-
摘要: 当高温引起了流动介质物性变化的时候, 介质微团的物理化学变化显著地改变了介质流动的宏观规律, 超出了气体动力学基本假设和研究范畴, 高温气体动力学诞生了. 当航空航天技术不断拓展人类活动空间的时候, 在探索下一代空天飞行核心技术的过程中, 高温气体动力学发展了. 高温气体动力学是技术科学发展的典范, 在应用驱动学科机制的作用下, 引领着气体动力学的发展与创新. 本文选择了高温气体动力学的四个主要研究领域, 进行了综述和分析, 期望能够助力高温气体流动的学科发展. 第一部分是关于高超声速地面试验装置和测量技术, 重点介绍了三种典型高焓激波风洞, 它们的应用已经能够产生和测量的气流速度达到了1.5 ~ 10 km/s的范围, 可以模拟20 ~ 100 km的飞行高度. 先进科学试验装置对于学科前沿的拓展和流体物理新现象的发现是非常重要的, 该研究领域的进展也凸显了这个道理. 第二部分介绍了高超声速气体流动的理论与实验, 包括物理数学模型的建立、计算方法的发展和实验观测. 到目前为止, 高温气体流动物理模型的发展远低预期, 局限在早期物理模型的应用和改进; 计算方法发展迅速, 能够计算的流动现象越来越多, 准确度也越来越高; 地面实验观测研究进展可期, 表现在一些复现高超声速飞行条件下的大模型实验, 揭示的气动物理现象与飞行试验数据一致良好. 第三部分是关于超声速燃烧和超燃冲压发动机. 这是一个已经持续热了几十年的前沿领域, 虽然理论和技术研究进展巨大、飞行试验硕果累累, 但是超燃冲压发动机依然难以满足工程需求, 超声速燃烧理论依然难以解决超燃冲压发动机研发遇到的问题. 所以, 超声速燃烧和超燃冲压发动机研究都亟需理论创新和技术突破. 第四部分是关于爆轰物理和斜爆轰发动机. 斜爆轰发动机与超燃冲压发动机概念皆生于同一时代, 但它仅在最近20多年才得到重新关注. 爆轰理论和斜爆轰研究都有了创新性突破, 斜爆轰发动机设计方法和风洞实验技术也有了长足的进展. 斜爆轰冲压发动机利用了自然界燃烧速度最快、热效率最高、进气压缩损失最小的增压燃烧现象作为其热力循环, 有着独特的优势. 最后, 论文对于上述研究领域的理论技术及其实践进行了总结和展望, 期望能够给该学科发展提供一些有益的启示.Abstract: The high-temperature gas dynamics was originated from significant changes of macroscopic laws of the gas flows due to physical property changes of the gas mediums when its temperature become extremely high, which goes beyond basic assumptions and research scopes of the gas dynamics. The high-temperature gas dynamics was developed as the core technology for the next generation of aerospace industries is ceaselessly explored when human activities greatly are expanding into the space. This discipline is one of the best models of the engineering science and leads to the development and innovation of the gas dynamics which is pushed forward by the mechanism of application-driven-research. Four dominant research areas of the high-temperature gas dynamics are selected in this paper to conduct a general review with discussions, hoping to help more or less the development of high-temperature gas dynamics. The first area is about hypersonic ground test facilities and measurement technologies. Three typical high-enthalpy shock tunnels were introduced and have been applied to generate the flow velocity of 1.5 - 10 km/s at flight altitudes of 20-100 km. The advanced test facilities are very important for the frontier expansion of disciplines and the discovery of new phenomena in fluid flow physics. The progress in the research area also highlights this truth. The second area is about theories and experiments of hypersonic gas flows, which include their physical and mathematical models, computational methods and results of experimental observations and measurements. Among them, the development of gas physical models is much slower than expected since it is still limited to applications and improvements of the early-developed physical models. The computational method has been developed rapidly, so there are more and more flow phenomena that can be simulated. The progress on the experimental research also is promising due to some large test-model experiments that reproduced model-scaled effects of the hypersonic flow experiments, from which the high-temperature gas physics phenomena revealed is well consistent with hypersonic flight tests. The third one is about supersonic combustion and scramjet engines. This is a research field that has been hot for several decades, during which theoretical and technical researches had achieved a great progress and flight tests have also yielded fruitful results. However, the development of scramjet engines still cannot meet engineering needs and the scramjet engine theory still has difficulties to explain the problems encountered. Therefore, the research of the supersonic combustion and the scramjet engines urgently needs theoretical innovation and technological breakthroughs. The last is about detonation physics and oblique detonation engines. The oblique detonation engine was both almost in the same time with the scramjet engine together, and its research has received a renewed attention only from the beginning of this century. There have been innovative breakthroughs in detonation theory and oblique detonation research since then. And also, a great progress has been made in the standing oblique detonation engine and the hypersonic shock tunnel technology. The oblique detonation engine accepts the unique pressure-gain combustion phenomenon in nature, having the fastest combustion speed, the highest thermal efficiency for its thermal cycle and low heat loads so that it would have a great advantage over others. Finally, the theories, technologies and experiments are summarized about the four research areas of the high-temperature gas dynamics, with which it is expected to provide this discipline with some useful enlightenments.
-
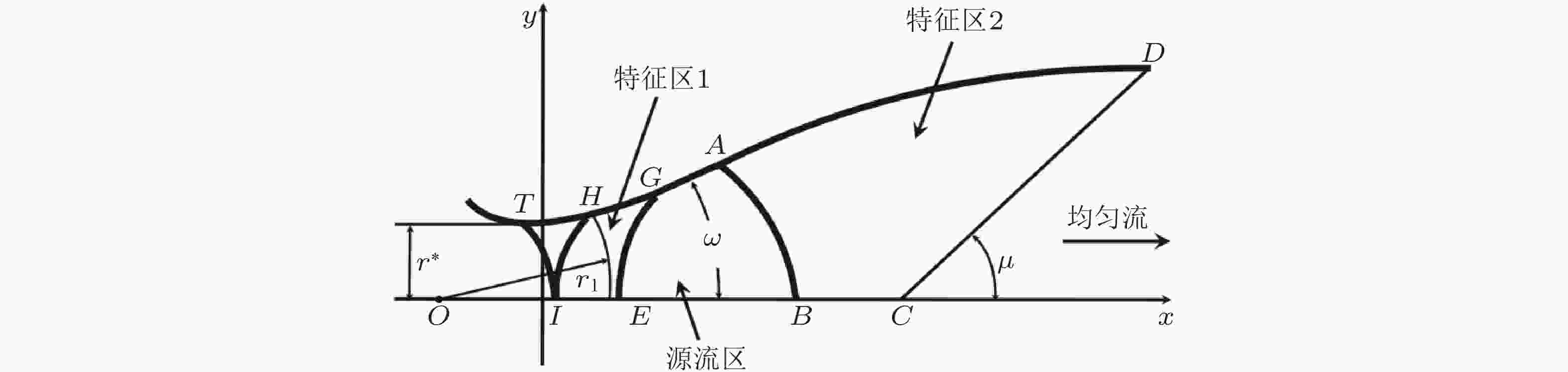
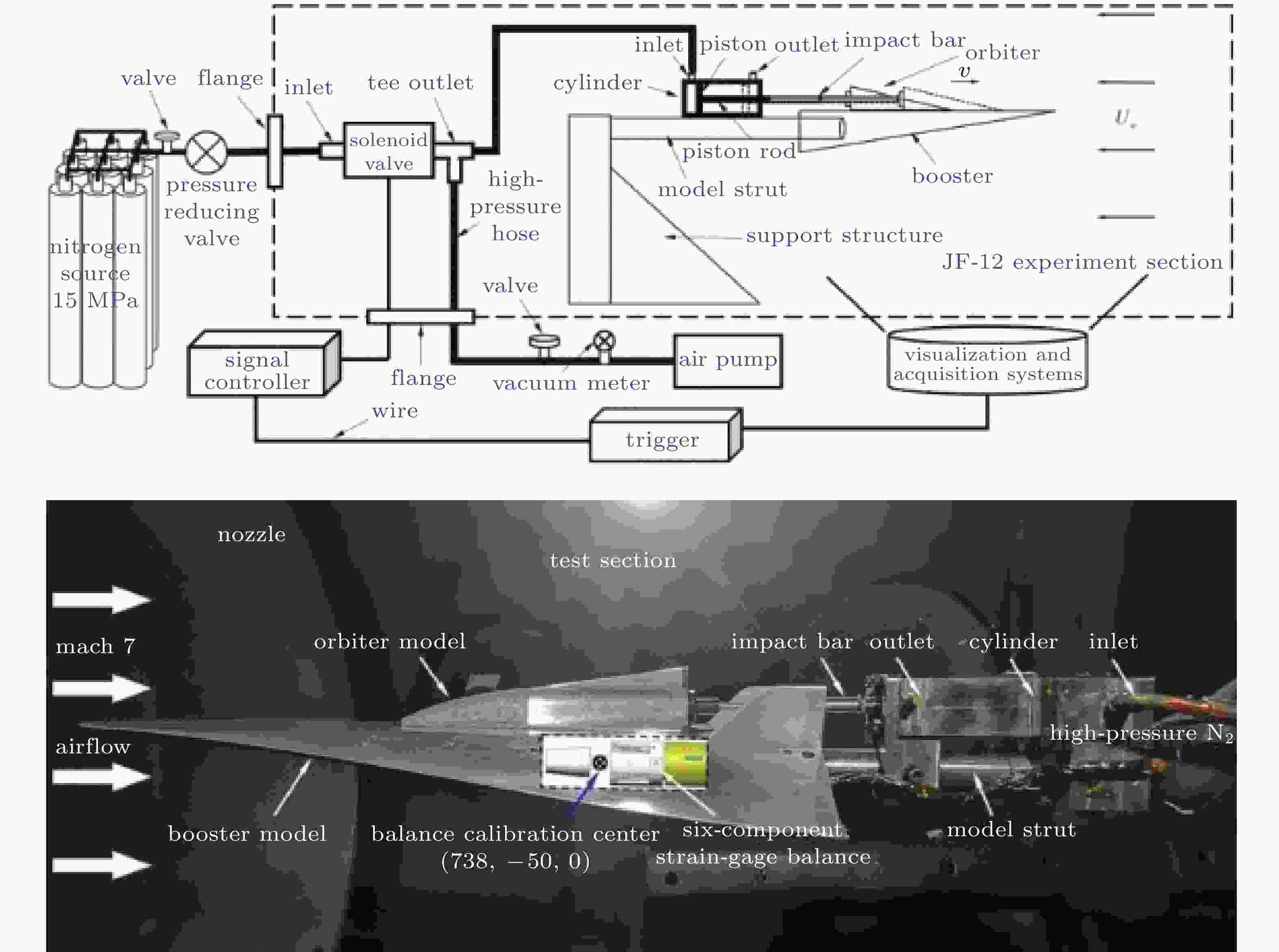
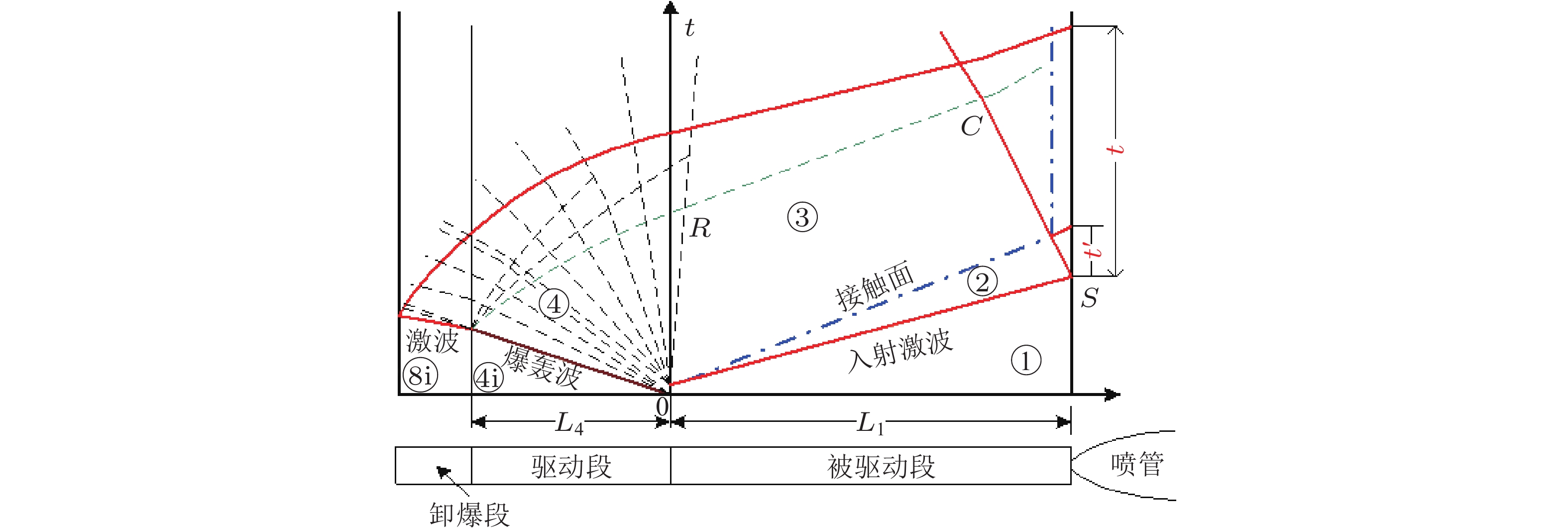
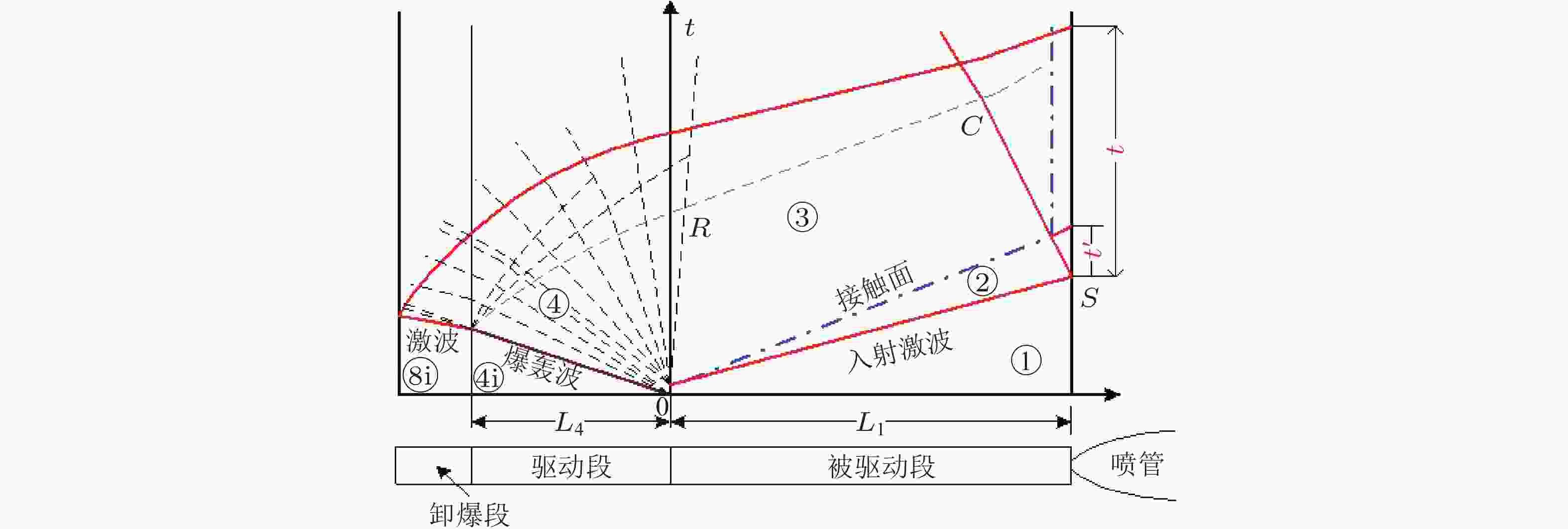
图 1 爆轰驱动激波风洞运行波系示意图(李et al., 2008)
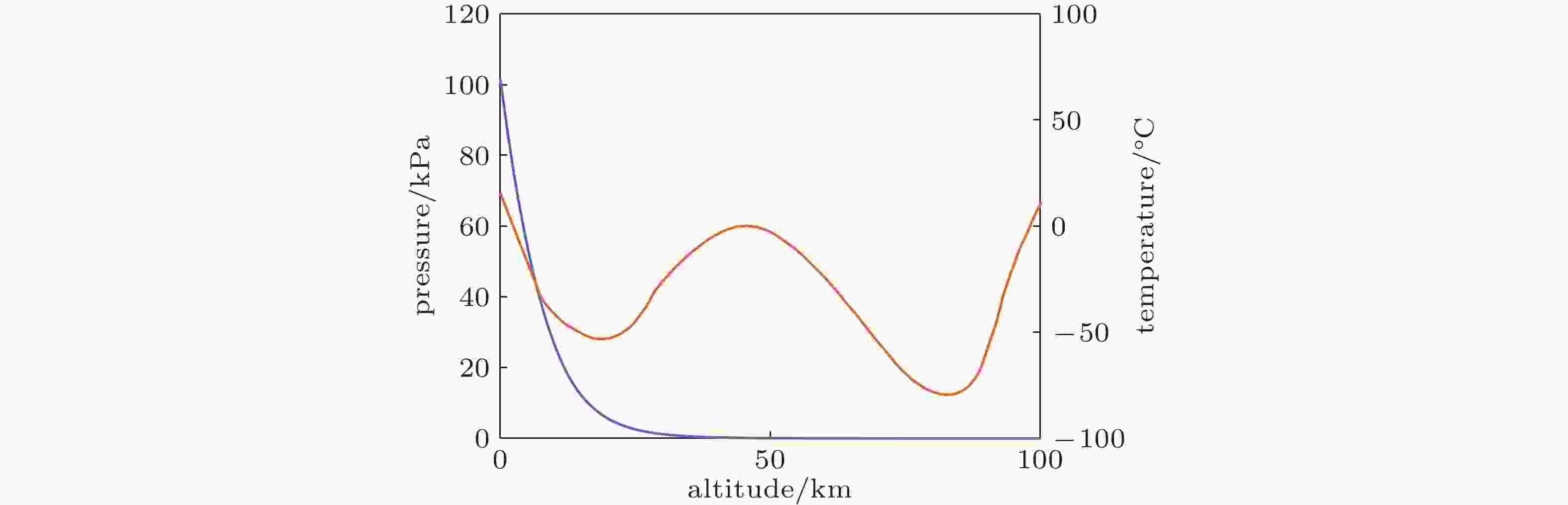
图 2 大气层温度和压力随高度的变化曲线(姜 et al., 2025)
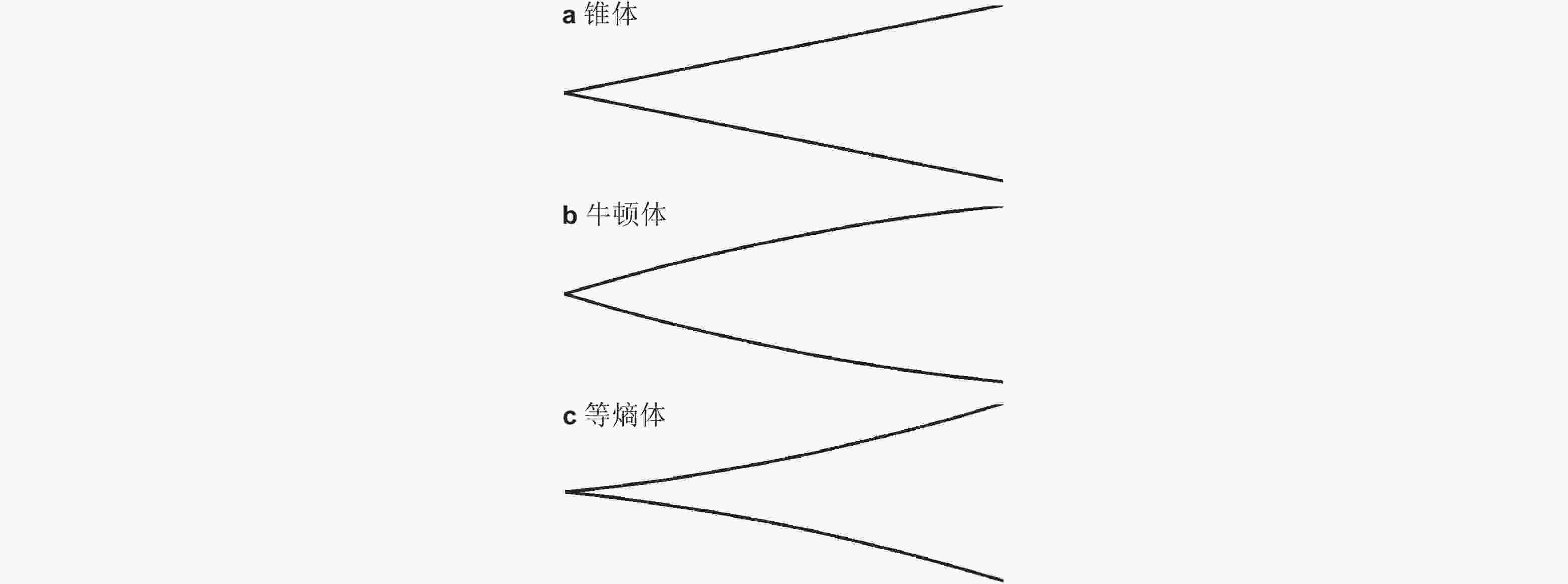
图 3 Sevells 的喷管设计方法示意图(汪et al., 2021)
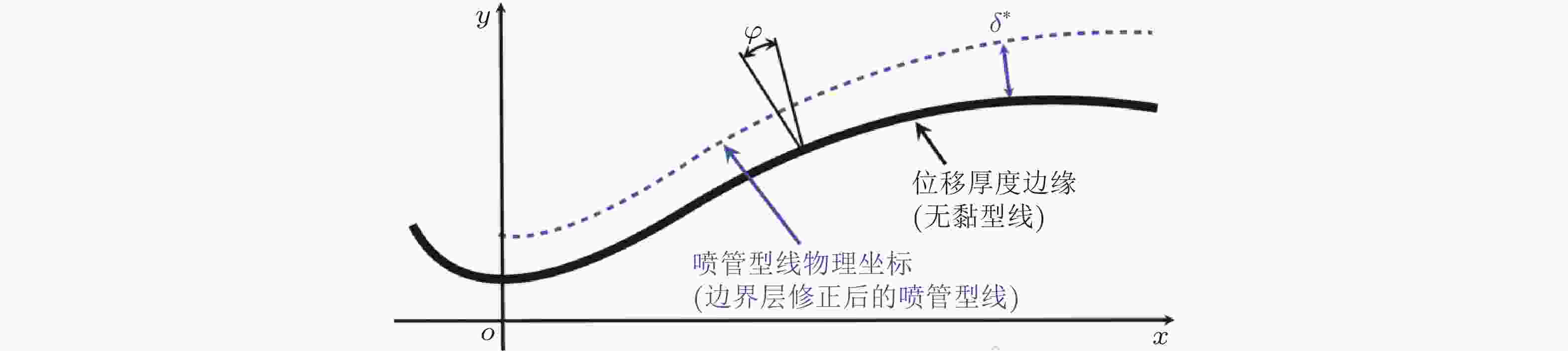
图 4 边界层位移厚度沿喷管型线分布示意图(Wang & Jiang, 2022)
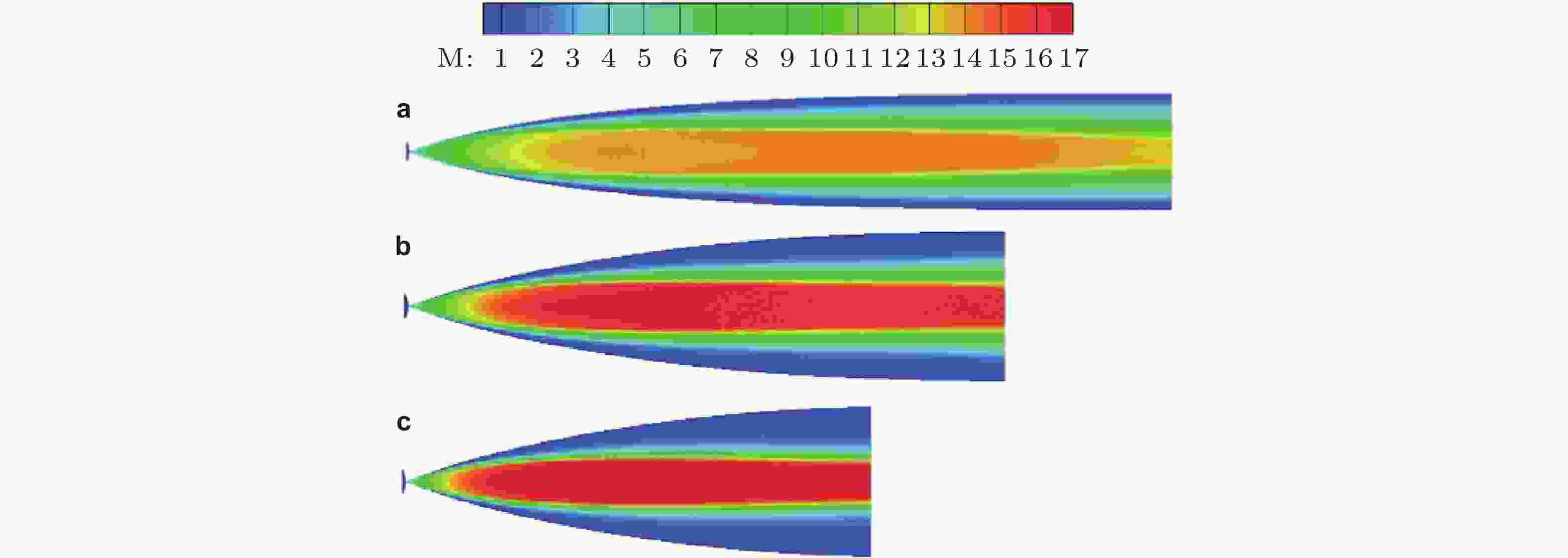
图 5 Ma17喷管马赫数分布优化设计结果示意图, (a) 无粘型线初值流场; (b) 第一次高温效应与边界层修正结果; (c) 第二次高温效应与边界层修正结果(汪et al., 2021).
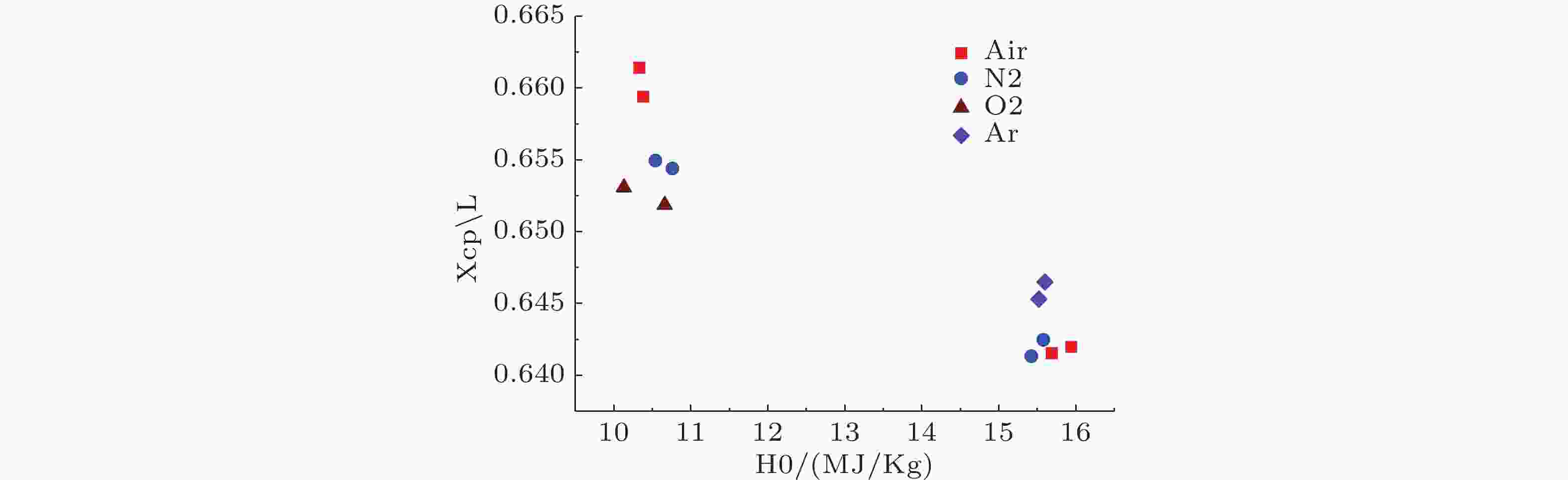
图 8 应用空气、氧气、氮气和氩气测得的飞行器压力中心数据对比(姜 et al., 2009)
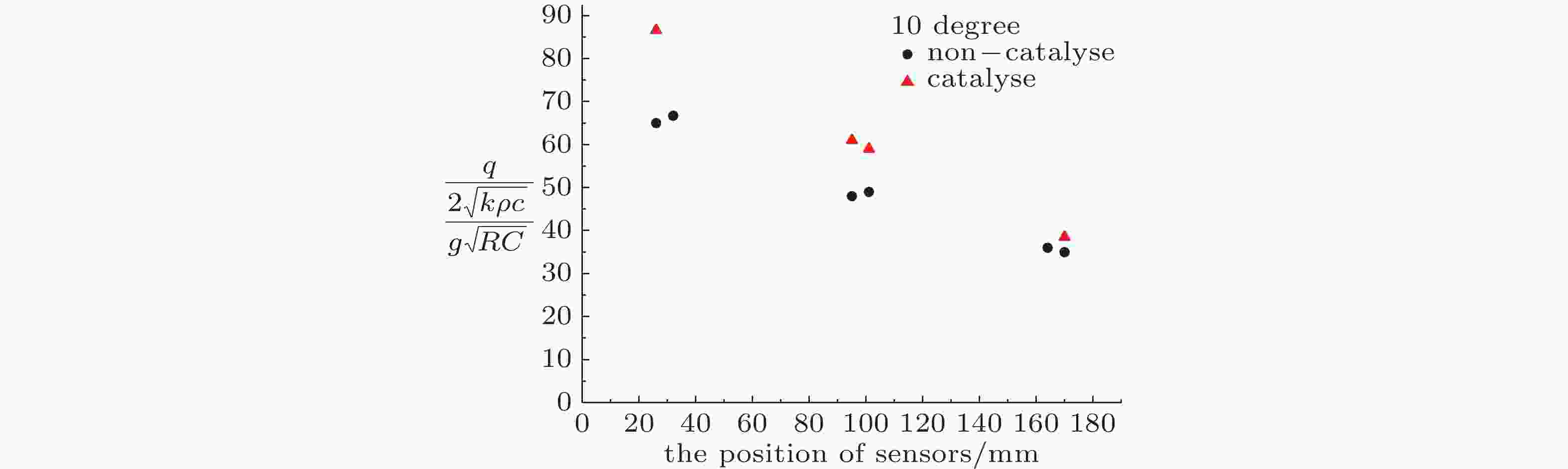
图 9 非催化壁和完全催化壁面热流值的试验比较(姜et al., 2009)
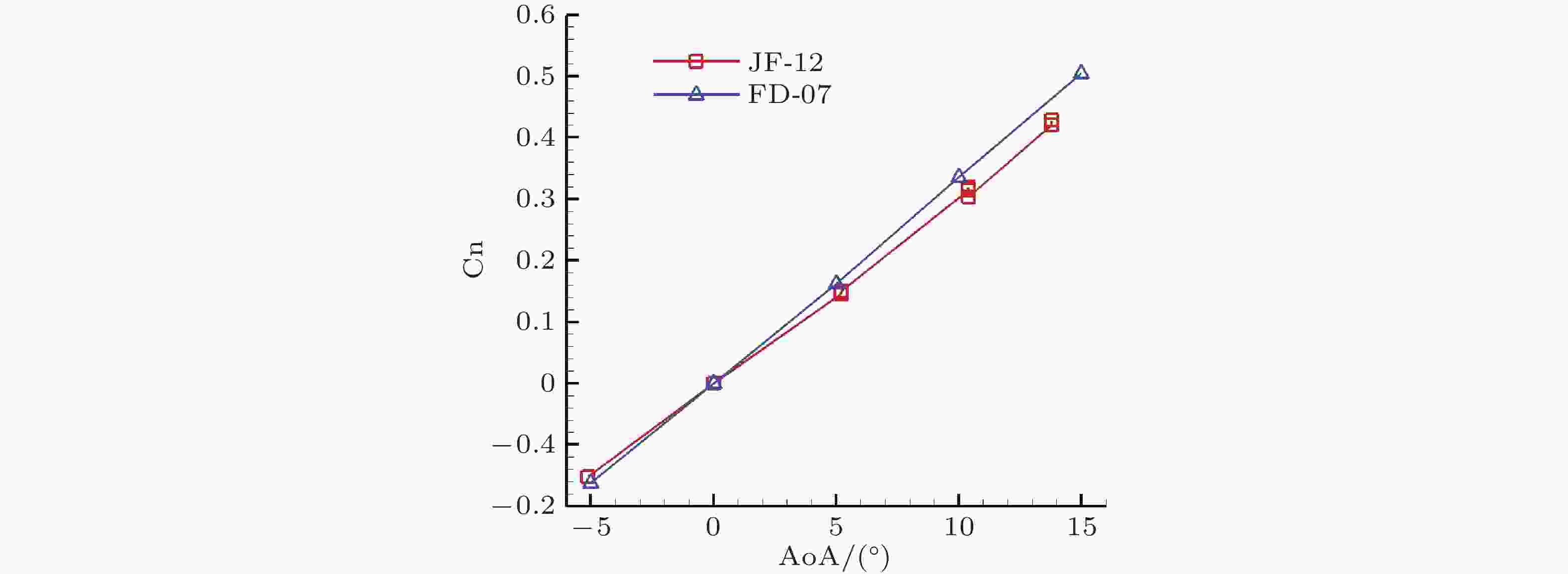
图 10 分子振动激发对尖锥模型法向力影响规律, 马赫7, 10o攻角(姜, 2022)
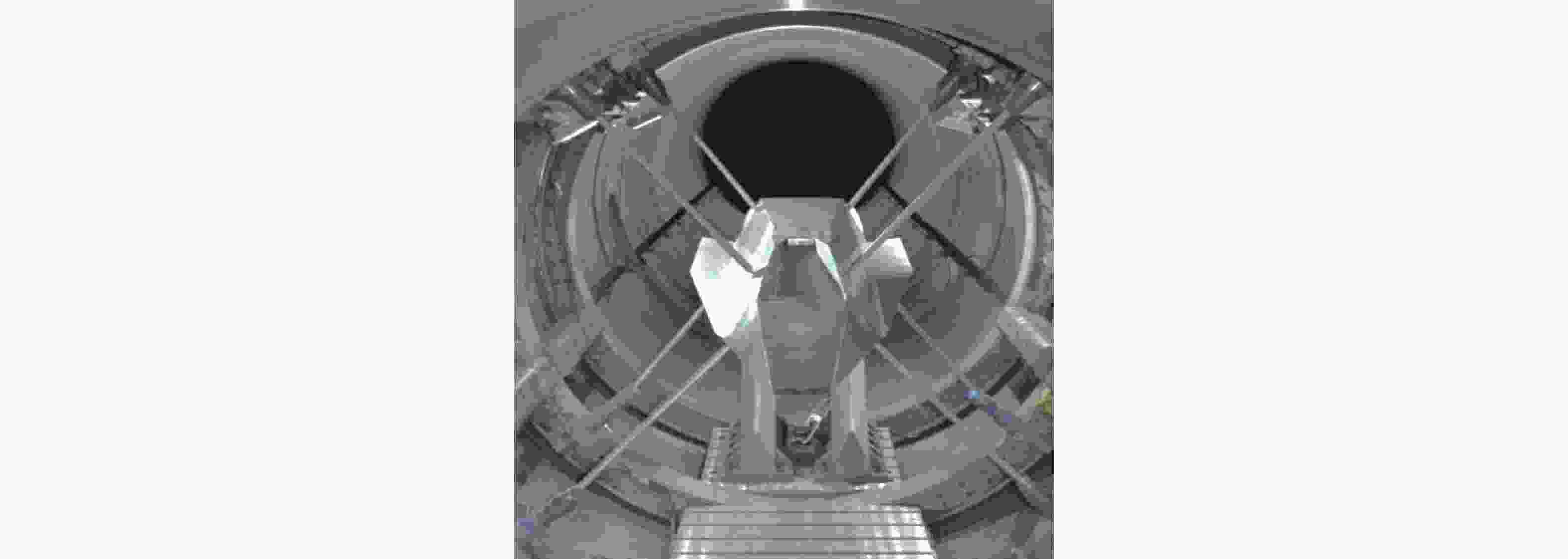
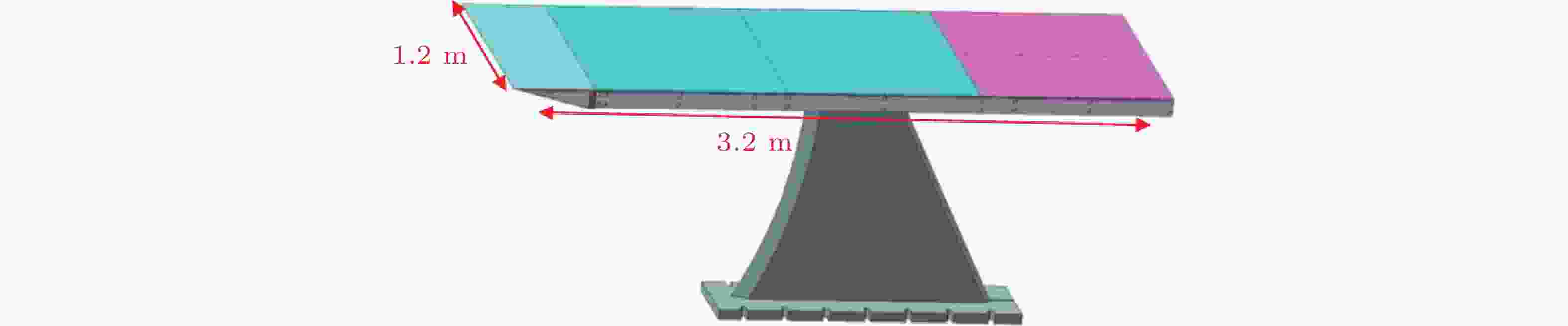
图 11 JF-12 复现风洞3.2 m尖前沿平板边界层实验模型示意图(Liu et al., 2022)
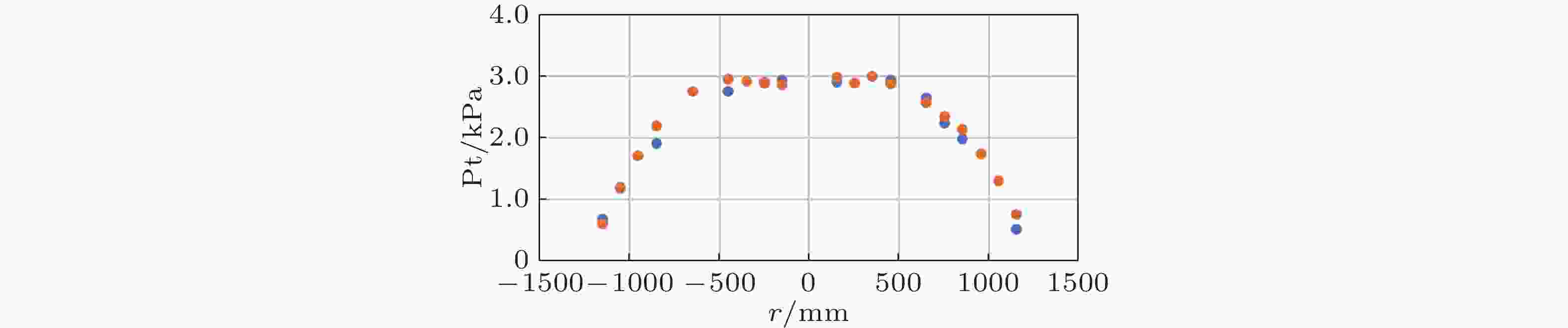
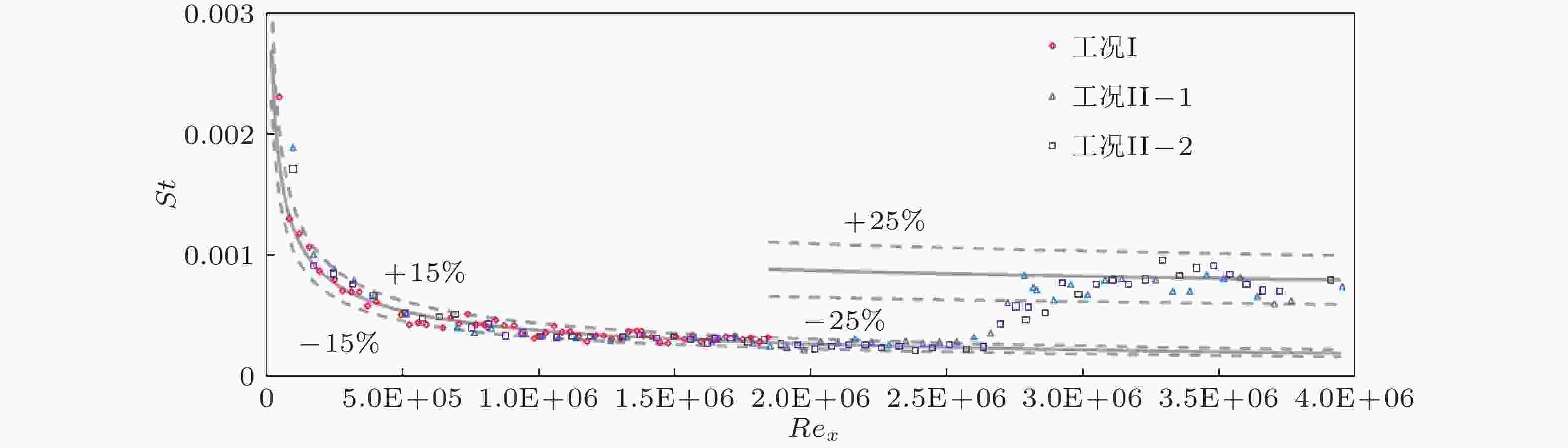
图 12 3.2 m平板边界层实验的热流分布(Li et al., 2024)
图 13 TSTO级间并联高超声速纵向分离风洞实验技术图解(王 et al., 2023)
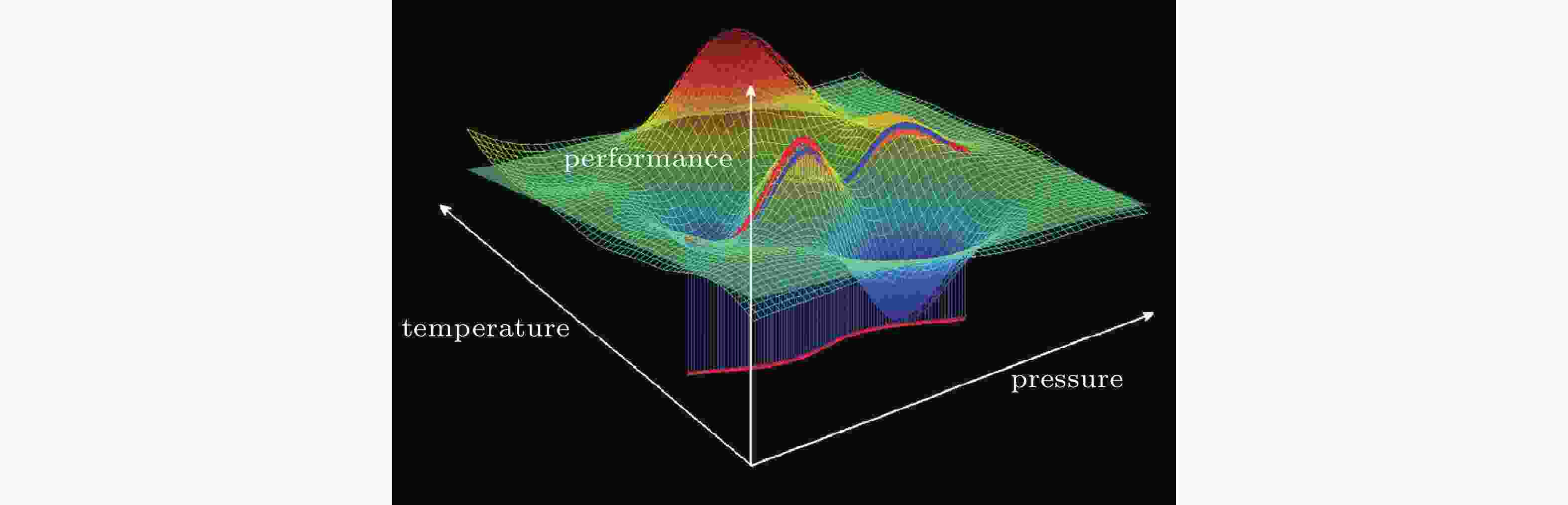
图 14 风洞实验数据多维空间相关理论示意图(姜 et al, 2015)
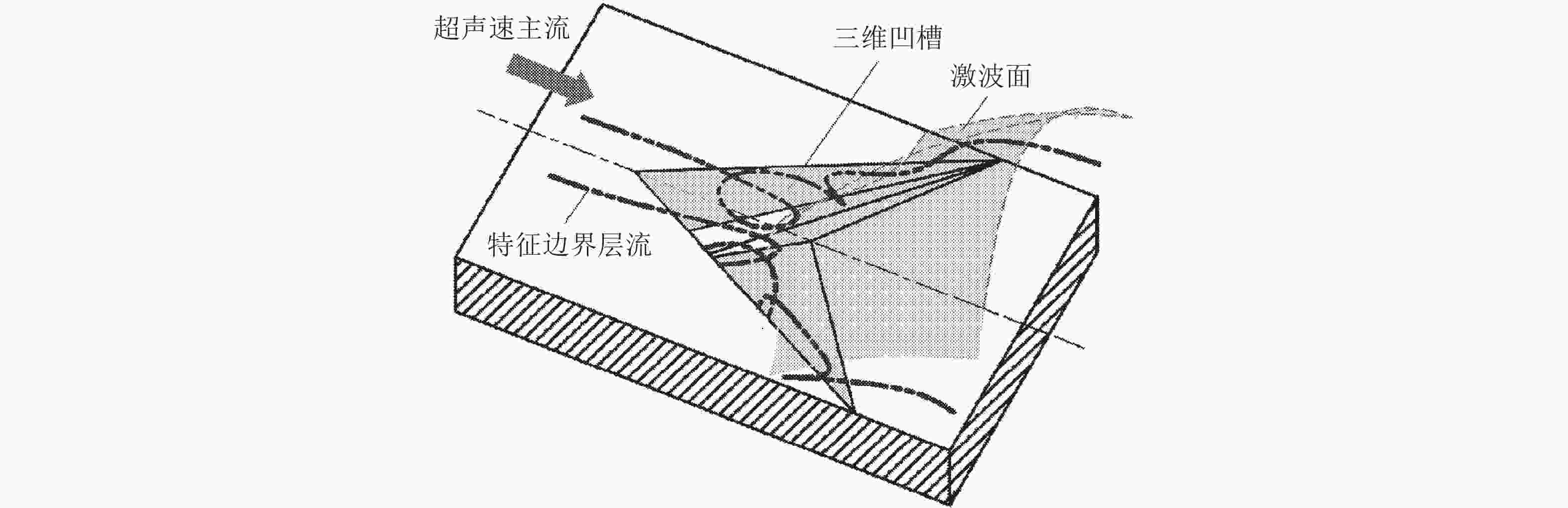
图 15 燕尾型稳焰凹槽的三维流线示意图(姜 et al., 2009)
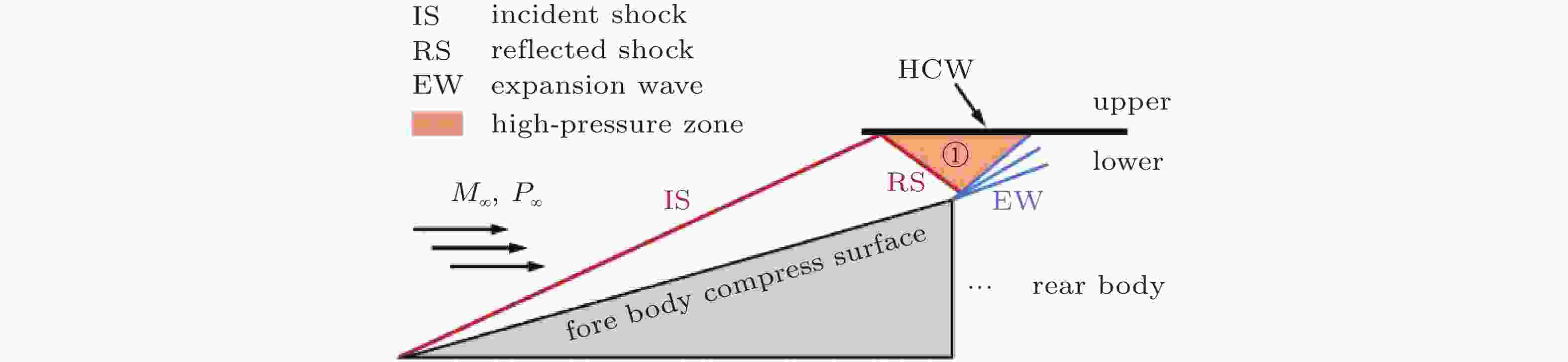
图 16 高超声速飞行器前体设计基本概念与激波压缩和等熵压缩示意图(姜et al., 2009)
图 17 高压捕获翼新概念气动布局设计原理(崔et al., 2013)
图 18 在马赫7飞行状态下X-43a的推/阻力的试验数据与计算预测(Peebles, 2008)
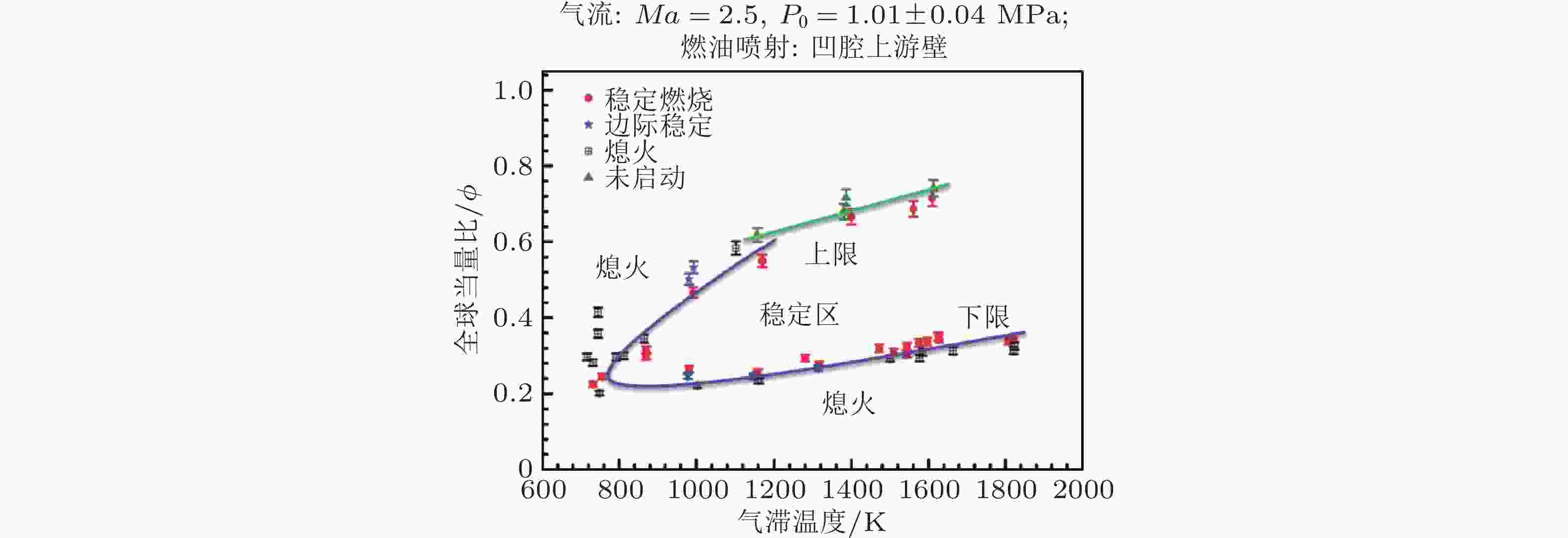
图 19 超临界态燃料在凹腔上游喷注时的稳定燃烧极限(俞et al., 2013)
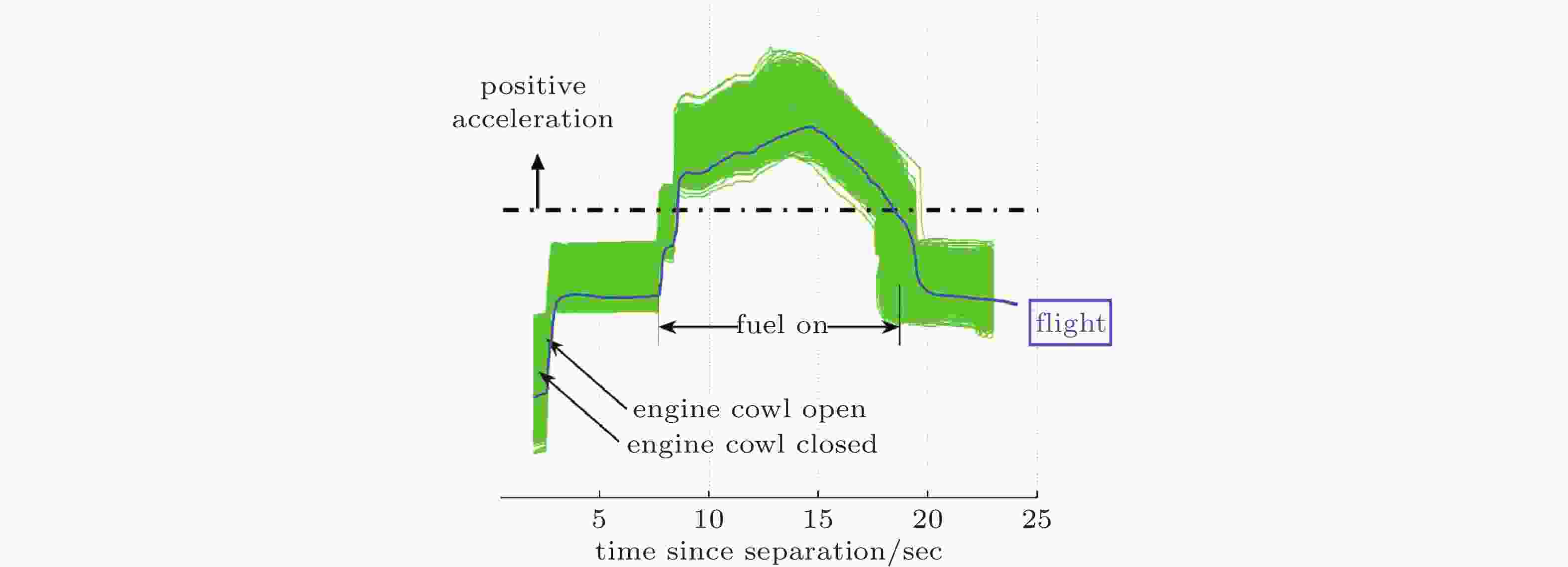
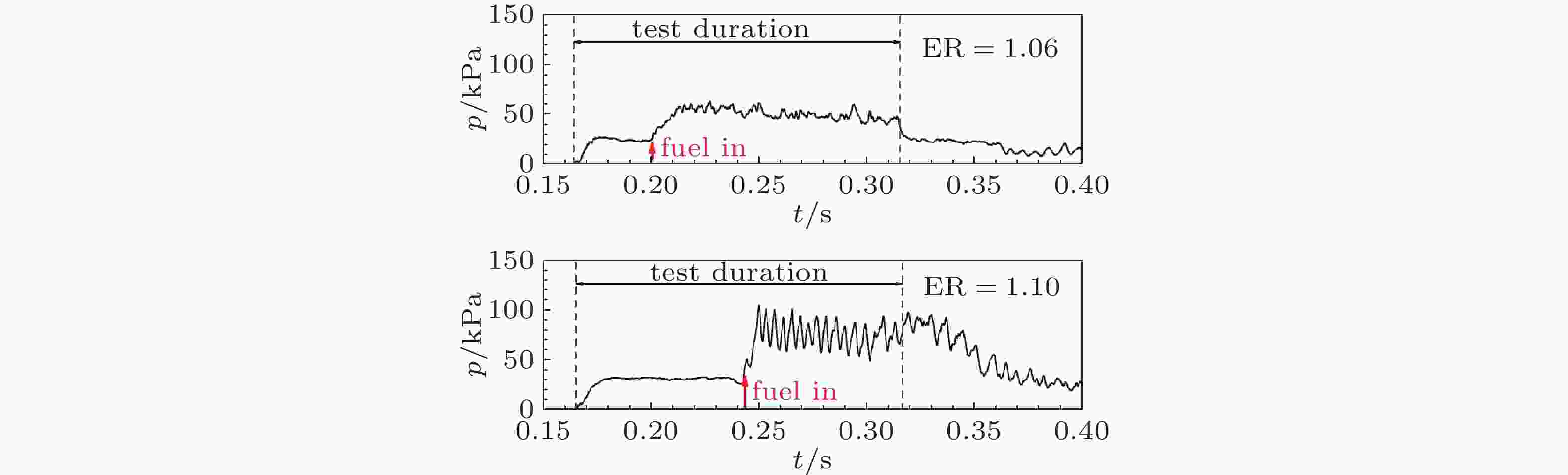
图 20 超燃冲压发动机发动机稳定燃烧与喘振现象(Austin et al., 2015)
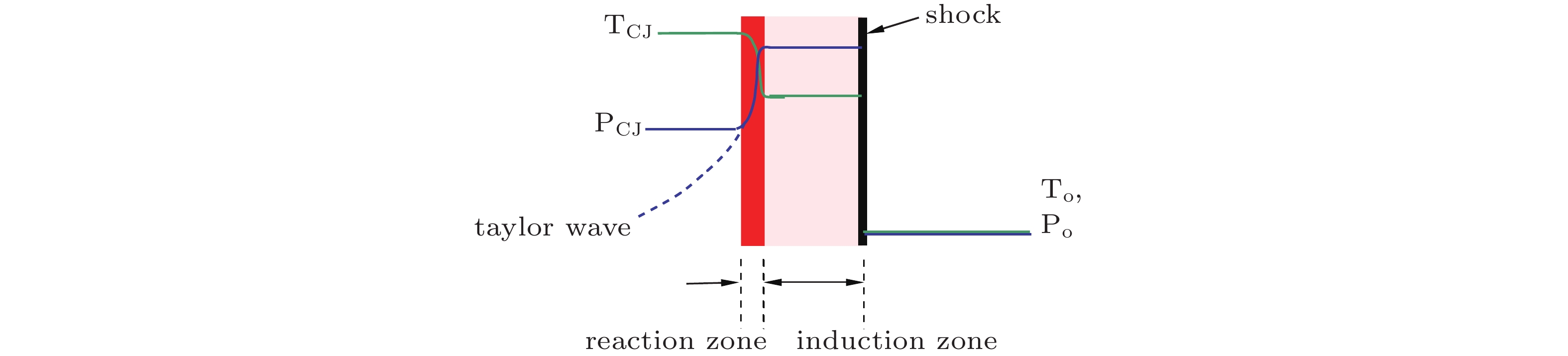
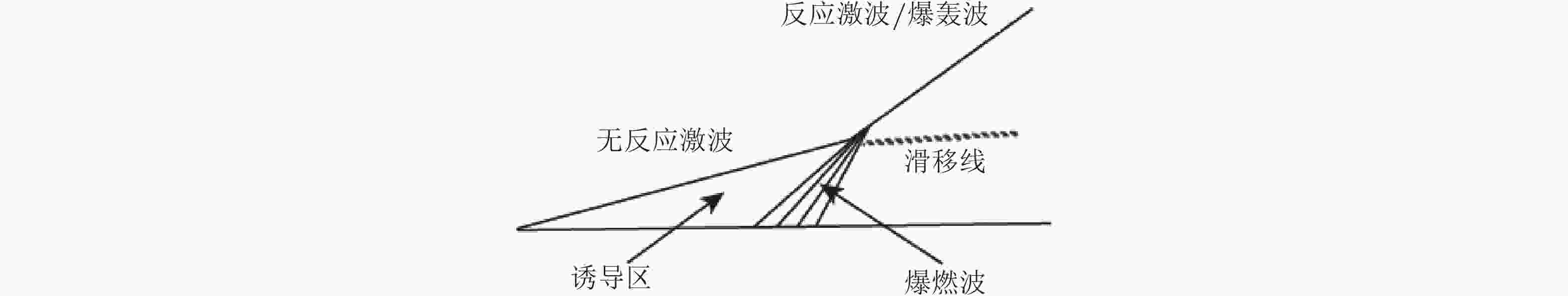
图 21 气相爆轰ZND模型物理概念示意图(姜et al., 2012)
图 22 斜爆轰起爆结构示意图(滕et al., 2020)
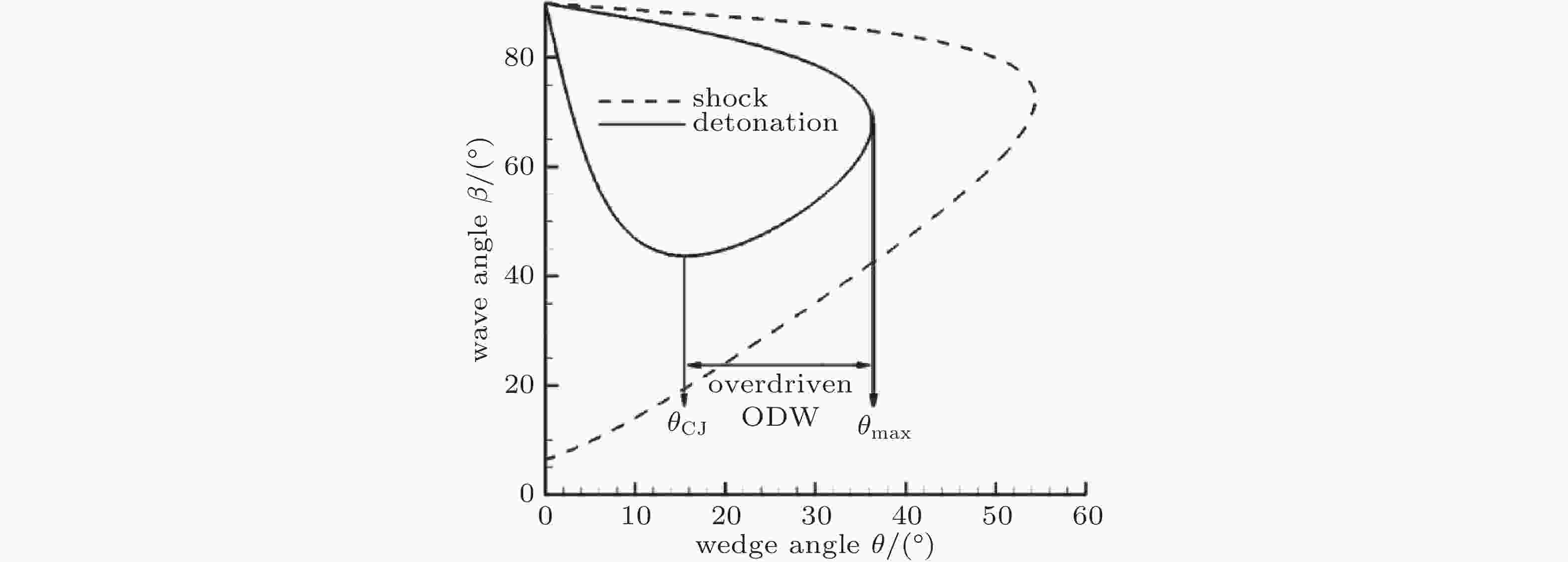
图 23 斜爆轰波极线、CJ 爆轰点与斜爆轰驻定窗口(Jiang, 2023)
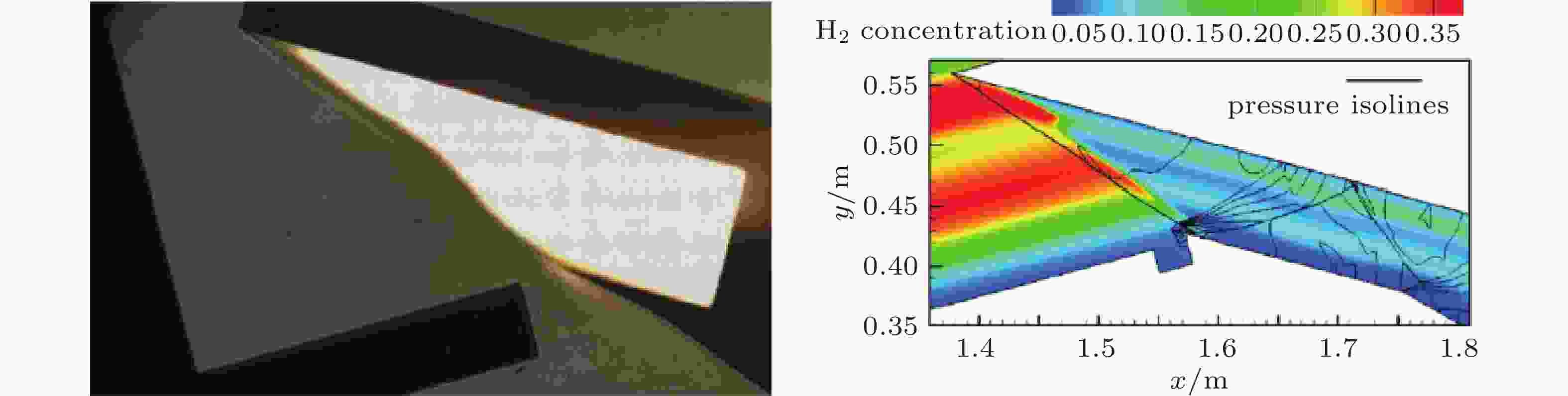
图 24 Sodramjet 发动机运行期间燃烧室的斜爆轰照片和氢燃料分布图(Jiang, 2023)
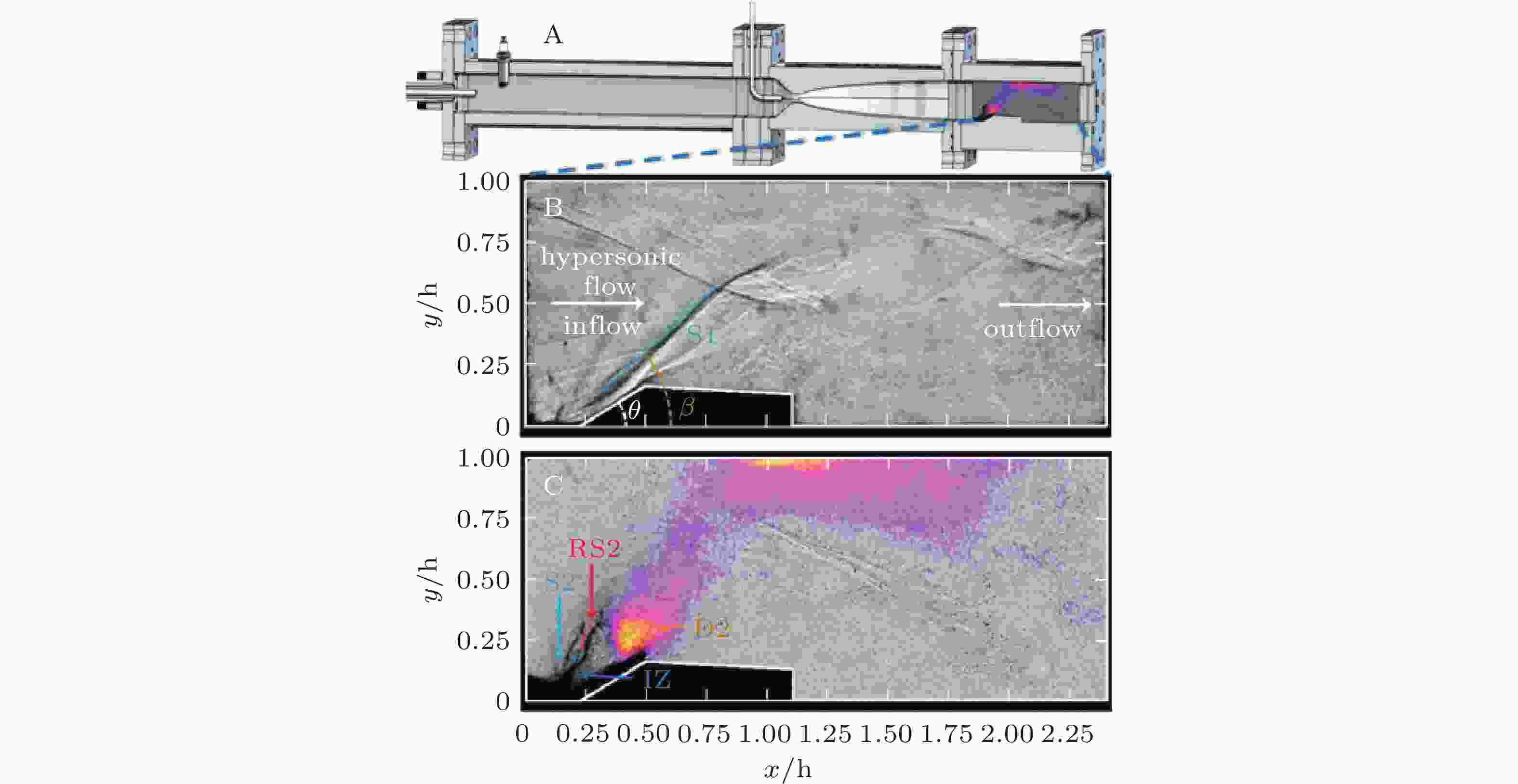
图 25 HyperReact试验装置和实验结果(Rosato et al., 2021)
-
[1] 崔凯, 李广利, 胡守超, 屈志朋. 2013. 高速飞行器高压捕获翼气动布局概念研究. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 43(05): 652-661 (Cui K, Li G L, Hu S C, et al. 2013. Conceptual studies of the high pressure zone capture wing configuration for high speed air vehicles. SciSin-Phys Mech Astron, 43(05): 652-661).Cui K, Li G L, Hu S C, et al. 2013. Conceptual studies of the high pressure zone capture wing configuration for high speed air vehicles. SciSin-Phys Mech Astron, 43(05): 652-661 [2] 顾诵芬, 史超礼. 1988. 世界航空发展史. 河南科学技术出版社. [3] 郭永怀. 1957. 现代空气动力学的问题. 科学通报, 10: 289-295. [4] 郭永怀. 2009. 激波的介绍. 郭永怀文集, 科学出版社, 北京. [5] 贺德馨. 2001. 风洞天平. 国防工业出版社, 北京. [6] 洪启臻. 2022. 高温热化学非平衡流动的精细模拟研究 [D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. [7] 姜宗林. 2009. 关于吸气式高超声速推进技术研究的思考. 力学进展, 39(4): 398-405. [8] 姜宗林. 2021. 关于超声速燃烧与高超动力. 力学进展, 51 (1): 130-140 (Jiang Z L. 2021. On supersonic combustion and hypersonic propulsion: Advances in Mechanics, 51: 130-140).Jiang Z L. 2021. On supersonic combustion and hypersonic propulsion: Advances in Mechanics, 51: 130-140 [9] 姜宗林, 滕宏辉. 2012. 气相规则胞格爆轰波起爆与传播统一框架的几个关键基础问题研究. 中国科学 G, 42(4): 421-435 (Jiang Z L, Teng H H. 2012. Research on some fundamental problems of the universal framework for regular gaseous detonation initiation and propagation. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 42(4): 421-435).Jiang Z L, Teng H H. 2012. Research on some fundamental problems of the universal framework for regular gaseous detonation initiation and propagation. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 42(4): 421-435 [10] 姜宗林. 2020. 气体爆轰物理及其统一框架理论. 科学出版社, 北京. [11] 姜宗林, 李进平, 赵伟, 刘云峰, 俞鸿儒. 2012. 长试验时间爆轰驱动激波风洞技术研究. 力学学报, 44(5): 824-831 (Jiang Z L, Li J P, et al. 2012. Investigating into techniques for extending thetest-duration of detonation-driven shock tunnels. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 44(5): 824-831).Jiang Z L, Li J P, et al. 2012. Investigating into techniques for extending thetest-duration of detonation-driven shock tunnels. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 44(5): 824-831 [12] 姜宗林. 2022. 中国高超风洞的理论创新与工程实践. 工程研究 - 跨学科视野中的工程, 14(6): 469-482 (Jiang Z L. 2022. Theoretical Innovation and Engineering Practice of ChineseHypervelocity Wind Tunnels. Journal of Engineering Studies, 14(6): 469-482). doi: 10.3724/j.issn.1674-4969.22061501Jiang Z L. 2022. Theoretical Innovation and Engineering Practice of ChineseHypervelocity Wind Tunnels. Journal of Engineering Studies, 14(6): 469-482 doi: 10.3724/j.issn.1674-4969.22061501 [13] 姜宗林, 韩桂来, 汪运鹏, 刘云峰, 苑朝凯, 罗长童, 王春, 胡宗民, 刘美宽, 2025. JF-22 超高速风洞理论基础与关键技术. 航空学报, 46 (5): 531130 (Jiang Z L, Han G L, Wang Y P, et al. 2025. Theoretical bases and key technologies of JF-22 hypervelocity wind tunnel. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 46(5): 531130).Jiang Z L, Han G L, Wang Y P, et al. 2025. Theoretical bases and key technologies of JF-22 hypervelocity wind tunnel. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 46(5): 531130 [14] 姜宗林, 李进平, 胡宗民, 刘云峰, 俞鸿儒. 2018. 高超声速飞行复现风洞理论与方法. 力学学报, 50(6): 1283-1291 (Jang Z L, Li J P, Hu Z M, Liu Y F, Yu H R. 2018. Shock tunnel theory and methods for duplicating hypersonic flightconditions. Chinese Jounal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 50(6): 1283-1291). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-238Jang Z L, Li J P, Hu Z M, Liu Y F, Yu H R. 2018. Shock tunnel theory and methods for duplicating hypersonic flightconditions. Chinese Jounal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 50(6): 1283-1291 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-238 [15] 姜宗林. 2019. 高超声速高焓风洞试验技术研究进展. 空气动力学学报, 37(3): 347-355 (Jang Z L. 2019. Progresses on experimental techniques of hypersonic and high-enthalpy wind tunnels. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 37(3): 347-355). doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2019.0009Jang Z L. 2019. Progresses on experimental techniques of hypersonic and high-enthalpy wind tunnels. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 37(3): 347-355. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2019.0009 [16] 姜宗林. 2006. 触摸高温气体动力学. 力学与实践, 28 (5): 1-7 (Jang Z L. 2006. Feeling high temperature gas dynamics: Mechanics in Engineering, 28 (5): 1-7).Jang Z L. 2006. Feeling high temperature gas dynamics: Mechanics in Engineering, 28 (5): 1-7 [17] 姜宗林, 赵伟, 孙英英, 俞鸿儒, 林贞彬, 刘云峰 2009. 超高速高焓流动研究进展. 空气动力学学报, 27: 13-20 (Jiang Z L, Zhao W, Sun Y Y, Yu H R, Lin Z B, Liu Y F. 2009. Research progress on high-enthalpy and hypervelocity flows[J]. ACTA AERODYNAMICA SINICA, 27: 13-20).Jiang Z L, Zhao W, Sun Y Y, Yu H R, Lin Z B, Liu Y F. 2009. Research progress on high-enthalpy and hypervelocity flows[J]. ACTA AERODYNAMICA SINICA, 27: 13-20 [18] 姜宗林, 罗长童, 胡宗民, 刘云峰. 2015. 高超声速风洞实验数据的多维空间相关理论与关联方法. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 45: 124705 (Jiang Z L, Luo C T, Hu Z M, Liu Y F. 2015. Multi-dimensional interrelation theory for hypersonic wind-tunnel experimental data and its correlation algorithm. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 45: 124705). doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2015-00447Jiang Z L, Luo C T, Hu Z M, Liu Y F. 2015. Multi-dimensional interrelation theory for hypersonic wind-tunnel experimental data and its correlation algorithm. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 45: 124705. doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2015-00447 [19] 姜宗林, 滕宏辉, 刘云峰. 2012. 气相爆轰物理的若干研究进展. 力学进展, 42 (2): 128-138 (Jiang Z L, Teng H H, Liu Y F. Some research progress on gaseous detonation physics. Advances in Mechanics, 42 (2): 128-138).Jiang Z L, Teng H H, Liu Y F. Some research progress on gaseous detonation physics. Advances in Mechanics, 42 (2): 128-138 [20] 焦子涵, 付秋军, 邓帆, 陈林, 范宇, 尘军. 2017. 全速域可变形飞行器气动布局设计及试验研究. 固体火箭技术, 40(05): 653-659 (Jiao Z H, Fu Q J, Deng F, Chen L, Fan Y, Chen J. 2017. Aerodynamic configuration design and experimental study of all-speed morphing aircraft. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 40(05): 653-659).Jiao Z H, Fu Q J, Deng F, Chen L, Fan Y, Chen J. 2017. Aerodynamic configuration design and experimental study of all-speed morphing aircraft. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 40(05): 653-659 [21] 李进平, 冯珩, 姜宗林. 2008. 爆轰驱动激波管缝合激波马赫数计算. 空气动力学学报, 26(3): 291-296 (Li J P, Feng H, Jiang Z L. 2008. Numerical computation on the tailored shock Mach numbers for a hydrogen-oxygen detonation shock tube. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 26(3): 291-296). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2008.03.004Li J P, Feng H, Jiang Z L. 2008. Numerical computation on the tailored shock Mach numbers for a hydrogen-oxygen detonation shock tube. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 26(3): 291-296 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2008.03.004 [22] 廉筱纯. 2005. 航空发动机原理. 西北工业大学出版社. [23] 林敬周, 解福田, 钟俊, 邹东阳, 皮阳军. 2023. 高超声速风洞双体同步分离捕获轨迹试验技术. 空气动力学学报, 41(5): 77-86 (Lin J Z, Xie F T, Zhong J, et al. 2023. Dual-body synchronous captive trajectory test technique in hypersonic wind tunnel. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 41(5): 77-86). doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2022.0088Lin J Z, Xie F T, Zhong J, et al. 2023. Dual-body synchronous captive trajectory test technique in hypersonic wind tunnel. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 41(5): 77-86 doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2022.0088 [24] 刘大响, 程荣辉. 2002. 世界航空动力技术的现状及发展动向. 北京航空航天大学学报, 28(5): 490-496 (Liu D X, Cheng R H. 2002. Current Status and Development Direction of Aircraft Power Technology in the World. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 28(5): 490-496). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2002.05.002Liu D X, Cheng R H. 2002. Current Status and Development Direction of Aircraft Power Technology in the World. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 28(5): 490-496 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2002.05.002 [25] 孟宝清, 韩桂来, 姜宗林. 2016. 结构振动对大型激波风洞气动力测量的干扰. 力学学报, 48(1): 102-110 (Meng B Q, Han G L, Jiang Z L. 2016. Theoretical investigation on aerodynamic force measurement interfered by structural vibrations in large shock tunnel. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 48(1): 102-110). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-152Meng B Q, Han G L, Jiang Z L. 2016. Theoretical investigation on aerodynamic force measurement interfered by structural vibrations in large shock tunnel. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 48(1): 102-110 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-152 [26] 聂少军, 汪运鹏. 2022. 基于时频变换的激波风洞天平信号分析与处理. 力学学报, 54(1): 232-243 (Nie S J, Wang Y P. 2022. Signal analysis and processing of shock tunnel balance based on time-frequency transform. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 54(1): 232-243).Nie S J, Wang Y P. 2022. Signal analysis and processing of shock tunnel balance based on time-frequency transform. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 54(1): 232-243 [27] 沈清. 2021. TSTO 级间分离气动问题与试验模型. 第十二届全国实验流体力学学术会议, 湖南长沙. [28] 谭慧俊, 黄河峡, 卜焕先, 饶彩燕, 王娇. 2015. 一种高超声速内转式进气道的内通道设计方法. CN105205220A. [29] 唐蓓, 汪运鹏, 姜宗林. 2019. 大尺度高焓激波风洞喷管设计研究. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 49 (07): 63-72 (Tang B, Wang Y P, Jiang Z L. 2019. Nozzle design for a large-scale high-enthalpy shock tunnel. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 49: 074701).Tang B, Wang Y P, Jiang Z L. 2019. Nozzle design for a large-scale high-enthalpy shock tunnel. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 49: 074701 [30] 唐蓓. 2019. 超高速高焓激波风洞喷管设计研究 [D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. [31] 滕宏辉, 姜宗林. 2020. 斜爆轰的多波结构及其稳定性研究进展. 力学进展, 50(1): 202002 (Teng H H, Jiang Z L. 2020. Progress in multi-wave structure and stability of oblique detonations. Advances in Mechanics, 50(1): 202002). doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-19-011Teng H H, Jiang Z L. 2020. Progress in multi-wave structure and stability of oblique detonations. Advances in Mechanics, 50(1): 202002 doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-19-011 [32] 汪运鹏, 姜宗林. 2021. 高超声速喷管设计理论与方法. 力学进展, 51: 202100 (Wang Y P, Jiang Z L. 2021. A review of theories and methods for hypersonic nozzle design. Advances in Mechanics, 51(2): 257-294).Wang Y P, Jiang Z L. 2021. A review of theories and methods for hypersonic nozzle design. Advances in Mechanics, 51(2): 257-294 [33] 汪运鹏, 李小刚, 姜宗林. 2020. 脉冲型天平高精度全自动校准系统. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 50: 064702 (Wang YP, Li X G, Jiang Z L. 2020. High-accuracy fully automatic calibration system for impulse balance. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 50: 064702).Wang YP, Li X G, Jiang Z L. 2020. High-accuracy fully automatic calibration system for impulse balance. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 50: 064702 [34] 汪运鹏, 刘云峰, 苑朝凯, 罗长童, 王春, 胡宗民, 韩桂来, 赵伟, 姜宗林. 2016. 长试验时间激波风洞测力技术研究. 力学学报, 48(3): 545-556 (Wang Y p, Liu YF, Yuan C K, Luo C T, Wang C, Hu Z M, Han G L, Zhao W, Jiang Z L. 2016. Study on force measurement in long-test duration shock tunnel. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 48(3): 545-556). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-295Wang Y p, Liu YF, Yuan C K, Luo C T, Wang C, Hu Z M, Han G L, Zhao W, Jiang Z L. 2016. Study on force measurement in long-test duration shock tunnel. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 48(3): 545-556 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-295 [35] 汪运鹏, 聂少军, 王粤, 姜宗林. 2023. 卷积神经网络在风洞天平静态校准中的应用. 空气动力学学报, 41(3): 25-32 (Wang Y P, Nie S J, Wang Y, et al. 2023. Application of convolutional neural network in static calibration of wind tunnel balance. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 41(3): 25-32). doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2022.0096Wang Y P, Nie S J, Wang Y, et al. 2023. Application of convolutional neural network in static calibration of wind tunnel balance. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 41(3): 25-32 doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2022.0096 [36] 汪运鹏, 杨瑞鑫, 聂少军, 姜宗林. 2020. 基于深度学习技术的激波风洞智能测力系统研究. 力学学报, 52(5): 1304-1313 (Wang Y P, Yang R X, Nie S J, Jiang Z L. 2020. Deep-learning-based intelligent force measurement system using in a shock tunnel. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 52(5): 1304-1313). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-20-190Wang Y P, Yang R X, Nie S J, Jiang Z L. 2020. Deep-learning-based intelligent force measurement system using in a shock tunnel. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 52(5): 1304-1313 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-20-190 [37] 王卫星, 朱婷, 张仁涛, 李宥晨. 2020. 高超声速内转式进气道型面流场重构. 航空学报, 41(3): 123493 (Wang W X, Zhu T, Zhang R T, Li Y C. 2020. Flow field reconstruction of hypersonic inward turning inlet based on configuration. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 41(3): 123493).Wang W X, Zhu T, Zhang R T, Li Y C. 2020. Flow field reconstruction of hypersonic inward turning inlet based on configuration. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 41(3): 123493 [38] 王粤, 汪运鹏, 姜宗林. 2023. 激波风洞两级入轨飞行器纵向级间分离试验技术. 航空学报, 44(17): 128126 (Wang Y, Wang Y P, Jiang Z L. 2023. Test technology of longitudinal stage separation for two-stage-to-orbit vehicle in shock tunnel. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 44(17): 128126). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2022.28126Wang Y, Wang Y P, Jiang Z L. 2023. Test technology of longitudinal stage separation for two-stage-to-orbit vehicle in shock tunnel. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 44(17): 128126. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2022.28126 [39] 杨耀栋, 王复. 1982. 用于脉冲风洞的有惯性补偿的三分量压电天平. 气动实验测控技术, 2. [40] 余西龙. 2002. 高焓非平衡流的诊断技术研究. 中国科学院力学研究所博士论文. [41] 俞刚, 范学军. 2013. 超声速燃烧与高超声速推进. 力学进展, 43 (5): 449 (Yu G, Fan X J. 2013. Supersonic combustion and hypersonic propulsion. Advances in Mechanics, 43(5): 449-471).Yu G, Fan X J. 2013. Supersonic combustion and hypersonic propulsion. Advances in Mechanics, 43(5): 449-471 [42] 俞鸿儒, 李斌, 陈宏. 2007. 克服 "高超声障" 的途径. 力学进展, 37(3): 472-476 (Yu H R, Li B, Chen H. 2007. An approach for surmounting “hypersonic barrier”. Advances in Mechanics, 37(3): 472-476). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2007.03.014Yu H R, Li B, Chen H. 2007. An approach for surmounting “hypersonic barrier”. Advances in Mechanics, 37(3): 472-476 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2007.03.014 [43] 俞鸿儒, 李仲发, 李静美, 颜坤志, 林贞彬, 单译珍, 唐贵明, 1976. 激波管风洞传热测量用的塞形铜箔量热计. 力学进展, 6 (4): 117-126. [44] 俞鸿儒. 2009. 郭永怀先生引导我做实验. 力学与实践, 31(2): 97-99. [45] 张堃元. 2018. 高超声速进气道曲面压缩技术综述. 推进技术, 39(10): 2227-2235. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2018.10.008 [46] 张敏莉, 易仕和, 赵玉新. 2007. 超声速短化喷管的设计与实验研究. 空气动力学学报, 25(4): 500-503 (Zhang M L, Yi S H, Zhao Y X. 2007. The design and experimental investigations of supersonic length-shorted nozzle. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 25(4): 500-503). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2007.04.016Zhang M L, Yi S H, Zhao Y X. 2007. The design and experimental investigations of supersonic length-shorted nozzle. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 25(4): 500-503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2007.04.016 [47] 张文硕, 杨鹏飞, 姜宗林, 刘云峰. 2021. 一维与二维爆轰传播的时空关联特性数值研究. 力学学报, 53(7): 2069-2078 (Zhang W S, Yang P F, Jiang Z L, Liu Y F. 2021. Numerical investigation on the space-time correlation between oblique detonation and normal detonation propagation. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 53(7): 2069-2078).Zhang W S, Yang P F, Jiang Z L, Liu Y F. 2021. Numerical investigation on the space-time correlation between oblique detonation and normal detonation propagation. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 53(7): 2069-2078 [48] 张新宇. 2002. 发展超燃冲压发动机地面模拟实验技术的探讨. 第 185 次香山科学会议(高超声速技术持续发展驻留讨论会). [49] 张阳, 韩忠华, 周正, 汤继斌, 张科施, 文萍. 2021. 面向高超声速飞行器的宽速域翼型优化设计. 空气动力学学报, 39(6): 111-127 (Zhang Y, Han Z H, Zhou Z, et al. 2021. Aerodynamic design optimization of wide-Mach-number-range airfoils for hypersonic vehicles. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 39(6): 111-127). doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0384Zhang Y, Han Z H, Zhou Z, et al. 2021. Aerodynamic design optimization of wide-Mach-number-range airfoils for hypersonic vehicles. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 39(6): 111-127 doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0384 [50] 郑晓刚, 胡占仓, 蔡泽君, 施崇广, 朱呈祥, 尤延铖. 2025. 考虑巡航攻角的三维内转进气道设计. 航空学报, 46(8): 631233 (Zheng X G, Hu Z C, Cai Z J, Shi C G, Zhu C X, You Y C. 2025. Design of 3D inward-turning inlet considering cruising angle of attack. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 46(8): 631233). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2024.31233Zheng X G, Hu Z C, Cai Z J, Shi C G, Zhu C X, You Y C. 2025. Design of 3D inward-turning inlet considering cruising angle of attack. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 46(8): 631233 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2024.31233 [51] 郑晓刚, 施崇广, 张加乐, 张咪, 朱文磊, 朱呈祥, 尤延铖. 2025. 高超声速三维内转进气道研究进展综述. 航空学报, 46(8): 631245 (Zheng X G, Shi C G, Zhang J L, Zhang M, Zhu W L, Zhu C X, You Y C. 2025. Research progress review on hypersonic three-dimensional inward-turning inlet. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 46(8): 631245). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2024.31245Zheng X G, Shi C G, Zhang J L, Zhang M, Zhu W L, Zhu C X, You Y C. 2025. Research progress review on hypersonic three-dimensional inward-turning inlet. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 46(8): 631245 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2024.31245 [52] 中国科学院. 2014. 中国学科发展战略. 航天运输系统 [M]. 科学出版社, 北京. [53] Adamson T C, Morrison R B. 1955. On the classification of normal detonation waves. Jet Propulsion, 25(8): 400-403. [54] Anderson G, Kumar A, Erdos J. 1990. Progress in hypersonic combustion technology with computation and experiment. AIAA 1990-5254. [55] Anderson J D. 1989. Hypersonic and High Temperature Gas Dynamics. McGraw-Hill, New York. [56] Arnaiz H H, Peterson J B, Daugherty J C. 1980. Wind-tunnel/flight correlation study of aerodynamic characteristics of a large flexible supersonic cruising airplane (XB-70-1). Technical Report, NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton VA. [57] Austin J, Ju Y G. 2015. Exploring combustion and supersonic flow. Aviation Week & Space Technology, pp. 57-58, Nov. [58] Bakos R J, Erdos J I. 1995. Options for enhancement of the performance of shock-expansion tubes and tunnels. AIAA Paper 95-0799. [59] Ben-Yakar A, Hanson R K. 1994. Cavity flame-holders for ignition and flame stabilization in scramjet: An overview. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 17: 869-877. doi: 10.2514/2.5818 [60] Bernstein L. 1975. Force measurement in short-duration hypersonic facilities. AGARDograph No. 214. [61] Bertin J J, Cummings R M. 2003. Fifty years of hypersonics: where we’ve been, where we’re going. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 39: 511-536. doi: 10.1016/S0376-0421(03)00079-4 [62] Bertin J J, Cummings R M. 2006. Critical hypersonic aerothermodynamic phenomena. Annu Rev Fluid Mech, 38: 129-57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.38.050304.092041 [63] Bertin J J. 1994. Hypersonic Aerothermodynamics. AIAA, Inc. , Washington DC. [64] Bhat M K, Bose T K. 1973. Fluid flow with variable properties in a two-dimensional channel. Phys. Fluids, 16(11): 2007-2009. doi: 10.1063/1.1694247 [65] Billig F S C. 1993. Research on supersonic combustion. Journal of Propulsion & Power, 9(4): 499-514. doi: 10.2514/3.23652 [66] Billig F S, Orth R C, Lasky M. 1971. A unified analysis of gaseous jet penetration. AIAA Journal, 9(6). [67] Bird G A. 1957. A note on combustion driven tubes. Royal Aircraft Establishment, AGARD Rep. , pp. 146, May. [68] Bose T K. 2004. Hypersonic and High Temperature Gas Dynamics. Springer, New York. [69] Brandstetter A, Rocci Denis S, Kau H-P, Rist D. 2002. Experimental investigation of supersonic combustor with strut injector. AIAA 2002-5242. [70] Builder C H. 1964. On the Thermodynamic Spectrum of Air-breathing Propulsion. AIAA Paper 64–243. [71] Buttsworth D R. 2001. Assessment of effective thermal product of surface junction thermocouples on millisecond and microsecond time scales. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 25: 409-420. doi: 10.1016/S0894-1777(01)00093-0 [72] Candler G V, et al. 2002. CFD validation for hypersonic flight: hypersonic double-cone flow simulations. AIAA Paper 2002-0581, Jan. [73] Chan W Y K, Jacobs P A, Smart M K, et al. 2018. Aerodynamic design of nozzles with uniform outflow for hypervelocity ground-test facilities. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 34: 1467-1478. doi: 10.2514/1.B36938 [74] Chapman D L. 1899. On the rate of explosion in gases. Philos. Mag., 47: 90-104. [75] Chinzei N. 2001. Progress in Scramjet engine tests at NAL-KRC. AIAA Paper 2001-1883. [76] Chue R S M, et al. 2022. NASAs HYPULSE facility at GASL – a dual mode, dual driver reflected-shock/expansion tunnel. Advanced Hypersonic Test Facilities, eds. by Frank Lu and Dan Marren, pp. 29-72. [77] Coates P B, Gaydon A G. 1965. A simple shock tube with detonating driver gas. Proc. Roy. Soc. , London, A, 283: 18-32. [78] Colonna G, Bonelli F, Pascazio G. 2019. Impact of fundamental molecular kinetics on macroscopic properties of high-enthalpy flows, the case of hypersonic atmospheric entry. Physical Review Fluids, 4: 033404. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.033404 [79] Cui K, Li G L, Xiao Y, et al. 2017. High-pressure capturing wing configurations. AIAA J, 55(06): 1909-1919. doi: 10.2514/1.J055395 [80] Decker J P. 1969. Aerodynamic interference effects caused by parallel-staged simple aerodynamic configurations at Mach numbers of 3 and 6. NASA-TN-D-5379, NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, Washington. [81] Doring W. 1943. On detonation processes in gases. Ann. Phys., 43: 421-436. [82] Echnreth A C. 1996. Laser Diagnostics for Combustion Temperature and Species. CRC Press. [83] Eitelberg G. 1994. First results of calibration and use of the HEG. AIAA Paper 94-2525. [84] Emmons H W. 1967. Arc measurement of high temperature gas transport properties. Phys. Fluids, 10: 1135. doi: 10.1063/1.1762255 [85] Erdos J I, Calleja J, Tamagno J. 1994. Increases in the hypervelocity test envelope of the Hypulse shock-expansion tube. AIAA Paper 94-2524. [86] Fang Y, Hu Z, Teng H. 2018. Numerical investigation of oblique detonations induced by a finite wedge in a stoichiometric hydrogen-air mixture. Fuel, 234: 502-507. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.07.048 [87] Fang Y, Zhang Y, Deng X, Teng H. 2019. Structure of wedge-induced oblique detonation in acetylene-oxygen-argon mixtures. Physics of Fluids, 31: 026108. doi: 10.1063/1.5086235 [88] Fedorov A V, Soudakov V G, Malmuth N D. 2010. Theoretical modeling of two-body interaction in supersonic flow. AIAA J, 48(2): 258-266. doi: 10.2514/1.40592 [89] Ferri A, Libby P A, Zakkay V. 1962. Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Supersonic Combustion. Polytechnicinst of Brooklyn, NewYork. [90] Foelsch K. 1949. The analytical design of an axially symmetric laval nozzle for a parallel and uniform jet. Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences, 16(3): 161-166. doi: 10.2514/8.11758 [91] Guentert E C, Neumann H E. 1959. Design of axisymmetric exhaust nozzles by method of characteristics incorporating a variable isentropic exponent. NASA TR R-33. [92] Guy Norris. 2011. X-51A scramjet fails on second attempt. Aviation Week & Space Technology. [93] Hallion R. 1987. The Hypersonic Revolution. Wright-Patterson AFB, OH. [94] Hammerling P, Teare J D, Kivel B. 1959. Theory of radiation from luminous shock waves in nitrogen. Physics of Fluids, 2(4): 422-426. doi: 10.1063/1.1724413 [95] Hecklen J. 1971. Gas-phase chemistry of re-entry. AIAA J., 5(1): 4-15. doi: 10.2514/3.3901 [96] Heiser W H, Pratt D T. 1994. Hypersonic Airbreathing Propulsion. AIAA Inc. , Washington, DC. [97] Heiser W H, Pratt D T. 1994. Hypersonic Air-breathing Propulsion. Reston, AIAA Ins. [98] Holden M S, Wadhams T P, Candler G V. 2004. A review of experimental studies in the LENS shock tunnel and expansion tunnel to examine real-gas effects in hypervelocity flows. AIAA Paper 2004-0916. [99] Holden M S. 1993. Recent advances in hypersonic test facilities and experimental research. AIAA Paper 93-5005. [100] Holden M S. 2015. Extension of LENS shock tunnel test time and lower Mach number capability. AIAA SciTech AIAA 2015-2017. [101] Hong Q, Storchi L, Sun Q, Bartolomei M, Pirani F, Coletti C. 2023. Improved quantum–classical treatment of N2-N2 inelastic collisions: effect of the potentials and complete rate coefficient data sets. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 19(23): 8557-8571. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.3c01103 [102] Hornung H G. 1988. The piston motion in a free-piston driver for shock tubes and tunnels. GALCIT Rep. FM88-1. [103] Hornung H G. 1992. Performance data of the new free-piston shock tunnel at GALCIT. AIAA Paper 92-3943. [104] Itoh K, et al. 1998. Improvement of a free piston driver for a high-enthalpy shock tunnel. Shock Waves, 8: 215-233. doi: 10.1007/s001930050115 [105] Jiang Z, Chue S M. 2023. Theories and technologies of hypervelocity shock tunnel. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press. [106] Jiang Z, Li J, Hu Z, Liu Y, Yu H. 2020. On theory and methods for advanced detonation-driven hypervelocity shock tunnels. National Science Review, 7(7): 1198-1207. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa050 [107] Jiang Z, Teng H. 2022. Gaseous Detonation Physics and Its Universal Framework Theory. Springer Nature, Singapore, ISBN: 978-981-19-7001-6. [108] Jiang Z, Yu H. 2017. Theories and technologies for duplicating hypersonic flight conditions for ground testing. National Science Review, 4(3): 290-296. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx007 [109] Jiang Z, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Wang C, Luo C. 2021. Criteria for hypersonic airbreathing propulsion and its experimental verification. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 34(3): 94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.11.001 [110] Jiang Z, Zhao W, Wang C, Takayama K. 2002. Forward-running detonation drivers for high-enthalpy shock tunnels. AIAA J, 40(10): 2009-2016. doi: 10.2514/2.1533 [111] Jiang Z. 2023. Standing oblique detonation for hypersonic propulsion: A review. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 143: 100955. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2023.100955 [112] Jouguet E. 1905. On the propagation of chemical reactions in gases. J. De Mathematiques Pures et Appliqquees, 1: 347-425. [113] Kerrebrock J L. 1962. Conduction in gases with elevated electron temperature. Engineering Aspects of Magnetohydrodynamics, Columbia Press, New York, pp. 327–346. [114] Kerrebrock J L. 1965. Magneto-hydrodynamic generators with non-equilibrium ionization. AIAA J., 3: 591. [115] Knab H, Fruhauf E M. 1995. Theory and validation of the physically consistent coupled vibration-chemistry-vibration model. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf., 9(2): 219-226. doi: 10.2514/3.649 [116] Kuo Y H. 1957. Dissociation effects in hypersonic viscous flows. J. of the aeronautical sciences, 24(5): 345-350. doi: 10.2514/8.3847 [117] Lee D B, Goodrich W D. 1972. The aerothermodynamic environment of the Apollo command module during super-orbital entry. NASA TN D-6792, April. [118] Lee J H S. 1977. Initiation of gaseous detonation. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem., 28: 75-104. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.28.100177.000451 [119] Lee J H S. 2008. The Detonation Phenomenon. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. [120] Li J, Chen H, Zhang S, Zhang X, Yu H. 2017. On the response of coaxial surface thermocouples for transient aerodynamic heating measurements. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 86: 141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2017.04.011 [121] Li J, Yu G, Zhang Y, Li Y, Qian D. 1997. Experimental studies on self-ignition of hydrogen/air supersonic combustion. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 13 (4). [122] Li Z, Liu M, Han G, Wang D, Jiang Z. 2023. Numerical simulation of hypersonic flat-plate boundary-layer blowing control. Physics of Fluids, 35: 126111. doi: 10.1063/5.0174498 [123] Li Z, Liu M, Han G, Wang D, Jiang Z. 2024. Experimental study on aerodynamic heating of hypersonic boundary-layer lowing. AIAA Journal, 62(10): 4011-4016. doi: 10.2514/1.J064454 [124] Liu M, Han G, Jiang Z. 2022. Experimental study on the evolution of mode waves in laminar boundary layer on a largescale flat plate. Physics of Fluids, 34: 013612. doi: 10.1063/5.0075710 [125] Liu M, Han G, Li Z, Jiang Z. 2022. Experimental study on the effects of the cone nose-tip bluntness. Physics of Fluids, 34: 101703. doi: 10.1063/5.0110928 [126] Liu X Z. 2008. Review of scramjet research in China. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 29(4): 385-395. [127] Liu Y, Qian Z S, Lu W, et al. 2020. Numerical investigation on the safe stage-separation mode for a TSTO vehicle. Aerospace Science and Technology, 107: 106349. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106349 [128] Lu F K, Marren D E. 2002. Advanced Hypersonic Test Facilities. Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics, Vol. 198. [129] Luo C, Zhang S L. 2012. Parse-matrix evolution for symbolic regression. Eng. Appl Artif Intell, 25: 1182-1193. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2012.05.015 [130] Marrone P, Treanor C. 1963. Chemical relaxation with preferential dissociation from excited vibrational levels. Physics of Fluids, 6(9): 1215-1221. doi: 10.1063/1.1706888 [131] Mathews G, Goldenstein C. 2020. Near‐GHz scanned‐wavelength‐modulation spectroscopy for MHz thermometry and H2O measurements in aluminized fireballs of energetic materials. Applied Physics B, 126(11): 189. [132] Meng B, Han G, Luo C, Jiang Z. 2018. Numerical investigation of the axial impulse load during the startup in the shock tunnel. Aerospace Science and Technology, 73: 332-342. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2017.12.013 [133] Meng B, Han G, Zhang D, Jiang Z. 2017. Aerodynamic measurement of a large aircraft model in hypersonic flow. Chinese Physics B, 26(11): 114702. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/26/11/114702 [134] Micka D J, Driscoll J F. 2009. Combustion characteristics of a dual-mode scramjet combustor with cavity flame-holder. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 32: 2397-2404. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2008.06.192 [135] Miyajima H. 1994. Design concept of the NAL/NASDA high-enthalpy shock tunnel. In: 4th Int Workshop on Shock Tube Technologies, Sept. 20-24. [136] Morelli E A, Derry S D, Smith M S. 2005. Aerodynamic parameter estimation of the X-43A (Hyper-X) from flight test data. AIAA Paper 2005-5921. [137] Morris J C, Garrison R L. 1966. Bremsstrahlung and recombination radiation of atomic and ionic oxygen. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf., 6: 899. [138] Morrison R B. 1980. Oblique Detonation Wave Ramjet. NASA Contract Report No. 159192, January. [139] Nagnibeda E, Kustova E. 2009. Non-equilibrium reacting gas flows: kinetic theory of transport and relaxation processes. Springer Science and Business Media. [140] Nair A P, Minesi N Q, Jelloian C, et al. 2022. Extended tuning of distributed-feedback lasers in a bias-tee circuit via waveform optimization for MHz-rate absorption spectroscopy. Measurement Science and Technology, 33(10): 105104. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ac7b13 [141] Naughton J W, Settles G S. 1992. Experiments on the enhancement of compressible mixing via streamwise vortices. AIAA 92-3547. [142] Olejniczak J, Candler G. 1995. Vibrational energy conservation with vibration-dissociation coupling: general theory and numerical study. Physics of Fluids, 7(7): 1764-1774. doi: 10.1063/1.868491 [143] Pan L J, Kuo Y H. 1956. Compressible viscous flow past a wedge moving at hypersonic speeds. J. of Mathematics and Physics, 35(2): 179-193. doi: 10.1002/sapm1956351179 [144] Park C. 1988. Assessment of two-temperature kinetics model for dissociation and weakly-inozing nitrogen. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf., 2(1): 8-16. [145] Peebles C. 2008. Road to Mach 10: Lessons Learned from the X-43A Flight Research Program. AIAA Inc. , Reston, VA. [146] Peedles C. 2007. Road to Mach 10: Lessons Learned from the X-43A Flight Research Program. Reston, AIAA Ins. [147] Prandtl L, Busemann A. 1929. Naherungsverfahren zur zeichnerischen ermittlung von ebenen stromungen mit übershllgeschwindigkeit. Füssli Verlag, Zurich, Switzerland. [148] Qi L, Han G, Hu Z, Wang C, Jiang Z. 2022. Numerical investigations of the lateral heat transfer in coaxial thermocouples. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 82(6): 280-298. [149] Qi L, Han G, Jiang Z. 2023. Optimal design of E-type coaxial thermocouples for transient heat measurements in shock tunnels. Applied Thermal Engineering, 218: 119388. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.119388 [150] Qiao W Y, Yu A Y, Gao W, et al. 2019. Design method with controllable velocity direction at throat for inward turning inlets. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 32(6): 1403-1415. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.04.012 [151] Rogers R C. 1971. Mixing of hydrogen injected from multiple injectors normal to a supersonic airstream. NASA TND-6476, Sept. [152] Rosato D, Thornton M R, Sosa J, Bachman C, Goodwin G B, Ahmed K. 2021. Stabilized detonation for hypersonic propulsion. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 118(20). [153] Rufolo G C, Roncioni P, Marini M, et al. 2008. Post flight aerodynamic analysis of the experimental vehicle PRORA USV1. AIAA Paper 2008-2661. [154] Sarma G. 2000. Physico-chemical modeling in hypersonic flow simulation. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 36: 281-349. [155] Schultz D L, Jones T V. 1973. Heat-transfer measurements in short-duration hypersonic facilities. AGARDograph No. 165. [156] Séror S, Druguet M, Schall E, et al. 1998. Coupled vibration-dissociation-exchange reactions model for hypersonic airflow computations. AIAA Journal, 36(4): 532-538. doi: 10.2514/2.426 [157] Shi C G, You Y C, Zheng X G, et al. 2023. Analytical model for curved-shock Mach reflection. Physics of Fluids, 35(3): 031702. doi: 10.1063/5.0139784 [158] Shi C G, Zhu C X, You Y C, et al. 2021. Method of curved-shock characteristics with application to inverse design of supersonic flow-fields. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 920: A36. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2021.454 [159] Shope F L. 2006. Contour design techniques for super/hypersonic wind tunnel nozzles. 24th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, AIAA Paper 2006-3665. [160] Sivells J C. 1978. A computer program for the aerodynamic design of axisymmetric and planar nozzles for supersonic and hypersonic wind tunnels[R]. AEDC-TR-78-63. [161] Sivells J C. 2012. Aerodynamic design of axisymmetric hypersonic wind-tunnel nozzles. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 7: 1292-1299. doi: 10.2514/6.1969-337 [162] Stalker R J. 1967. A study of the free-piston shock tunnel. AIAA J., 5: 2160-2165. doi: 10.2514/3.4402 [163] Stalker R T, Morrson W R D. 1989. New generation of free piston shock tunnel facilities. Proceeding of 17th International Symposium on Shock Tube and Waves, Bethem. [164] Tanno H, et al. 2001. Experimental study on flow establishment in a large-scale Scramjet. AIAA Paper 2001-1889. [165] Teng H, Jiang Z, Ng H D. 2014. Numerical study on unstable surfaces of oblique detonations. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 744: 111-128. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2014.78 [166] Thakur A, Segal C. 2004. Flame-holding analyses in supersonic flow. AIAA 2004-3831. [167] Tibère-Inglesse A, Cruden B A. 2022. Analysis of nonequilibrium atomic and molecular nitrogen radiation in pure N2 shockwaves. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 290: 108302. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2022.108302 [168] Treanor C, Marrone P. 1962. Effects of dissociation on the rate of vibrational relaxation. Physics of Fluids, 5(9): 1022-1026. doi: 10.1063/1.1724467 [169] Tsien H S, et al. 2001. Proposal and study for construction of a Pilot hypersonic wind tunnel at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 钱学森手稿, 山西教育出版社, p. 121. [170] Tsien H S. 1946. Similarity laws of hypersonic flows. J. Math and Phys., 25: 247-251. doi: 10.1002/sapm1946251247 [171] Tsien H S. 1946. Superaerodynamics mechanics of rarefied gases. J Aero Sci, 13: 653-664. doi: 10.2514/8.11476 [172] Verreault J, Higgins A J, Stowe R A. 2012. Formation and structure of steady oblique and conical detonation waves. AIAA Journal, 50: 1766-1772. doi: 10.2514/1.J051632 [173] Verreault J, Higgins A J, Stowe R A. 2013. Formation of transverse waves in oblique detonations. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 34: 1913-1920. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2012.07.040 [174] Viguier C, Silva L F F, Desbordes D, Deshaies B. 1996. Onset of oblique detonation waves: comparison between experimental and numerical results for hydrogen-air mixtures. Symp. (Int. ) Combust., 26(2): 3023-3031. doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(96)80146-9 [175] von Neumann J. 1942. Theory of detonation waves. In: John von Neumann. Collected Works. Vol. 6, ed. A. J. Taub. New York: Macmillam. [176] Wang C, Jiang Z. 2008. Numerical investigation on the flow field of “swallowtail" cavity for supersonic mixing enhancement. Proceeding of the Fourth Across-strait Workshop on Shock Wave/Vortex Interaction, Dali, Yunnan. [177] Wang X, Guo J, Hong Q, Li S. 2023. High-fidelity state-to-state modeling of hypersonic flow over a double cone. Physics of Fluids, 35 (11). [178] Wang X, Hong Q, Hu Y, Sun Q. 2023. On the accuracy of two-temperature models for hypersonic nonequilibrium flow. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 39(2): 122193. doi: 10.1007/s10409-022-22193-x [179] Wang Y, Jiang Z. 2020. Impulse force-measurement system. Shock Waves, 30(6): 1-11. [180] Wang Y, Jiang Z. 2020. Intelligent force-measurement system use in shock tunnel. Sensors, 20(26): 6179. doi: 10.3390/s20216179 [181] Wang Y, Jiang Z. 2022. Theories and methods for designing hypersonic high-enthalpy flow nozzles. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 35(1): 318-339. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.01.018 [182] Wang Y, Liu Y, Jiang Z. 2016. Design of a pulse-type strain gauge balance for a long-test-duration hypersonic shock tunnel. Shock waves, 26(6): 835-844. doi: 10.1007/s00193-015-0616-x [183] Wang Y, Liu Y, Luo C, Jiang Z. 2016. Force measurement using strain-gauge balance in a shock tunnel with long test duration. Review of Scientific Instruments, 87: 055108. doi: 10.1063/1.4950781 [184] Wang Y, Wang Y, Jiang L. 2022. Numerical investigation of aerodynamic separation schemes for two-stage-to-orbit-like two-body system. Aerospace Science and Technology, 131(Part A): 107995. [185] Wang Y, Wang Y, Jiang Z. 2022. Experimental study of longitudinal stage separation of two-body configuration in shock tunnel. AIAA Journal, 60(12): 6940-6946. doi: 10.2514/1.J062135 [186] Wang Y, Wang Y, Jiang Z. 2023. Unsteady interaction mechanism of transverse stage separation in hypersonic flow for a two-stage-to-orbit vehicle. Physics of Fluids, 35(5): 056120. doi: 10.1063/5.0151663 [187] Wang Y, Wang Y, Jiang Z. 2024. Experimental and numerical investigation on the unsteady interaction in longitudinal stage separation for parallel-staged two-body configuration. Physics of Fluids, 36(1): 016116. doi: 10.1063/5.0184293 [188] Wang Y, Wang Y, Wang C, Jiang L. 2023. Numerical investigation on longitudinal stage separation of spiked two-stage-to-orbit vehicle. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 60(1): 215-229. doi: 10.2514/1.A35390 [189] Wang Y, Wang Y. 2024. Unsteady interaction and dynamic stability analysis of a two-stage-to-orbit vehicle during transverse stage separation. Acta Astronautica, 216: 488-503. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2024.01.002 [190] Weber R J, MacKay J S. 1958. An Analysis of Ramjet Engines Using Supersonic Combustion. National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Washington D C. [191] Weiland C. 2014. Aerodynamic Data of Space Vehicles. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg. [192] Yang P, Teng H, Jiang Z, Ng H D. 2018. Effects of inflow Mach number on oblique detonation initiation with a two-step induction-reaction kinetic model. Combustion and Flame, 193: 246-256. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2018.03.026 [193] Yang P, Teng H, Ng H D, Jiang Z. 2019. A numerical study on the instability of oblique detonation waves with a two-step induction reaction kinetic model. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 37: 3537-3544. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.05.090 [194] Young J C, et al. 1981. Space shuttle entry aerodynamic comparison of flight preflight predictions. AIAA Paper 81-2476, The First Flight Testing Conference, Las Vegas, NV, Nov. 11-13. [195] Yu H, Esser B, Lenartz M, Gronig H. 1992. Gaseous detonation driver for a shock tunnel. Shock Waves, 2: 245-254. doi: 10.1007/BF01414760 [196] Yu M, Gu H, et al. 2019. Experimental study of mode transition characteristics of a cavity-based scramjet combustor during acceleration. Aerospace Science and Technology, 93: 105316. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.105316 [197] Yu R. 1989. Recent developments in shock tune application. In: Takayama ed. Proc of the 1989 National Symp. on Shock Wave Phenomena, Sagamihara, Japan, Tohoku Print, Sendai, pp. 1-9. [198] Zeitoun D, et al. 1995. Vibration-dissociation coupling in non-equilibrium hypersonic viscous flows. AIAA Journal, 33(1): 79-85. doi: 10.2514/3.12335 [199] Zel’dovich Y B. 1940. On the theory of the propagation of detonation in gaseous systems. Journal of experimental and theoretical physics, 10: 543-568. doi: 10.1515/9781400862979.411 [200] Zhang Y, Fang Y, Ng H D, Teng H. 2019. Numerical investigation on the initiation of oblique detonation waves in stoichiometric acetylene-oxygen mixtures with high argon dilution. Combustion and Flame, 204: 391-396. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2019.03.033 [201] Zhou G, Li F, Lin X, Li R, et al. 2023. Research on flame temperature measurement method based on water vapor emission spectrum. Measurement Science and Technology, 34(5): 054001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/acb3e9 [202] Zhou G, Wang W, Li F, et al. 2024. Multidimensional high-temperature field measurement method for flame based on near infrared radiation spectrum of water vapor. Optics and Lasers in engineering, 174: 13. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107972 -




 下载:
下载: