Advances in matrix engineering and matrix therapy driven by extracellular matrix mechanics
-
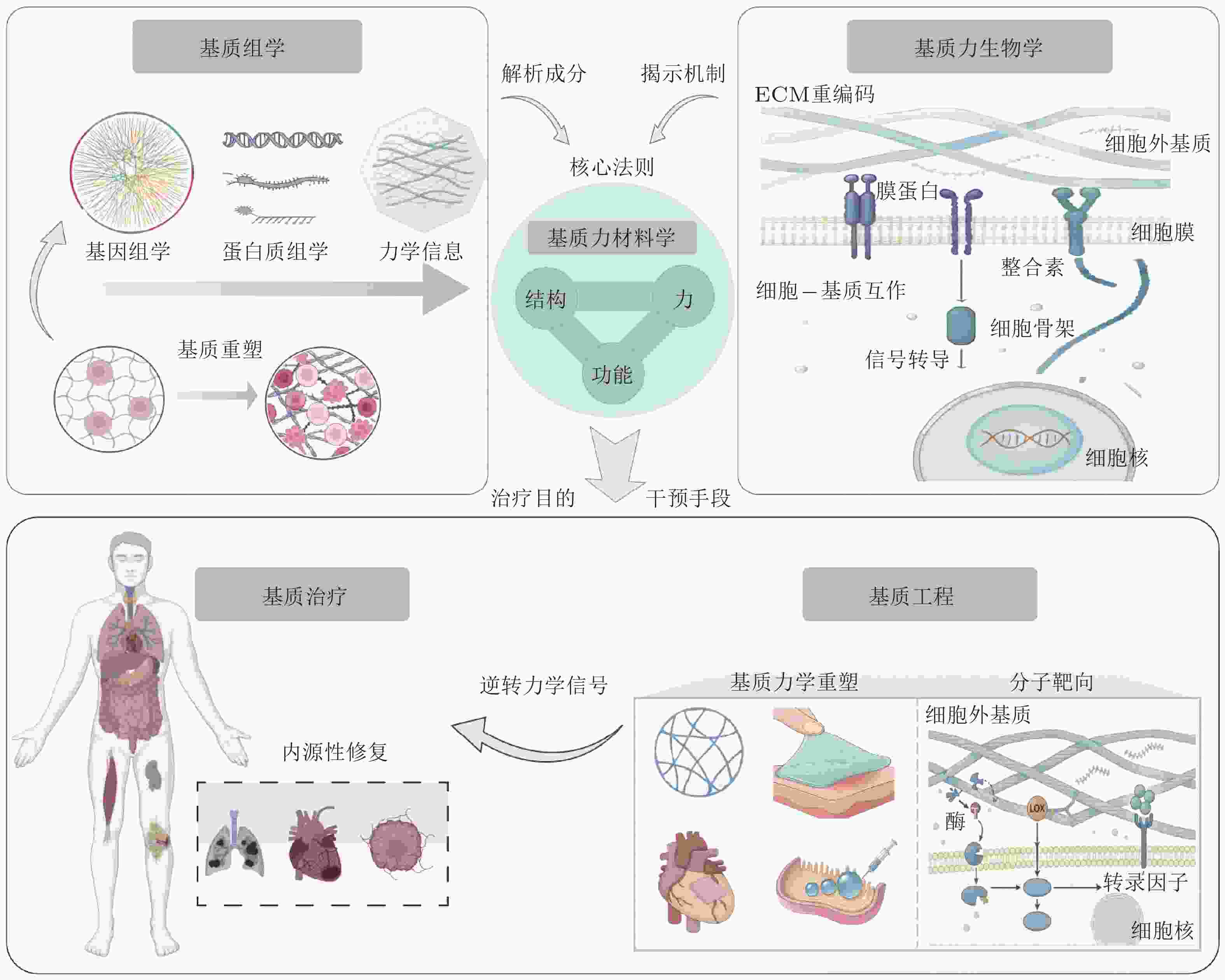
摘要: 随着全球人口老龄化和慢性病的高发, 心血管疾病、肿瘤、糖尿病等重大难治性疾病已成为全球公共健康和社会经济发展的主要挑战. 其病理进程通常伴随着细胞外基质(ECM)的异常重塑与力学稳态失衡, 导致传统治疗方法难以有效逆转. 近期研究揭示, 结合材料学与工程学原理主动调控ECM的力化属性以精准介导细胞行为, 能够有效激活组织内源性修复从而显著促进组织再生. 该研究策略被称为力材料学, 即通过对材料进行主动设计, 利用力−结构−功能关系对生命系统的力学环境进行主动控制. 基于此概念, 本文提出从基质组学角度系统鉴定ECM的分子组成并解构其力学信息编码; 利用基质力生物学认识细胞-ECM互作机制并解析病理ECM“重编码”过程; 在深入认知和理解ECM力学微环境基础上结合基质力材料学的研究思路, 探索对异常ECM“去编码”与功能恢复的基质工程技术; 最终实现组织内源性修复的基质治疗目的. 具体而言, 本文在介绍ECM的组成与动态编码的基础上, 系统总结了异常ECM力学微环境的生理/病理变化, 着重提出并构建基于分子靶向与材料重建的基质工程与治疗新策略, 旨在为重大难治性疾病的干预和再生医学的发展提供新的理论依据和创新思路.Abstract: With the global aging population and high incidence of chronic diseases, major intractable conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, tumors, and diabetes have become primary challenges to public health and socioeconomic development worldwide. Their pathological processes are often accompanied by abnormal remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and disruption of mechanical homeostasis, rendering traditional treatments ineffective in reversing these conditions. Recent studies reveal that actively modulating the mechanical properties of the ECM through principles of materials science and engineering to precisely mediate cellular behavior can effectively activate endogenous tissue repair, significantly promoting tissue regeneration. This research strategy, termed force-materials science, involves actively designing materials to leverage force-structure-function relationships for proactive control of the mechanical environment within biological systems. Based on this concept, this paper proposes: systematically identifying the molecular composition of the ECM from a matrixomics perspective and deconstructing its mechanical information encoding; utilizing matrix biomechanics to understand cell-ECM interaction mechanisms and decipher pathological ECM “re-encoding” processes; and, grounded in deep understanding of the ECM's mechanical microenvironment, exploring matrix engineering technologies for “de-encoding” abnormal ECM and restoring function by integrating matrix biomechanics principles. ultimately achieving the goal of matrix therapy for endogenous tissue repair. Specifically, this paper introduces the composition and dynamic coding of the ECM, systematically summarizes the physiological/pathological changes in abnormal ECM mechanical microenvironments, and emphasizes the proposal and construction of novel matrix engineering and therapeutic strategies based on molecular targeting and material reconstruction. These efforts aim to provide new theoretical foundations and innovative approaches for the intervention of major intractable diseases and the advancement of regenerative medicine.
-
Key words:
- Extracellular Matrix /
- Matrix Mechanics /
- Matrix Mechanobiology /
- Matrix Therapy /
- Matrix Engineering.
-
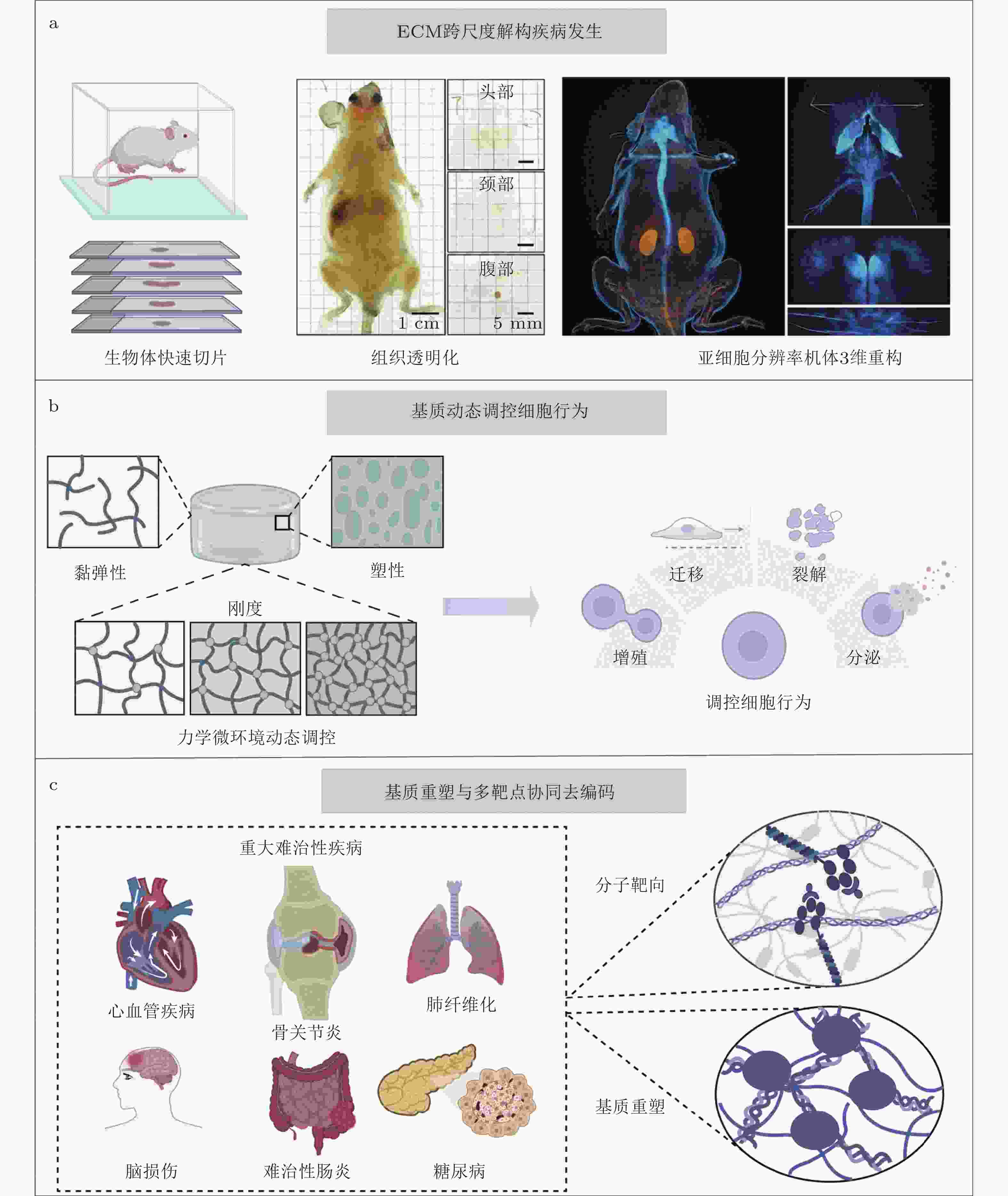
图 5 基质工程与基质治疗潜在应用. (a) ECM跨尺度解构疾病发生: 利用高分辨率整体成像建立从微观分子交联到宏观组织力学特性的全景力学图谱(Shi et al. 2025). (b)动态调控细胞行为: 通过光控水凝胶等智能技术, 在时间和空间维度上模拟生理或病理的动态力学变化. (c)基质力学重塑与多靶点协同去编码: 通过智能响应平台将基质力学重塑与分子靶向治疗深度融合, 实现复杂组织的内源性修复与功能再生
表 1 专业术语及释义
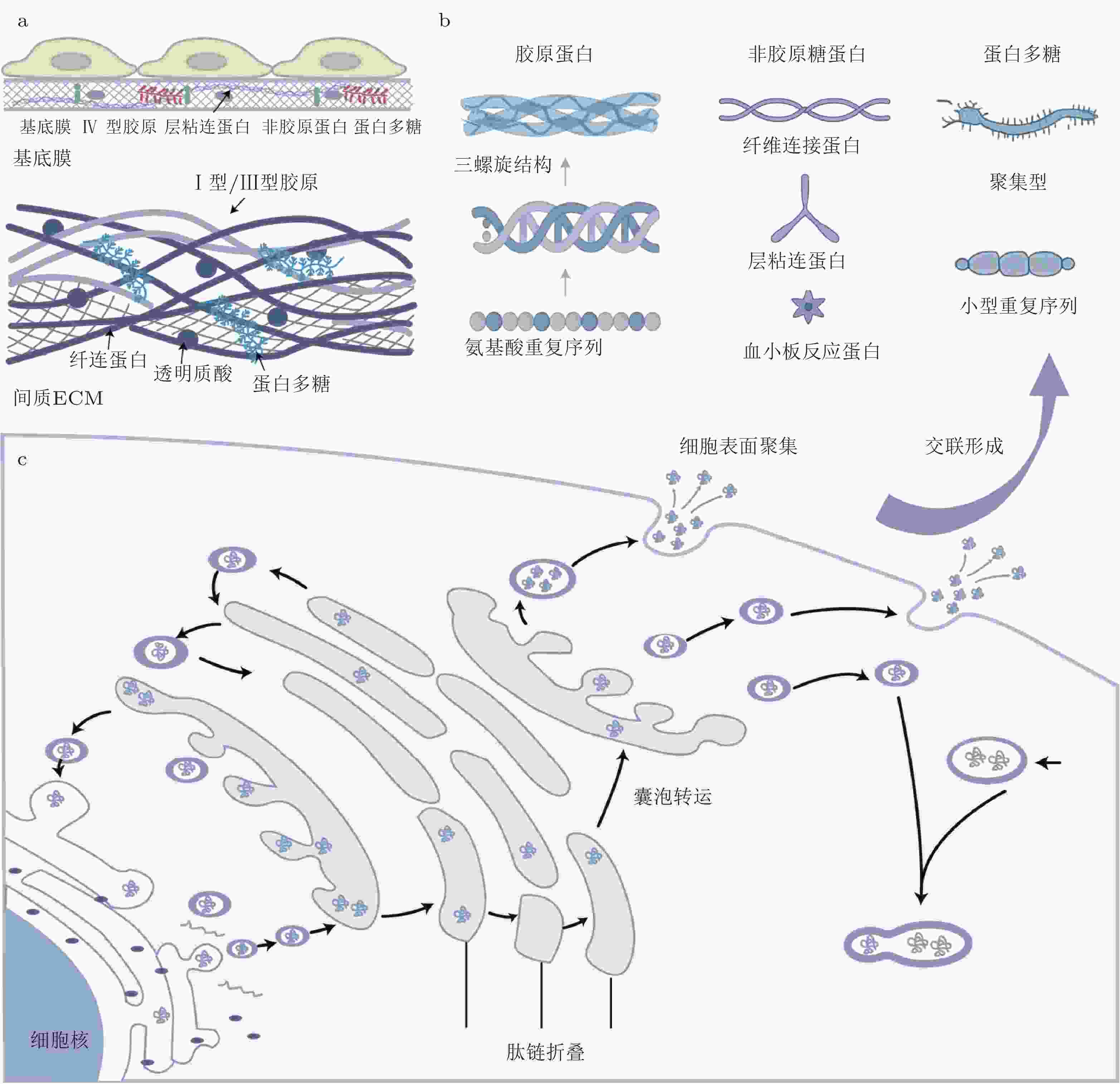
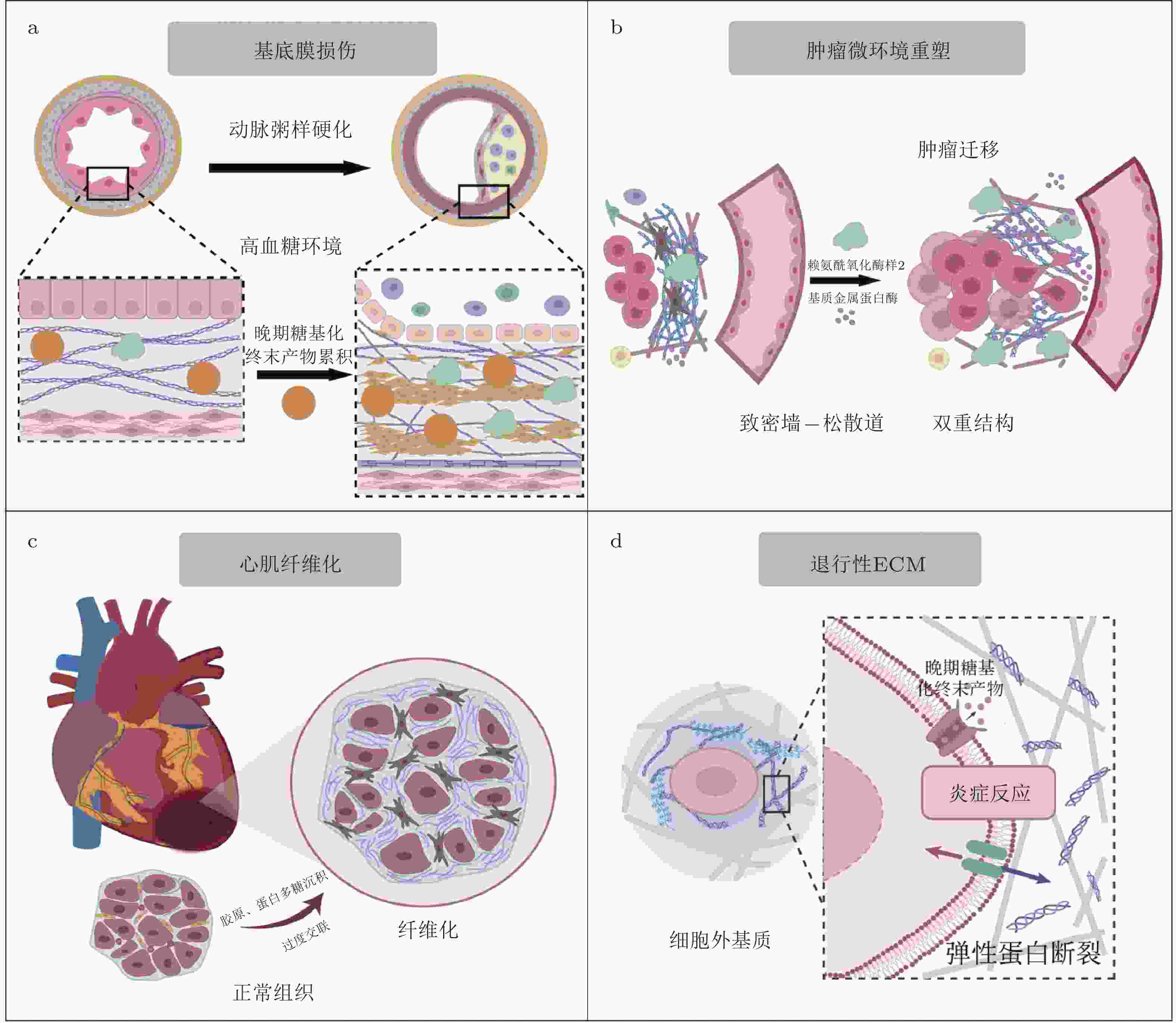
术语 英文 中文解释 细胞外基质 Extracellular Matrix (ECM) 细胞外基质是细胞之间的一种结构网络, 提供支持、信号传导以及调控细胞行为的作用. 基质力学重塑 Matrix Mechanics Remodeling ECM的组成和结构在不同生理或病理状态下的动态变化过程. 透明质酸 Hyaluronan ECM中的重要糖胺聚糖之一, 参与细胞的迁移、增殖和修复
过程.层粘连蛋白 Laminin ECM中的重要糖蛋白, 参与基底膜的结构稳定和细胞粘附. 整合素 Integrins 一类细胞膜受体, 参与细胞与ECM的连接, 调节细胞的形态、迁移、增殖和存活. 胶原蛋白 Collagen ECM中最重要的蛋白之一, 提供结构支持, 影响组织的强度和弹性. 纤维连接蛋白 Fibronectin ECM中的重要糖蛋白, 参与细胞粘附、迁移及信号转导. 基质金属蛋白酶 Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP) 基质金属蛋白酶, 降解ECM蛋白质, 参与组织重塑、伤口愈合及肿瘤转移等过程. 基质金属蛋白酶抑制因子 Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases (TIMP) 一类抑制基质金属蛋白酶的蛋白, 调节ECM的降解. 成纤维细胞 Fibroblasts 负责合成和分泌ECM成分的细胞, 尤其在组织修复和纤维化过程中发挥重要作用. 肌成纤维细胞 Myofibroblasts 成纤维细胞的一种类型, 具有类似平滑肌的功能, 在纤维化组织中发挥重要作用. 转化生长因子β Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) 一类多功能细胞因子, 参与细胞的增殖、分化、迁移等过程, 在纤维化、肿瘤发展等中发挥重要作用. 晚期糖基化终产物 Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) 糖化反应过程中生成的产物, 与多种衰老和退行性疾病相关. JNK JNK (c-Jun N-terminal Kinase) 一类MAPK家族的激酶, 参与细胞应激反应、炎症及细胞凋亡. RAGE受体 RAGE (Receptor for AGEs) 一种细胞表面受体, 能识别晚期糖基化终产物, 参与慢性炎症反应及多种疾病的进展. YAP/TAZ
信号通路YAP/TAZ signaling 细胞机制中, Hippo信号通路的下游效应器, 调控细胞的增殖、形态和组织发育. 黏着斑激酶 Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) 参与细胞与ECM粘附的酶, 调节细胞迁移和信号传导. PI3K/Akt
信号通路PI3K/Akt Pathway 重要的信号转导通路, 参与细胞的增殖、存活和代谢调控. MAPK通路 MAPK Pathway 一类广泛存在的细胞内信号转导通路, 参与细胞增殖、分化和应激反应. FAK/Src通路 FAK/Src signaling 由黏着斑激酶(FAK)与Src家族激酶通过磷酸化级联反应形成的信号复合体 ERK ERK (Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase) MAPK信号通路的一部分, 调控细胞增殖、分化和存活. SMAD信号通路 SMAD Signaling 参与转化生长因子β(TGF-β)信号传导的关键通路, 调节细胞的增殖、分化和迁移. 热休克蛋白47 HSP47 (Heat Shock Protein 47) 一种分子伴侣蛋白, 主要与胶原蛋白的折叠和稳定化过程相关, 参与ECM的合成. 赖氨酸氧化酶 LOX (Lysyl Oxidase) 参与胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白交联的酶, 调节ECM的稳定性. 血小板源生长因子 PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor) 一种生长因子, 调节细胞增殖和组织修复, 尤其在伤口愈合中发挥作用. 白细胞介素6 IL-6 (Interleukin 6) 一种细胞因子, 参与炎症反应、免疫调节和肿瘤免疫逃逸. NF-kB NF-kB (Nuclear Factor kappa B) 重要的转录因子, 调节免疫反应、细胞存活和炎症过程. Hippo Hippo Pathway 一种重要的信号通路, 调节细胞增殖、形态保持和组织发育. -
[1] 程波, 卢梦楠, 贾渊博, et al. 2025. 细胞的力学智能. 力学进展, 55(2): 340-377 (Cheng B, Lu M N, Jia Y B, et al. 2025. Cellular mechanical intelligence. Advances in Mechanics, 55(2): 340-377). doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-24-028Cheng B, Lu M N, Jia Y B, et al. 2025. Cellular mechanical intelligence. Advances in Mechanics, 55(2): 340-377. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-24-028 [2] 李林达, 丁奇寒, 陈深宝, et al. 2021. CD44-配体相互作用的生物力学与功能调控. 力学学报, 53(2): 539-553 (Li Linda, Ding Qihan, Chen Shenbao, et al. 2021. Biomechanics and Functional Regulations of CD44–Ligand Interactions. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 53(2): 539-553).Li Linda, Ding Qihan, Chen Shenbao, et al. 2021. Biomechanics and Functional Regulations of CD44–Ligand Interactions. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 53(2): 539-553. [3] 吕东媛, 周吕文, 龙勉, et al. 2017. 干细胞的生物力学研究. 力学进展, 47(1): 534-585 ((Dongyuan Lü, Lüwen ZHOU, Mian LONG. 2017. Biomechanics of stem cells. Advances in Mechanics, 47(1): 534-585).(Dongyuan Lü, Lüwen ZHOU, Mian LONG. 2017. Biomechanics of stem cells. Advances in Mechanics, 47(1): 534-585 [4] Akkiz H, Gieseler R KCanbay A. 2024. Liver Fibrosis: From Basic Science towards Clinical Progress, Focusing on the Central Role of Hepatic Stellate Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(14): 7873. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147873 [5] Al-u’datt D a, Allen B GNattel S. 2019. Role of the lysyl oxidase enzyme family in cardiac function and disease. Cardiovascular Research, 115(13): 1820-1837. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz176 [6] Aranapakam V, Grosu G T, Davis J M, et al. 2003. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of alpha-sulfonylhydroxamic acids as novel, orally active matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 46(12): 2361-2375. doi: 10.1021/jm0205548 [7] Aumailley M. 2013. The laminin family. Cell Adh Migr, 7(1): 48-55. doi: 10.4161/cam.22826 [8] Balestrini J L, Chaudhry S, Sarrazy V, et al. 2012. The mechanical memory of lung myofibroblasts. Integrative Biology, 4(4): 410-21. doi: 10.1039/c2ib00149g [9] Bates M E, Troop L, Brown M E, et al. 2023. Temporal application of lysyl oxidase during hierarchical collagen fiber formation differentially effects tissue mechanics. Acta Biomaterialia, 160: 98-111. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.02.024 [10] Bei Y-r, Zhang S-c, Song Y, et al. 2022. EPSTI1 promotes monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells in vitro via upregulating VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 44(1): 71-80. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-00923-5 [11] Benn M C, Weber W, Klotzsch E, et al. 2019. Tissue transglutaminase in fibrosis — more than an extracellular matrix cross-linker. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering, 10: 156-164. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2019.06.003 [12] Bhadriraju K, Yang M, Alom Ruiz S, et al. 2007. Activation of ROCK by RhoA is regulated by cell adhesion, shape, and cytoskeletal tension. Experimental Cell Research, 313(16): 3616-23. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.07.002 [13] Byun K, Yoo Y, Son M, et al. 2017. Advanced glycation end-products produced systemically and by macrophages: A common contributor to inflammation and degenerative diseases. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 177: 44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.030 [14] Cai P, Wang C, Gao H, et al. 2021. Mechanomaterials: A Rational Deployment of Forces and Geometries in Programming Functional Materials. Advanced Materials, 33(46): 2007977. doi: 10.1002/adma.202007977 [15] Cazzanelli PWuertz-Kozak K. 2020. MicroRNAs in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Mechanobiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10): 3601. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103601 [16] Chakraborty S, Dutta A, Roy A, et al. 2025. The theatrics of collagens in the myocardium: the supreme architect of the fibrotic heart. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 328(6): 1893-1920. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.01043.2024 [17] Charlesworth C T, Hsu I, Wilkinson A C, et al. 2022. Immunological barriers to haematopoietic stem cell gene therapy. Nature Reviews Immunology, 22(12): 719-733. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00698-0 [18] Chaudhuri O, Gu L, Klumpers D, et al. 2016. Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity. Nature Materials, 15(3): 326-334. doi: 10.1038/nmat4489 [19] Chen X, Giles J, Yao Y, et al. 2022. The path to healthy ageing in China: a Peking University–Lancet Commission. The Lancet, 400(10367): 1967-2006. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01546-X [20] Chen Y, Chen L, Zhang J-Y, et al. 2019. Oxymatrine reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells by depressing αⅤβ3 integrin/FAK/PI3K/Akt signaling activation. OncoTargets and Therapy, 12: 6253-6265. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S209056 [21] Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Orend G, Chiquet M, et al. 2014. Tenascins in stem cell niches. Matrix Biology, 37: 112-23. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.01.007 [22] Chitty J L, Yam M, Perryman L, et al. 2023. A first-in-class pan-lysyl oxidase inhibitor impairs stromal remodeling and enhances gemcitabine response and survival in pancreatic cancer. Nature Cancer, 4(9): 1326-1344. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00614-y [23] Cho C, Horzempa C, Jones D, et al. 2016. The fibronectin III-1 domain activates a PI3-Kinase/Akt signaling pathway leading to αvβ5 integrin activation and TRAIL resistance in human lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer, 16: 574. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2621-6 [24] Cho S, Rhee S, Madl C M, et al. 2025. Selective inhibition of stromal mechanosensing suppresses cardiac fibrosis. Nature, 642(8068): 766-775. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08945-9 [25] Chopra V, Sangarappillai R M, Romero-Canelón I, et al. 2020. Lysyl Oxidase Like-2 (LOXL2): An Emerging Oncology Target. Advanced Therapeutics, 3(2): 1900119. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201900119 [26] Clezardin P. 2018. Thrombospondin. H√§mostaseologie, 07(06): 172-182. doi: 10.1007/springerreference_177452 [27] Cox T R, Bird D, Baker A-M, et al. 2013. LOX-mediated collagen crosslinking is responsible for fibrosis-enhanced metastasis. Cancer Research, 73(6): 1721-32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2233 [28] D'Amore A, Yoshizumi T, Luketich S K, et al. 2016. Bi-layered polyurethane - Extracellular matrix cardiac patch improves ischemic ventricular wall remodeling in a rat model. Biomaterials, 107: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.07.039 [29] De Boeck KAmaral M D. 2016. Progress in therapies for cystic fibrosis. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 4(8): 662-674. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)00023-0 [30] de Vos L C, Lefrandt J D, Dullaart R P F, et al. 2016. Advanced glycation end products: An emerging biomarker for adverse outcome in patients with peripheral artery disease. Atherosclerosis, 254: 291-299. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.10.012 [31] Ding M, Huang Z, Wang X, et al. 2022. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans-mediated targeted delivery of TGF-β1-binding peptide to liver for improved anti-liver fibrotic activity in vitro and in vivo. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 209: 1516-1525. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.085 [32] Dong Y, Zheng Q, Wang Z, et al. 2019. Higher matrix stiffness as an independent initiator triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition and facilitates HCC metastasis. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 12(1): 112. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0795-5 [33] Dupont S, Morsut L, Aragona M, et al. 2011. Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature, 474(7350): 179-183. doi: 10.1038/nature10137 [34] Elfenbein ASimons M. 2010. Auxiliary and autonomous proteoglycan signaling networks. Methods Enzymol, 480: 3-31. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(10)80001-1 [35] Fan W, Adebowale K, Vancza L, et al. 2024. Matrix viscoelasticity promotes liver cancer progression in the pre-cirrhotic liver. Nature, 626(7999): 635-642. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06991-9 [36] Feng Y, Zou R, Zhang X, et al. 2021. YAP promotes ocular neovascularization by modifying PFKFB3-driven endothelial glycolysis. Angiogenesis, 24(3): 489-504. doi: 10.1007/s10456-020-09760-8 [37] Findlay A, Turner C, Schilter H, et al. 2021. An activity-based bioprobe differentiates a novel small molecule inhibitor from a LOXL2 antibody and provides renewed promise for anti-fibrotic therapeutic strategies. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 11(11): e572. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.572 [38] Gao W, Zhang X, Hu W, et al. 2024. Neutrophils exhibit flexible migration strategies and trail formation mechanisms on varying adhesive substrates. Biomaterials, 314: 122881. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122881 [39] Garantziotis SSavani R C. 2019. Hyaluronan biology: A complex balancing act of structure, function, location and context. Matrix Biology, 78: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.02.002 [40] Ge C, Li Y, Wu F, et al. 2023. Synthetic peptides activating discoidin domain receptor 2 and collagen‐binding integrins cooperate to stimulate osteoblast differentiation of skeletal progenitor cells. Acta Biomaterialia, 166: 109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.039 [41] Ge H, Tian M, Pei Q, et al. 2021. Extracellular Matrix Stiffness: New Areas Affecting Cell Metabolism. Frontiers in Oncology, 11: 631991. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.631991 [42] Gilbert P M, Havenstrite K L, Magnusson K E G, et al. 2010. Substrate Elasticity Regulates Skeletal Muscle Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Culture. Science, 329(5995): 1078-1081. doi: 10.1126/science.1191035 [43] Godwin A R F, Singh M, Lockhart-Cairns M P, et al. 2019. The role of fibrillin and microfibril binding proteins in elastin and elastic fibre assembly. Matrix Biology, 84: 17-30. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.06.006 [44] Gulley J L, Schlom J, Barcellos‐Hoff M H, et al. 2021. Dual inhibition of TGF-β and PD-L1: a novel approach to cancer treatment. Molecular Oncology, 16(11): 2117-2134. [45] Guo J, Niu Z, Lv R, et al. 2024. A novel GARP humanized mouse model for efficacy assessment of GARP-targeting therapies. International Immunopharmacology, 130: 111782. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111782 [46] Han B, Zheng R, Zeng H, et al. 2024. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. Journal of the National Cancer Center, 4(1): 47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2024.01.006 [47] Hashimoto H, Olson E NBassel-Duby R. 2018. Therapeutic approaches for cardiac regeneration and repair. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 15(10): 585-600. doi: 10.1038/s41569-018-0036-6 [48] He C-P, Chen C, Jiang X-C, et al. 2022a. The role of AGEs in pathogenesis of cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis. Bone & Joint Research, 11(5): 292-300. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.115.BJR-2021-0334.R1 [49] He Y, Li Q, Chen P, et al. 2022b. A smart adhesive Janus hydrogel for non-invasive cardiac repair and tissue adhesion prevention. Nature Communications, 13(1): 7666. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35437-5 [50] Hohenester E. 2019. Structural biology of laminins. Essays in Biochemistry, 63(3): 285-295. doi: 10.1042/EBC20180075 [51] Hu S C-SLan C-C E. 2016. High-glucose environment disturbs the physiologic functions of keratinocytes: Focusing on diabetic wound healing. Journal of Dermatological Science, 84(2): 121-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.07.008 [52] Hu Y, Jia Y, Wang S, et al. 2022. An ECM-Mimicking, Injectable, Viscoelastic Hydrogel for Treatment of Brain Lesions. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 12(1): 2201594. [53] Hu Y, Yu B, Jia Y, et al. 2023. Hyaluronate- and gelatin-based hydrogels encapsulating doxycycline as a wound dressing for burn injury therapy. Acta Biomaterialia, 164: 151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.04.021 [54] Huang H, Ke Q, Li N, et al. 2025. Advanced biomaterials and delivery modalities to alleviate cancer therapy-induced inflammation. Biomaterials, 324: 123419. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2025.123419 [55] Huang R, Fu PMa L. 2023. Kidney fibrosis: from mechanisms to therapeutic medicines. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 8(1): 129. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01379-7 [56] Hynes R O. 2009. The Extracellular Matrix: Not Just Pretty Fibrils. Science, 326(5957): 1216-1219. doi: 10.1126/science.1176009 [57] Iozzo R VSchaefer L. 2010. Proteoglycans in health and disease: novel regulatory signaling mechanisms evoked by the small leucine-rich proteoglycans. The FEBS Journal, 277(19): 3864-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07797.x [58] Ippolito L, Duatti A, Iozzo M, et al. 2024. Lactate supports cell-autonomous ECM production to sustain metastatic behavior in prostate cancer. EMBO Reports, 25(8): 3506-3531. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00180-z [59] Ito SNagata K. 2018. Roles of the endoplasmic reticulum-resident, collagen-specific molecular chaperone Hsp47 in vertebrate cells and human disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 294(6): 2133-2141. doi: 10.1074/jbc.tm118.002812 [60] Jahed Z, Domkam N, Ornowski J, et al. 2021. Molecular models of LINC complex assembly at the nuclear envelope. Journal of Cell Science, 134(12): 258194. doi: 10.1242/jcs.258194 [61] Jaillon S, Ponzetta A, Di Mitri D, et al. 2020. Neutrophil diversity and plasticity in tumour progression and therapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 20(9): 485-503. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0281-y [62] Jakubowska K, Pryczynicz A, Iwanowicz P, et al. 2016. Expressions of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-7, and MMP-9) and Their Inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology Research and Practice, 2016(1): 2456179. doi: 10.1155/2016/2456179 [63] Jandl K, Marsh L M, Hoffmann J, et al. 2020. Basement Membrane Remodeling Controls Endothelial Function in Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 63(1): 104-117. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0303OC [64] Jayadev RSherwood D R. 2017. Basement membranes. Current Biology, 27(6): 207-211. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.02.006 [65] Jia Y, Wei Z, Feng J, et al. 2024. A Heart Rate Matched Patch for Mechano-Chemical Treatment of Myocardial Infarction: Optimal Design and Transspecies Application. Research, 7: 0517. doi: 10.34133/research.0517 [66] Jiang S, Lan Z, Zhang X, et al. 2025. Bioenergetic-active hydrogel drives extracellular matrix synthesis for cartilage repair. Bioactive Materials, 54: 34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.07.043 [67] Jones L S, Rodriguez Cetina Biefer H, Mekkattu M, et al. 2025. Volumetric 3D Printing and Melt-Electrowriting to Fabricate Implantable Reinforced Cardiac Tissue Patches. Advanced Materials, 37(45): 2504765. doi: 10.1002/adma.202504765 [68] Jud PSourij H. 2019. Therapeutic options to reduce advanced glycation end products in patients with diabetes mellitus: A review. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 148: 54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.11.016 [69] Kim H N, Elgundi Z, Lin X, et al. 2023. Engineered short forms of perlecan enhance angiogenesis by potentiating growth factor signalling. Journal of Controlled Release, 362: 184-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.08.052 [70] Kimata M, Otani Y, Kubota T, et al. 2002. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor, Marimastat, Decreases Peritoneal Spread of Gastric Carcinoma in Nude Mice. Japanese Journal of Cancer Research, 93(7): 834-841. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2002.tb01326.x [71] Kisseleva TBrenner D. 2021. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 18(3): 151-166. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00372-7 [72] Kollert M R, Krämer M, Brisson N M, et al. 2025. Water and ions binding to extracellular matrix drives stress relaxation, aiding MRI detection of swelling-associated pathology. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 9(5): 772-786. doi: 10.1038/s41551-025-01369-w [73] Kollet O, Das A, Karamanos N, et al. 2023. Redefining metalloproteases specificity through network proteolysis. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 30(2): 147-163. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.11.001 [74] Kopyeva I, Brady R PDeForest C A. 2025. Light-based fabrication and 4D customization of hydrogel biomaterials. Nature Reviews Bioengineering, 3(2): 159-180. doi: 10.1038/s44222-024-00234-w [75] Korneenko T V, Pestov N B, Nevzorov I A, et al. 2023. At the Crossroads of the cGAS-cGAMP-STING Pathway and the DNA Damage Response: Implications for Cancer Progression and Treatment. Pharmaceuticals, 16(12): 1675. doi: 10.3390/ph16121675 [76] Kozel B AMecham R P. 2019. Elastic fiber ultrastructure and assembly. Matrix Biology, 84: 31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.10.002 [77] Kumar Pasupulati A, Chitra P SReddy G B. 2016. Advanced glycation end products mediated cellular and molecular events in the pathology of diabetic nephropathy. BioMolecular Concepts, 7(5-6): 293-309. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2016-0021 [78] Lan Z, Chen L, Feng J, et al. 2021. Mechanosensitive TRPV4 is required for crystal-induced inflammation. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 80(12): 1604-1614. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220295 [79] Leitinger B. 2014. Discoidin domain receptor functions in physiological and pathological conditions. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, 310: 39-87. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-800180-6.00002-5 [80] Li Y, Li L, Wang M, et al. 2023. O-alg-THAM/gel hydrogels functionalized with engineered microspheres based on mesenchymal stem cell secretion recruit endogenous stem cells for cartilage repair. Bioactive Materials, 28: 255-272. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.05.003 [81] Li Z, Wang X, Hong T-p, et al. 2021. Advanced glycosylation end products inhibit the proliferation of bone-marrow stromal cells through activating MAPK pathway. European Journal of Medical Research, 26(1): 94. doi: 10.1186/s40001-021-00559-x [82] Ligorio M, Sil S, Malagon-Lopez J, et al. 2019. Stromal Microenvironment Shapes the Intratumoral Architecture of Pancreatic Cancer. Cell, 178(1): 160-175. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.012 [83] Lin X, Liu Y, Bai A, et al. 2019a. A viscoelastic adhesive epicardial patch for treating myocardial infarction. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 3(8): 632-643. doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0380-9 [84] Lin Y-C, Guo Y R, Miyagi A, et al. 2019b. Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature, 573(7773): 230-234. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2 [85] Ling B, Watt K, Banerjee S, et al. 2017. A novel immunotherapy targeting MMP-14 limits hypoxia, immune suppression and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer models. Oncotarget, 8(35): 58372-58385. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17702 [86] Liu T, Hao Y, Zhang Z, et al. 2024. Advanced Cardiac Patches for the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation, 149(25): 2002-2020. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.067097 [87] Liu X, Yu L, Xiao A, et al. 2025. Analytical methods in studying cell force sensing: principles, current technologies and perspectives. Regenerative Biomaterials, 12: rbaf007. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbaf007 [88] Luo J, Xiang X, Gong G, et al. 2025. Cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated immune evasion: molecular mechanisms of stromal-immune crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment. Frontiers in Immunology, 16: 1617662. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1617662 [89] Mahendra Y, He M, Rouf M A, et al. 2021. Progress and prospects of mechanotransducers in shear stress-sensitive signaling pathways in association with arteriovenous malformation. Clinical Biomechanics, 88: 105417. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2021.105417 [90] Mai Z, Lin Y, Lin P, et al. 2024. Modulating extracellular matrix stiffness: a strategic approach to boost cancer immunotherapy. Cell Death & Disease, 15(5): 307. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06697-4 [91] Malandrino A, Mak M, Kamm R D, et al. 2018. Complex mechanics of the heterogeneous extracellular matrix in cancer. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 21: 25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.eml.2018.02.003 [92] Malhotra V. 2024. Tailored assemblies of COPII proteins in secretion. Journal of Cell Biology, 223(8): e202404013. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202404013 [93] Marchand M, Monnot C, Muller L, et al. 2018. Extracellular matrix scaffolding in angiogenesis and capillary homeostasis. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 89: 147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.08.007 [94] Marchant C L, Malmi-Kakkada A N, Espina J A, et al. 2022. Cell clusters softening triggers collective cell migration in vivo. Nature Materials, 21(11): 1314-1323. doi: 10.1038/s41563-022-01323-0 [95] Mascharak S, desJardins-Park H E, Davitt M F, et al. 2021. Preventing Engrailed-1 activation in fibroblasts yields wound regeneration without scarring. Science, 372(6540): eaba2374. doi: 10.1126/science.aba2374 [96] Miyoshi S, Kudo M, Shitara K, et al. 2016. TGF-β inhibitor LY2157299 (galunisertib) in combination with standard chemotherapy and inhibition of signaling to pSmad and EMT and suppression of tumor growth in gastric cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 34(4): 50-58. doi: 10.1200/jco.2016.34.4_suppl.50 [97] Mouw J K, Ou GWeaver V M. 2014. Extracellular matrix assembly: a multiscale deconstruction. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 15(12): 771-85. doi: 10.1038/nrm3902 [98] Muncie J M, Ayad N M E, Lakins J N, et al. 2020. Mechanical Tension Promotes Formation of Gastrulation-like Nodes and Patterns Mesoderm Specification in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Developmental Cell, 55(6): 679-694. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.10.015 [99] Naba A. 2024. Mechanisms of assembly and remodelling of the extracellular matrix. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 25(11): 865-885. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00767-3 [100] Naba A, Clauser K R, Hoersch S, et al. 2011. The matrisome: in silico definition and in vivo characterization by proteomics of normal and tumor extracellular matrices. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP, 11(4): 014647. [101] Olejarz W, Lacheta DKubiak-Tomaszewska G. 2020. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Biomarkers of Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11): 3946. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113946 [102] Panciera T, Azzolin L, Cordenonsi M, et al. 2017. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 18(12): 758-770. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.87 [103] Panzarini E, Leporatti S, Tenuzzo B, et al. 2022. Therapeutic Effect of Polymeric Nanomicelles Formulation of LY2157299-Galunisertib on CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11): 1812. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111812 [104] Pawar J S, Salam M A, Dipto M S U, et al. 2025. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Immunosuppressive Crosstalk with Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Implications for Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers, 17(15): 2484. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152484 [105] Pehrsson M, Mortensen J H, Manon-Jensen T, et al. 2021. Enzymatic cross-linking of collagens in organ fibrosis – resolution and assessment. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 21(10): 1049-1064. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2021.1962711 [106] Pelham R J, Jr. Wang Y. 1997. Cell locomotion and focal adhesions are regulated by substrate flexibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 94(25): 13661-13665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.25.13661 [107] Perryman LGray S G Fibrosis in Mesothelioma: Potential Role of Lysyl Oxidases. Cancers, 2022. 14, 981. [108] Phang J M. 2021. Perspectives, past, present and future: the proline cycle/proline-collagen regulatory axis. Amino Acids, 53(12): 1967-1975. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03103-7 [109] Piersma B, Bank R ABoersema M. 2015. Signaling in Fibrosis: TGF-β, WNT, and YAP/TAZ Converge. Frontiers in Medicine, 2: 59. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2015.00059 [110] Pirri C. 2025. PIEZO Channels in Mechano-Inflammation: Gatekeepers of Neuroimmune Crosstalk. Diseases, 13(8): 263. doi: 10.3390/diseases13080263 [111] Potente M, Gerhardt HCarmeliet P. 2011. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell, 146(6): 873-887. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.039 [112] Randles M J, Humphries M JLennon R. 2016. Proteomic definitions of basement membrane composition in health and disease. Matrix Biology, 57: 12-28. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.08.006 [113] Raote I, Chabanon M, Walani N, et al. 2020. A physical mechanism of TANGO1-mediated bulky cargo export. eLife, 9: e59426. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59426 [114] Reuten R, Zendehroud S, Nicolau M, et al. 2021. Basement membrane stiffness determines metastases formation. Nature Materials, 20(6): 892-903. doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-00894-0 [115] Revell C K, Jensen O E, Shearer T, et al. 2021. Collagen fibril assembly: New approaches to unanswered questions. Matrix Biology Plus, 12: 100079. doi: 10.1016/j.mbplus.2021.100079 [116] Ricard-Blum S. 2011. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 3(1): a004978. [117] Ricard‐Blum S, Vivès R R, Schaefer L, et al. 2024. A biological guide to glycosaminoglycans: current perspectives and pending questions. The FEBS Journal, 291(15): 3331-3366. doi: 10.1111/febs.17107 [118] Richter R P, Baranova N S, Day A J, et al. 2017. Glycosaminoglycans in extracellular matrix organisation: are concepts from soft matter physics key to understanding the formation of perineuronal nets. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 50: 65-74. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.12.002 [119] Roca-Cusachs P, Gauthier N C, del Rio A, et al. 2009. Clustering of α5β1 integrins determines adhesion strength whereas αvβ3 and talin enable mechanotransduction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(38): 16245-16250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902818106 [120] Rom S, Heldt N A, Gajghate S, et al. 2020. Hyperglycemia and advanced glycation end products disrupt BBB and promote occludin and claudin-5 protein secretion on extracellular microvesicles. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 7274. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64349-x [121] Rurik J G, Tombácz I, Yadegari A, et al. 2022. CAR T cells produced in vivo to treat cardiac injury. Science, 375(6576): 91-96. doi: 10.1126/science.abm0594 [122] Saraswathibhatla A, Indana DChaudhuri O. 2023. Cell–extracellular matrix mechanotransduction in 3D. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 24(7): 495-516. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00583-1 [123] Schwarzbauer J EDeSimone D W. 2011. Fibronectins, their fibrillogenesis, and in vivo functions. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 3(7): a005041. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005041 [124] Setargew Y F I, Wyllie K, Grant R D, et al. 2021. Targeting Lysyl Oxidase Family Meditated Matrix Cross-Linking as an Anti-Stromal Therapy in Solid Tumours. Cancers, 13(3): 491. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030491 [125] Shi M-Y, Yao Y, Wang M, et al. 2025. High-speed mapping of whole-mouse peripheral nerves at subcellular resolution. Cell, 188(14): 3897-3915. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.06.011 [126] Su B, Guo SZheng X. 2023. Transitions in Chronic Disease Mortality in China: Evidence and Implications. China CDC Wkly, 5(50): 1131-1134. [127] Su Y, Iacob R E, Li J, et al. 2022. Dynamics of integrin α5β1, fibronectin, and their complex reveal sites of interaction and conformational change. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 298(9): 102323. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102323 [128] Sutherland T E, Dyer D PAllen J E. 2023. The extracellular matrix and the immune system: A mutually dependent relationship. Science, 379(6633): eabp8964. doi: 10.1126/science.abp8964 [129] Taguchi KFukami K. 2023. RAGE signaling regulates the progression of diabetic complications. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 14: 1128872. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1128872 [130] Tani H, Sadahiro T, Yamada Y, et al. 2023. Direct Reprogramming Improves Cardiac Function and Reverses Fibrosis in Chronic Myocardial Infarction. Circulation, 147(3): 223-238. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.058655 [131] Thomas DRadhakrishnan P. 2019. Tumor-stromal crosstalk in pancreatic cancer and tissue fibrosis. Molecular Cancer, 18(1): 14. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0927-5 [132] Travers J G, Kamal F A, Robbins J, et al. 2016. Cardiac Fibrosis. Circulation Research, 118(6): 1021-1040. [133] Trounson AMcDonald C. 2015. Stem Cell Therapies in Clinical Trials: Progress and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell, 17(1): 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.06.007 [134] Tsukui T, Wolters P JSheppard D. 2024. Alveolar fibroblast lineage orchestrates lung inflammation and fibrosis. Nature, 631(8021): 627-634. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07660-1 [135] Usman K, Hsieh AHackett T-L. 2021. The Role of miRNAs in Extracellular Matrix Repair and Chronic Fibrotic Lung Diseases. Cells, 10(7): 1706. doi: 10.3390/cells10071706 [136] Venugopal H, Hanna A, Humeres C, et al. 2022. Properties and Functions of Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts in Myocardial Infarction. Cells, 11(9): 1386. doi: 10.3390/cells11091386 [137] Vilardi A, Przyborski S, Mobbs C, et al. 2024. Current understanding of the interplay between extracellular matrix remodelling and gut permeability in health and disease. Cell Death Discovery, 10(1): 258. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02015-1 [138] Vitale D L, Parnigoni A, Viola M, et al. 2024. Deciphering Drug Resistance: Investigating the Emerging Role of Hyaluronan Metabolism and Signaling and Tumor Extracellular Matrix in Cancer Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(14): 7607. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147607 [139] Wang K, Wen D, Xu X, et al. 2023. Extracellular matrix stiffness-The central cue for skin fibrosis. Front Mol Biosci, 10: 1132353. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1132353 [140] Wang L L, Chung J J, Li E C, et al. 2018. Injectable and protease-degradable hydrogel for siRNA sequestration and triggered delivery to the heart. J Control Release, 285: 152-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.07.004 [141] Wang M, Hong Y, Fu X, et al. 2024. Advances and applications of biomimetic biomaterials for endogenous skin regeneration. Bioactive Materials, 39: 492-520. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.04.011 [142] Wang N. 2017. Cellular adhesion: Instant integrin mechanosensing. Nature Materials, 16(12): 1173-1174. doi: 10.1038/nmat5041 [143] Wang T, Hamilla S, Cam M, et al. 2017. Extracellular matrix stiffness and cell contractility control RNA localization to promote cell migration. Nature Communications, 8(1): 896. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00884-y [144] Wang Y-D, Tan X-YZhang K. 2009. Correlation of plasma MMP-1 and TIMP-1 levels and the colonic mucosa expressions in patients with ulcerative colitis. Mediators of Inflammation, 2009(1): 275072. doi: 10.1155/2009/275072 [145] Wells J MWatt F M. 2018. Diverse mechanisms for endogenous regeneration and repair in mammalian organs. Nature, 557(7705): 322-328. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0073-7 [146] Whiteside E J, Jackson M M, Herington A C, et al. 2001. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 are key regulators of extracellular matrix degradation by mouse embryos. Biology of Reproduction, 64(5): 1331-1337. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod64.5.1331 [147] Wu J, Deng J, Theocharidis G, et al. 2024. Adhesive anti-fibrotic interfaces on diverse organs. Nature, 630(8016): 360-367. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07426-9 [148] Wu Y, Shi Y, Luo Z, et al. 2025. Spatial multi-omics analysis of tumor-stroma boundary cell features for predicting breast cancer progression and therapy response. Front Cell Dev Biol, 13: 1570696. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1570696 [149] Xia H, Li X, Gao W, et al. 2018. Tissue repair and regeneration with endogenous stem cells. Nature Reviews Materials, 3(7): 174-193. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0027-6 [150] Xie X, Wang Y, Deng B, et al. 2024. Matrix metalloproteinase-responsive hydrogels with tunable retention for on-demand therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. Acta Biomaterialia, 186: 354-368. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.07.054 [151] Xiong G, Stewart R L, Chen J, et al. 2018. Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase 1 is essential for HIF-1α stabilization and TNBC chemoresistance. Nature Communications, 9(1): 4456. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06893-9 [152] Yang S, Liu H, Chen B, et al. 2025. Mechanical signal-chromatin interactions: molecular networks from nuclear membrane force transmission to epigenetic regulation. Frontiers in Medicine, 12: 1631645. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1631645 [153] Yurchenco P D. 2011. Basement membranes: cell scaffoldings and signaling platforms. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 3(2): a004911. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a004911 [154] Zallocchi M, Johnson B M, Meehan D T, et al. 2013. α1β1 Integrin/Rac1-Dependent Mesangial Invasion of Glomerular Capillaries in Alport Syndrome. The American Journal of Pathology, 183(4): 1269-1280. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.06.015 [155] Zanconato F, Cordenonsi MPiccolo S. 2016. YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer. Cancer Cell, 29(6): 783-803. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.005 [156] Zapp C, Mundinger PBoehm H. 2023. Natural Presentation of Glycosaminoglycans in Synthetic Matrices for 3D Angiogenesis Models. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 9: 729670. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.729670 [157] Zhang L, Zhou JKong W. 2025. Extracellular matrix in vascular homeostasis and disease. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 22(5): 333-353. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01103-0 [158] Zhao Z, Li Q, Qu C, et al. 2025. A collagenase nanogel backpack improves CAR-T cell therapy outcomes in pancreatic cancer. Nature Nanotechnology, 20(8): 1131-1141. doi: 10.1038/s41565-025-01924-1 [159] Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, et al. 2019. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet, 394(10204): 1145-1158. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1 [160] Zhu P, Ren M, Yang C, et al. 2012. Involvement of RAGE, MAPK and NF-κB pathways in AGEs-induced MMP-9 activation in HaCaT keratinocytes. Experimental Dermatology, 21(2): 123-9. [161] Zhu W, Cui Y, Qiu J, et al. 2025. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of TGF-β Inhibitors for Liver Fibrosis: Targeting Multiple Signaling Pathways. Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology, 13(7): 588-598. doi: 10.14218/jcth.2025.00029 -




 下载:
下载: