling and engineering forecasting of cavitating flows, the paper identifies two critical theoretical challenges requiring quantitative characterization: (1) fundamental modeling of vapor-water mixture properties in cavitating regions; and (2) precise representation of spatiotemporal dynamics of cavitating flows.
2025, 55(4): 854-907.
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-003
Abstract:
Many engineering problems involve coupling effects of multiple physical fields, which pose significant challenges for numerical simulations. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a classic meshfree particle method that offers distinct advantages in simulating multi-physics coupling problems and has been widely applied in various fields of sciences and engineering. This paper focuses on recent advances in SPH and its applications in multi-physics simulations. The key topics include: (1) mechano-thermal coupled problems, such as heat and mass transfer, high-speed impacts, casting processes, and additive manufacturing; (2) mechano-thermal-chemical coupled problems, with complex scenarios including shaped charge jet formation and penetration effects, explosive welding, and underwater explosions; (3) mechano-thermal-electromagnetic coupled problems, including electromagnetic flow control and “X-pinch” phenomena. Finally, the future development of the SPH method in simulating multi-physics coupling problems is discussed and prospected.
Many engineering problems involve coupling effects of multiple physical fields, which pose significant challenges for numerical simulations. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a classic meshfree particle method that offers distinct advantages in simulating multi-physics coupling problems and has been widely applied in various fields of sciences and engineering. This paper focuses on recent advances in SPH and its applications in multi-physics simulations. The key topics include: (1) mechano-thermal coupled problems, such as heat and mass transfer, high-speed impacts, casting processes, and additive manufacturing; (2) mechano-thermal-chemical coupled problems, with complex scenarios including shaped charge jet formation and penetration effects, explosive welding, and underwater explosions; (3) mechano-thermal-electromagnetic coupled problems, including electromagnetic flow control and “X-pinch” phenomena. Finally, the future development of the SPH method in simulating multi-physics coupling problems is discussed and prospected.
2025, 55(4): 908-947.
doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-25-007
Abstract:
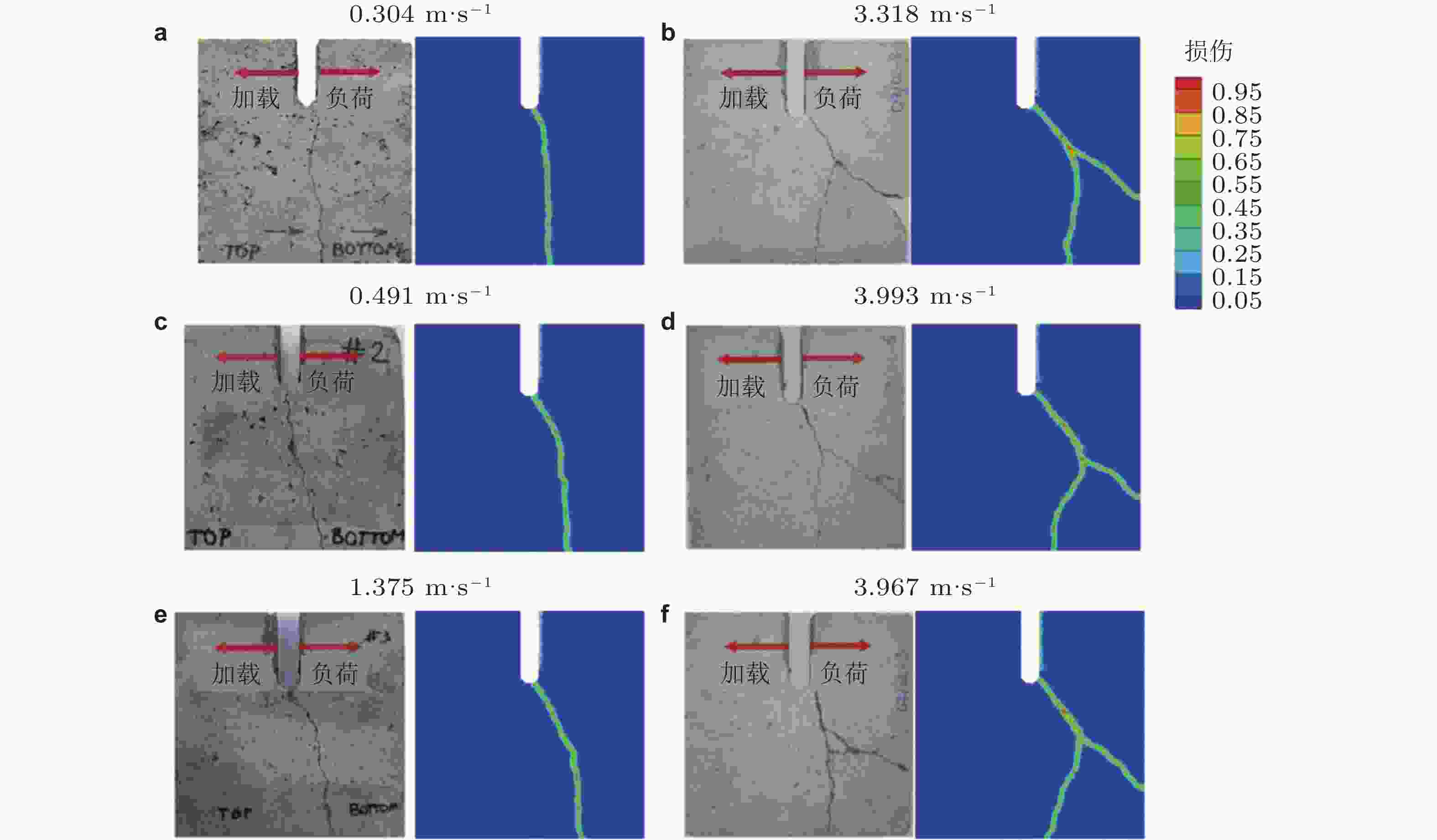
Peridynamics, as an emerging non-local continuum theory, has significant advantages over traditional continuum theories in simulating crack initiation and crack propagation along arbitrary paths. It is particularly well-suited for describing transient damage and fracture problems in brittle and quasi-brittle materials. This paper first provides an overview of the basic theory of peridynamics and failure criteria for material fracture and damage. It then presents a detailed review of recent research on damage prediction and fracture modeling of various brittle and quasi-brittle materials (such as ceramics, concrete, glass, and rocks) within the peridynamic framework. Finally, the paper discusses open issues in the peridynamic theory that warrant further investigation for these materials.
Peridynamics, as an emerging non-local continuum theory, has significant advantages over traditional continuum theories in simulating crack initiation and crack propagation along arbitrary paths. It is particularly well-suited for describing transient damage and fracture problems in brittle and quasi-brittle materials. This paper first provides an overview of the basic theory of peridynamics and failure criteria for material fracture and damage. It then presents a detailed review of recent research on damage prediction and fracture modeling of various brittle and quasi-brittle materials (such as ceramics, concrete, glass, and rocks) within the peridynamic framework. Finally, the paper discusses open issues in the peridynamic theory that warrant further investigation for these materials.
ArchiveMore>
- 2025 Vol. 3
- 2025 Vol. 2
- 2025 Vol. 1
- 2024 Vol. 4
- 2024 Vol. 3
- 2024 Vol. 2
- 2024 Vol. 1
- 2023 Vol. 4
- 2023 Vol. 3
- 2023 Vol. 2
- 2023 Vol. 1
- 2022 Vol. 4
- 2022 Vol. 3
- 2022 Vol. 2
- 2022 Vol. 1
- 2021 Vol. 4
- 2021 Vol. 3
- 2021 Vol. 2
- 2021 Vol. 1
- 2020 Vol. 1
- 2019 Vol. 1
- 2018 Vol. 1
- 2017 Vol. 1
- 2016 Vol. 1
- 2015 Vol. 1
- 2014 Vol. 1
- 2013 Vol. 6
- 2013 Vol. 5
- 2013 Vol. 4
- 2013 Vol. 3
- 2013 Vol. 2
- 2013 Vol. 1
- 2012 Vol. 6
- 2012 Vol. 5
- 2012 Vol. 4
- 2012 Vol. 3
- 2012 Vol. 2
- 2012 Vol. 1
- 2011 Vol. 6
- 2011 Vol. 5
- 2011 Vol. 4
- 2011 Vol. 3
- 2011 Vol. 2
- 2011 Vol. 1
- 2010 Vol. 6
- 2010 Vol. 5
- 2010 Vol. 4
- 2010 Vol. 3
- 2010 Vol. 2
- 2010 Vol. 1
- 2009 Vol. 6
- 2009 Vol. 5
- 2009 Vol. 4
- 2009 Vol. 3
- 2009 Vol. 2
- 2009 Vol. 1
- 2008 Vol. 6
- 2008 Vol. 5
- 2008 Vol. 4
- 2008 Vol. 3
- 2008 Vol. 2
- 2008 Vol. 1
- 2007 Vol. 4
- 2007 Vol. 3
- 2007 Vol. 2
- 2007 Vol. 1
- 2006 Vol. 4
- 2006 Vol. 3
- 2006 Vol. 2
- 2006 Vol. 1
- 2005 Vol. 4
- 2005 Vol. 3
- 2005 Vol. 2
- 2005 Vol. 1
- 2004 Vol. 4
- 2004 Vol. 3
- 2004 Vol. 2
- 2004 Vol. 1
- 2003 Vol. 4
- 2003 Vol. 3
- 2003 Vol. 2
- 2003 Vol. 1
- 2002 Vol. 4
- 2002 Vol. 3
- 2002 Vol. 2
- 2002 Vol. 1
- 2001 Vol. 4
- 2001 Vol. 3
- 2001 Vol. 2
- 2001 Vol. 1
- 2000 Vol. 4
- 2000 Vol. 3
- 2000 Vol. 2
- 2000 Vol. 1
- 1999 Vol. 4
- 1999 Vol. 3
- 1999 Vol. 2
- 1999 Vol. 1
- 1998 Vol. 4
- 1998 Vol. 3
- 1998 Vol. 2
- 1998 Vol. 1
- 1997 Vol. 4
- 1997 Vol. 3
- 1997 Vol. 2
- 1997 Vol. 1
- 1996 Vol. 4
- 1996 Vol. 3
- 1996 Vol. 2
- 1996 Vol. 1
- 1995 Vol. 4
- 1995 Vol. 3
- 1995 Vol. 2
- 1995 Vol. 1
- 1994 Vol. 4
- 1994 Vol. 3
- 1994 Vol. 2
- 1994 Vol. 1
- 1993 Vol. 4
- 1993 Vol. 3
- 1993 Vol. 2
- 1993 Vol. 1
- 1992 Vol. 4
- 1992 Vol. 3
- 1992 Vol. 2
- 1992 Vol. 1
- 1991 Vol. 4
- 1991 Vol. 3
- 1991 Vol. 2
- 1991 Vol. 1
- 1990 Vol. 4
- 1990 Vol. 3
- 1990 Vol. 2
- 1990 Vol. 1
- 1989 Vol. 4
- 1989 Vol. 3
- 1989 Vol. 2
- 1989 Vol. 1
- 1988 Vol. 4
- 1988 Vol. 3
- 1988 Vol. 2
- 1988 Vol. 1
- 1987 Vol. 4
- 1987 Vol. 3
- 1987 Vol. 2
- 1987 Vol. 1
- 1986 Vol. 4
- 1986 Vol. 3
- 1986 Vol. 2
- 1986 Vol. 1
- 1985 Vol. 4
- 1985 Vol. 3
- 1985 Vol. 2
- 1985 Vol. 1
- 1984 Vol. 4
- 1984 Vol. 3
- 1984 Vol. 2
- 1984 Vol. 1
- 1983 Vol. 4
- 1983 Vol. 3
- 1983 Vol. 2
- 1983 Vol. 1
- 1982 Vol. 4
- 1982 Vol. 3
- 1982 Vol. 2
- 1982 Vol. 1
- 1981 Vol. 4
- 1981 Vol. 3
- 1981 Vol. 2
- 1981 Vol. 1
- 1980 Vol. 4
- 1980 Vol. 2~3
- 1980 Vol. 1
- 1979 Vol. 4
- 1979 Vol. 3
- 1979 Vol. 2
- 1979 Vol. 1
- 1978 Vol. 2
- 1978 Vol. 1
- 1977 Vol. 2
- 1977 Vol. 1
- 1976 Vol. 4
- 1976 Vol. 3
- 1976 Vol. 2
- 1976 Vol. 1
- 1975 Vol. 2
- 1975 Vol. 1
- 1974 Vol. 2
- 1974 Vol. 1
- 1973 Vol. 6
- 1973 Vol. 5
- 1973 Vol. 4
- 1973 Vol. 3
- 1973 Vol. 2
- 1973 Vol. 1
- 1972 Vol. 12
- 1972 Vol. 11
- 1972 Vol. 10
- 1972 Vol. 9
- 1972 Vol. 8
- 1972 Vol. 7
- 1972 Vol. 6
- 1972 Vol. 5
- 1972 Vol. 4
- 1972 Vol. 3
- 1972 Vol. 2
- 1972 Vol. 1
- 1971 Vol. 6
- 1971 Vol. 5
- 1971 Vol. 4
- 1971 Vol. 3
- 1971 Vol. 2
- 1971 Vol. 1
NoticeMore >
Author CenterMore >
Top Cited
Top Down
Top Read
- Mechanical frontiers in shale-gas development
- Research progresses and prospects of unsteady hydrodynamics characteristics for cavitation
- Recent progress on finite element model updating: From linearity to nonlinearity
- Fundamental mechanics problems in metal additive manufacturing: A state-of-art review
- Mechanical problems in momentous projects of aerospace engineering
- Review on research progress of mechanical metamaterials and their applications in vibration and noise control
- Mechanics problems in application of acoustic black hole structures
- Coupling dynamics of floating wind turbines: History, progress and challenges
- Review on fluid-solid coupling and dynamic response of vortex-induced vibration of slender ocean cylinders
- Review on underwater sound absorption materials and mechanisms
- More >
- 1An overview on molecular dynamics simulation*
- 2Research advances in large eddy simulation of urban atmospheric environment
- More >
- 1Review on research progress of mechanical metamaterials and their applications in vibration and noise control
- 2Application of artificial intelligence in composite materials
- 3Thermofluid dynamics and its applications
- 4Mechanical frontiers in shale-gas development
- 5The extended finite element method and its applications ------ areview
- 6Characteristics of thermobaric explosives and their advances
- 7Fundamental mechanics problems in metal additive manufacturing: A state-of-art review
- 8AI for PDEs in solid mechanics: A review
- 9Research progress on the mechanics of high speed rails
- 10Review on underwater sound absorption materials and mechanisms
- More >
Related linksMore >

Follow WeChat

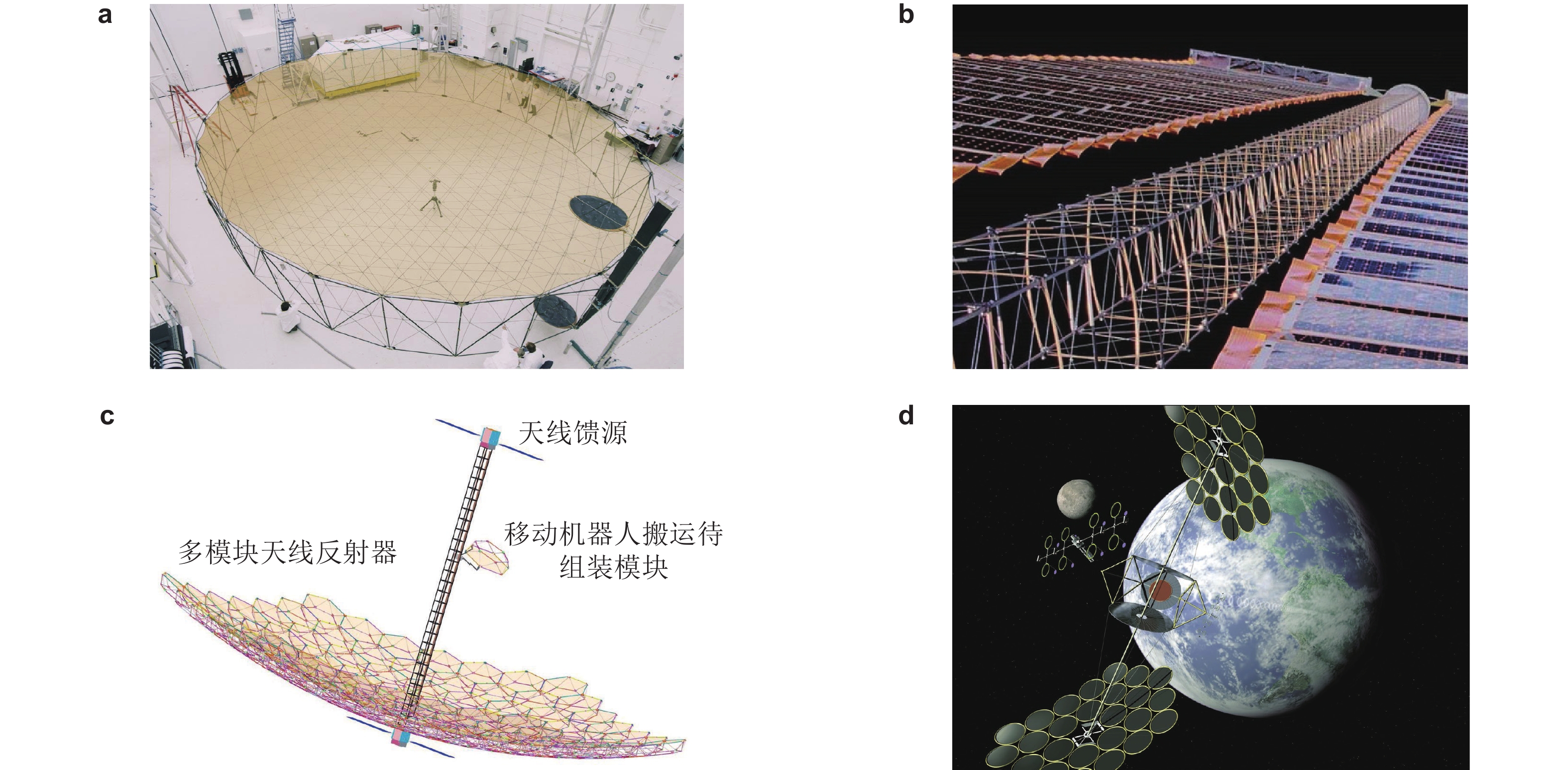
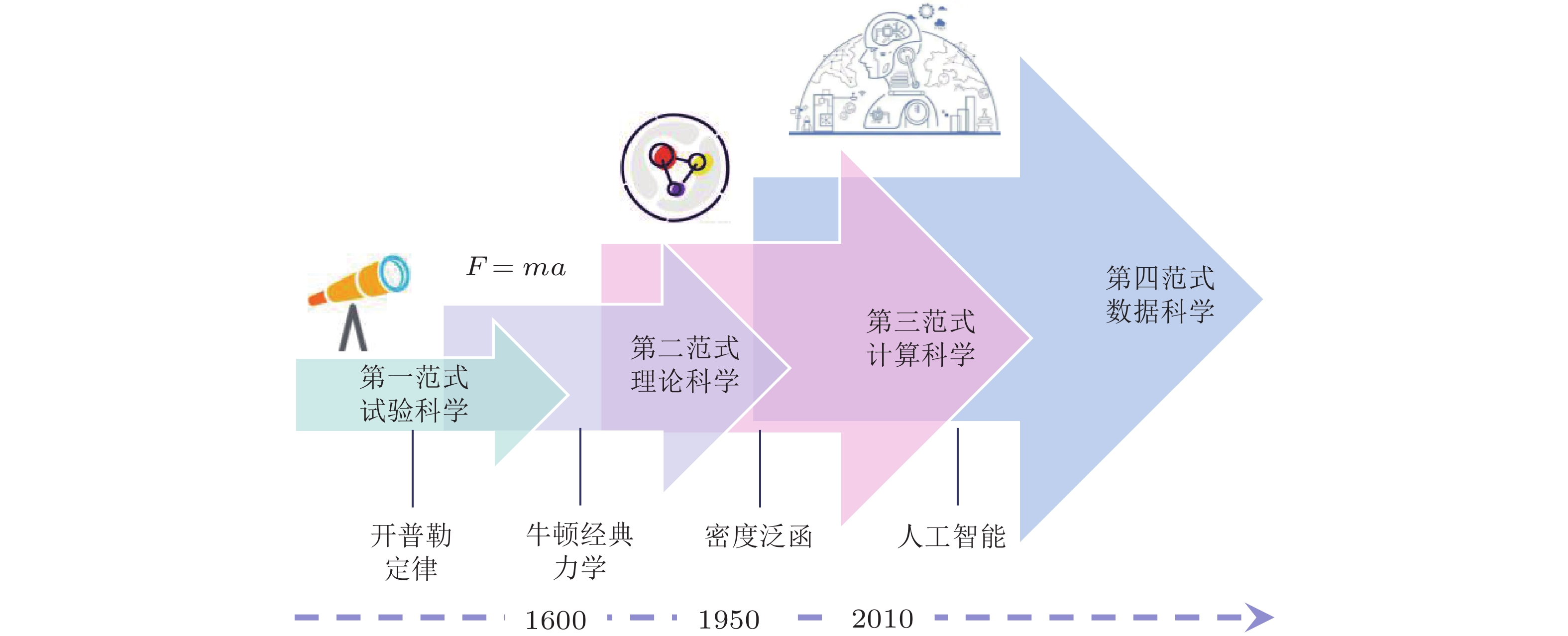
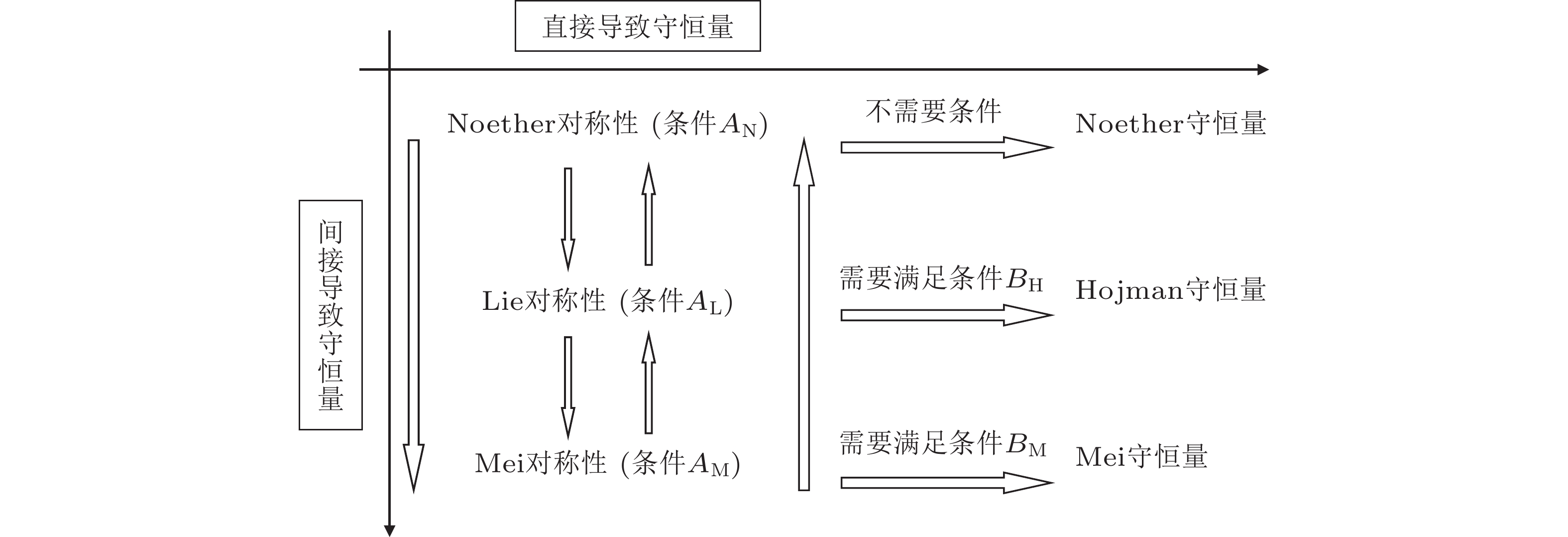
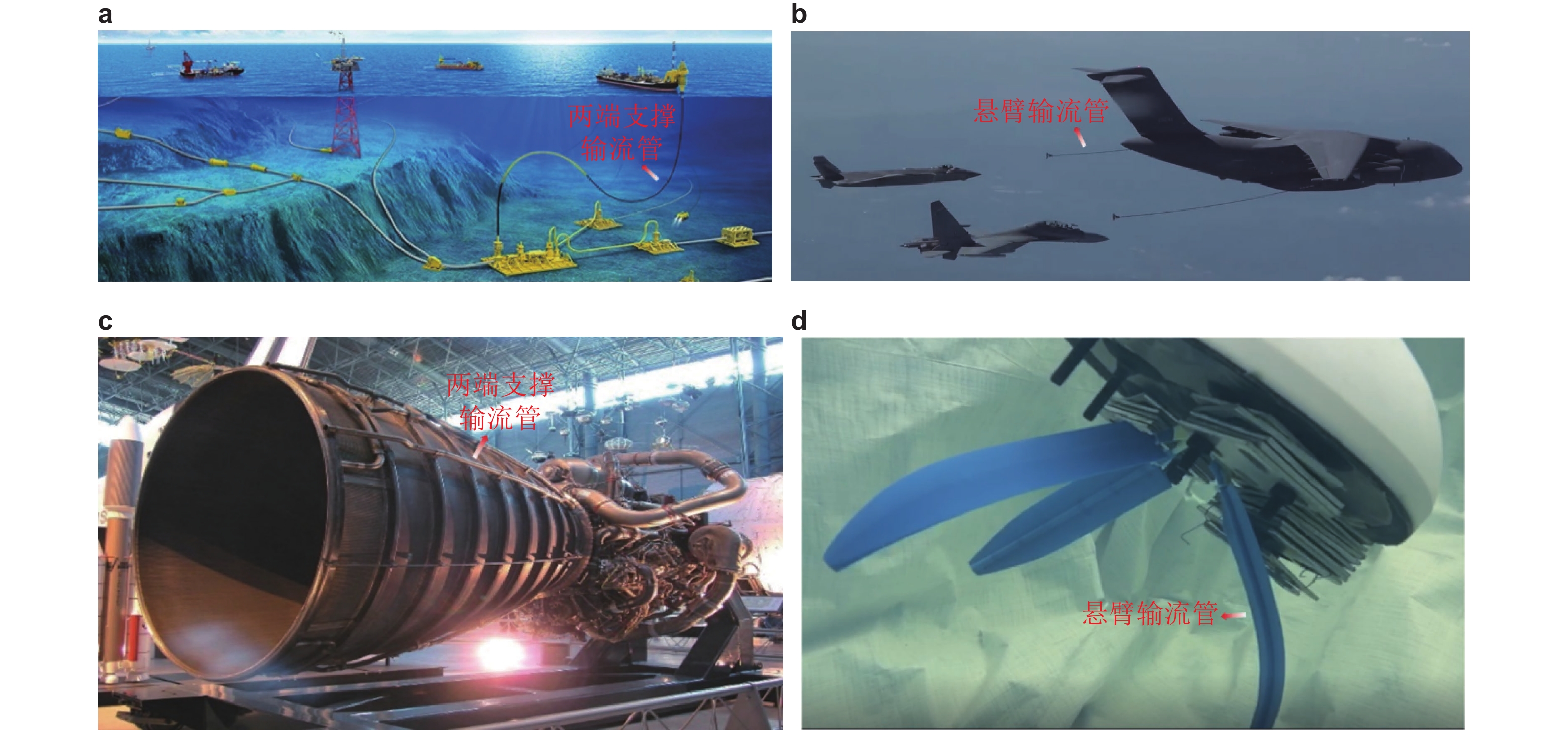




 Abstract
Abstract HTML
HTML PDF
PDF

 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS