Recent progress in multi-physics simulation based on the smoothed particle hydrodynamics
-
摘要: 工程科学众多问题涉及多物理场耦合效应, 其数值模拟往往面临巨大挑战. 光滑粒子法 (smoothed particle hydrodynamics, SPH) 是一种经典的无网格粒子方法, 在模拟多物理场耦合问题方面具有明显优势, 已在众多科学和工程领域取得广泛应用. 本文重点介绍近期SPH算法研究概况及其在多物理场耦合模拟方面的应用进展. 具体内容包括: (1) 力−热耦合问题, 涉及传热传质、高速撞击、铸造、增材制造等领域; (2) 力−热−化学反应耦合问题, 涵盖聚能射流、爆炸焊接、水下爆炸等应用; (3) 力−热−电磁耦合问题, 包括电磁场流场控制及“X-pinch”等问题. 最后, 对SPH方法模拟多物理场耦合问题的未来发展进行了讨论和展望.
-
关键词:
- 光滑粒子法(SPH) /
- 多物理场 /
- 爆炸冲击 /
- 增材制造 /
- 传热传质
Abstract: Many engineering problems involve coupling effects of multiple physical fields, which pose significant challenges for numerical simulations. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a classic meshfree particle method that offers distinct advantages in simulating multi-physics coupling problems and has been widely applied in various fields of sciences and engineering. This paper focuses on recent advances in SPH and its applications in multi-physics simulations. The key topics include: (1) mechano-thermal coupled problems, such as heat and mass transfer, high-speed impacts, casting processes, and additive manufacturing; (2) mechano-thermal-chemical coupled problems, with complex scenarios including shaped charge jet formation and penetration effects, explosive welding, and underwater explosions; (3) mechano-thermal-electromagnetic coupled problems, including electromagnetic flow control and “X-pinch” phenomena. Finally, the future development of the SPH method in simulating multi-physics coupling problems is discussed and prospected. -
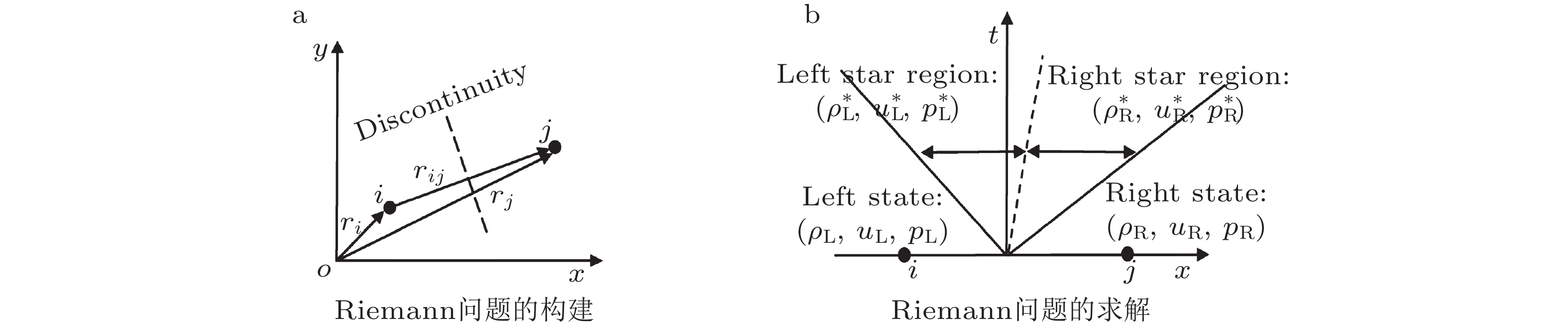
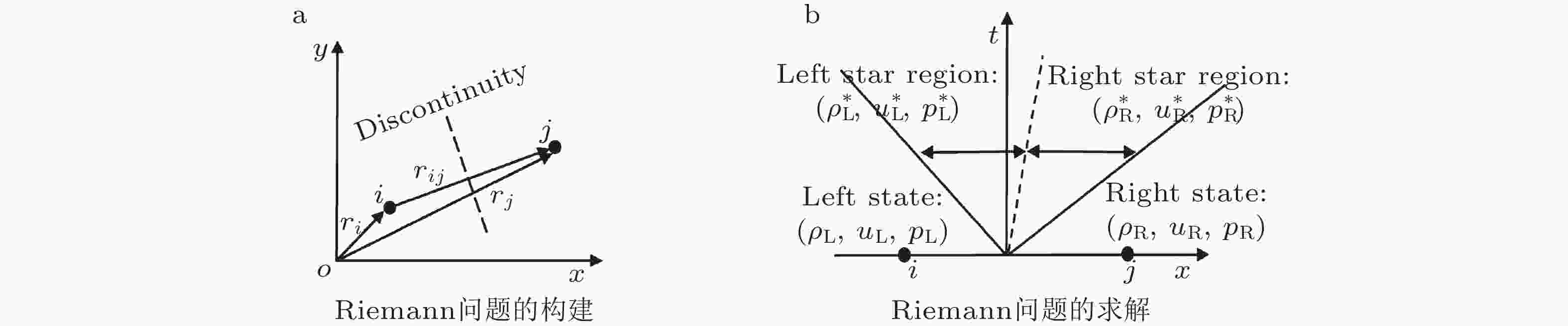
图 1 粒子对Riemann问题的构造与求解示意图 (Zhang et al. 2022a)
图 2 混合边界条件下的热传导过程. (a) 问题示意图, (b) 稳态温度分布, (c) 沿中线的温度曲线 (Ma et al. 2024)
图 3 SPH模拟的方形腔体内的自然对流现象. 从左至右分别为等温线、水平速度等值线、竖直速度等值线和流线图, 瑞利数范围为104至108 (Yang et al. 2021b)
图 4 液体撞击热壁面时动态蒸发过程的SPH模拟 (Yang & Kong 2017). (a) 相, (b) 温度, (c) 蒸气质量分数
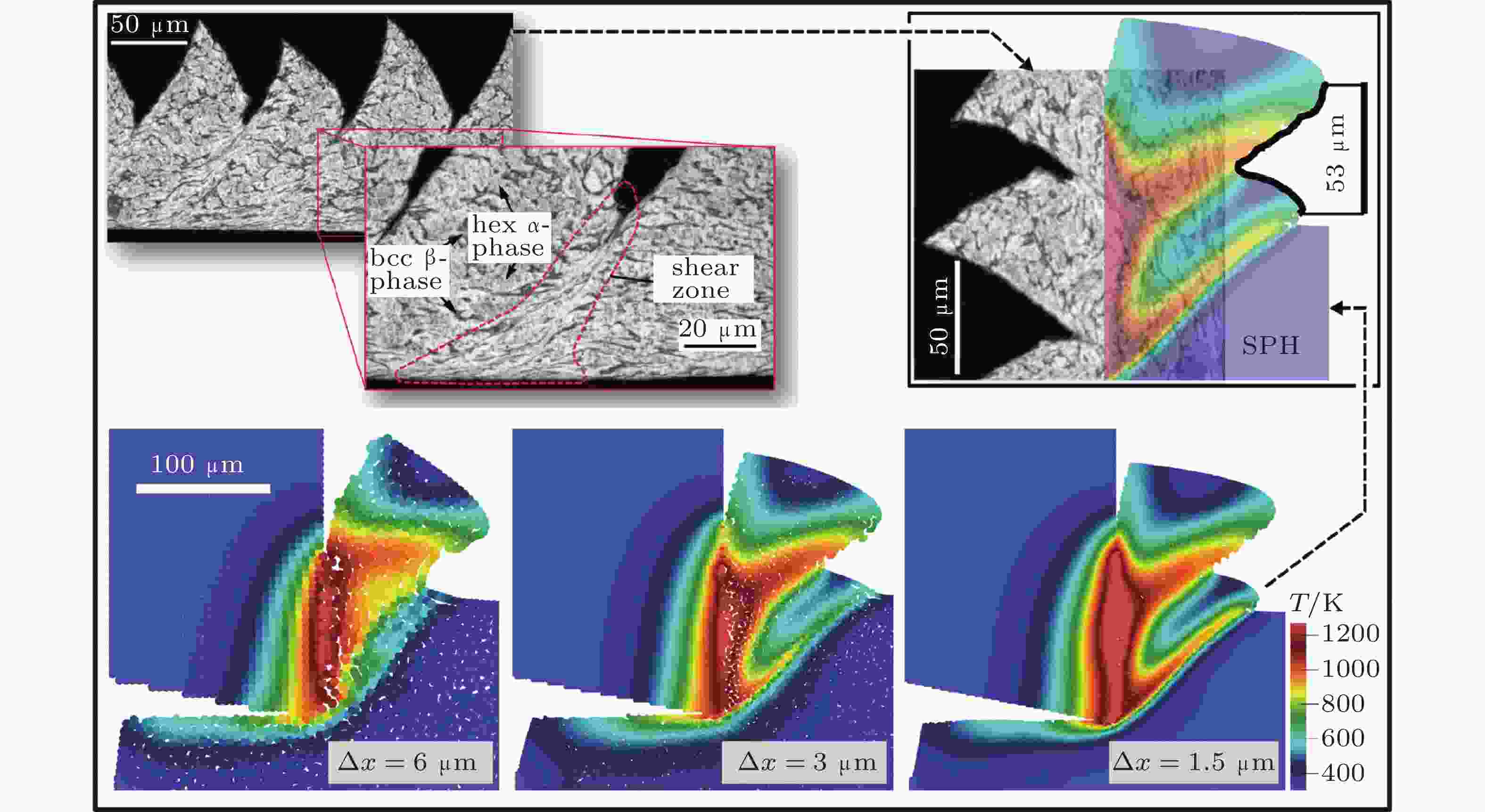
图 5 金属切削过程中瞬时的温度分布 (Afrasiabi et al. 2021b) 与相应实验结果 (Wyen 2011)
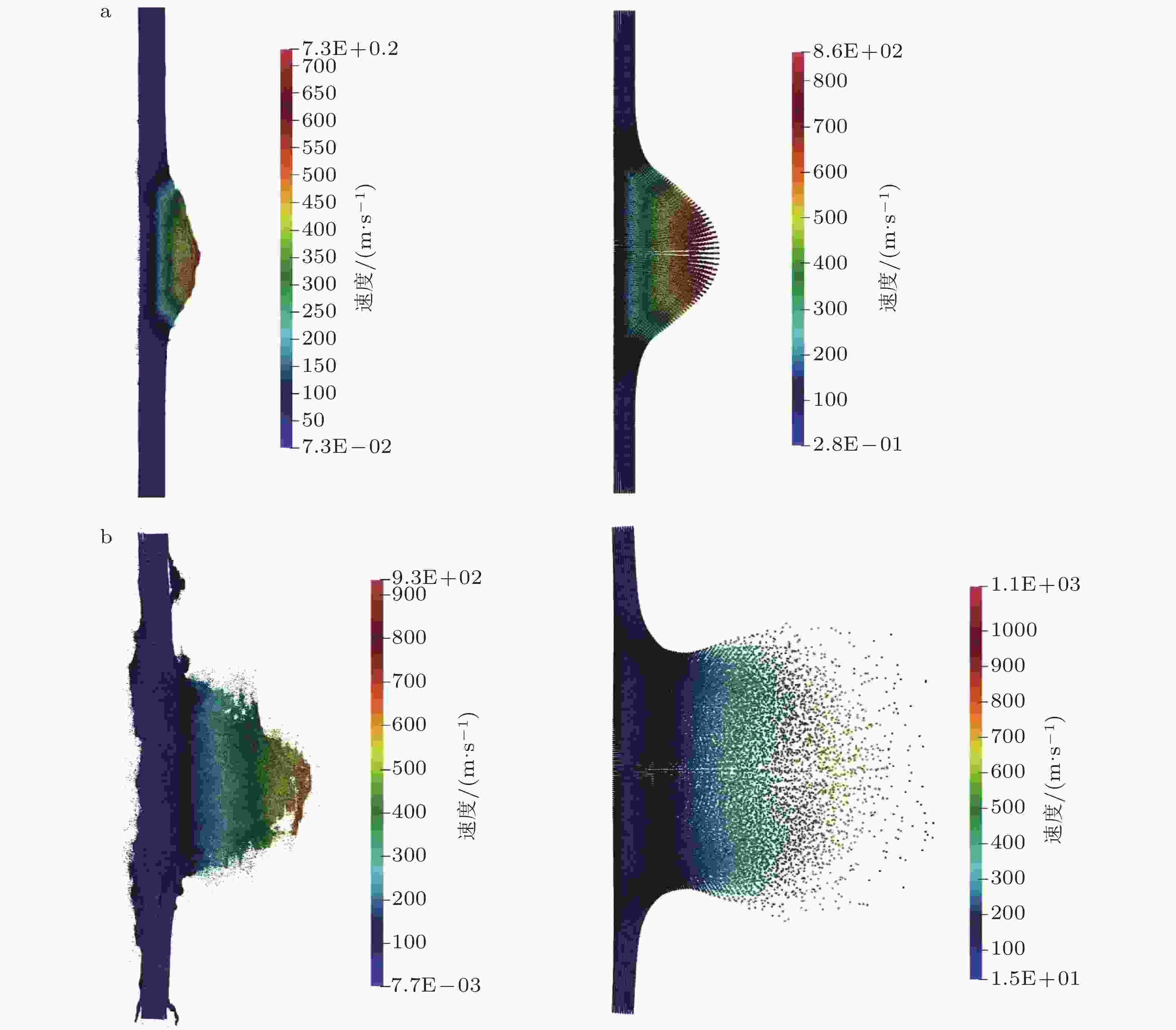
图 6 不同材料冲击侵彻过程的SPH模拟. 复合材料板 (左侧) 和铝板 (右侧) 分别在10 μs (a) 和25 μs (b) 时的速度分布对比 (Lu et al. 2023)
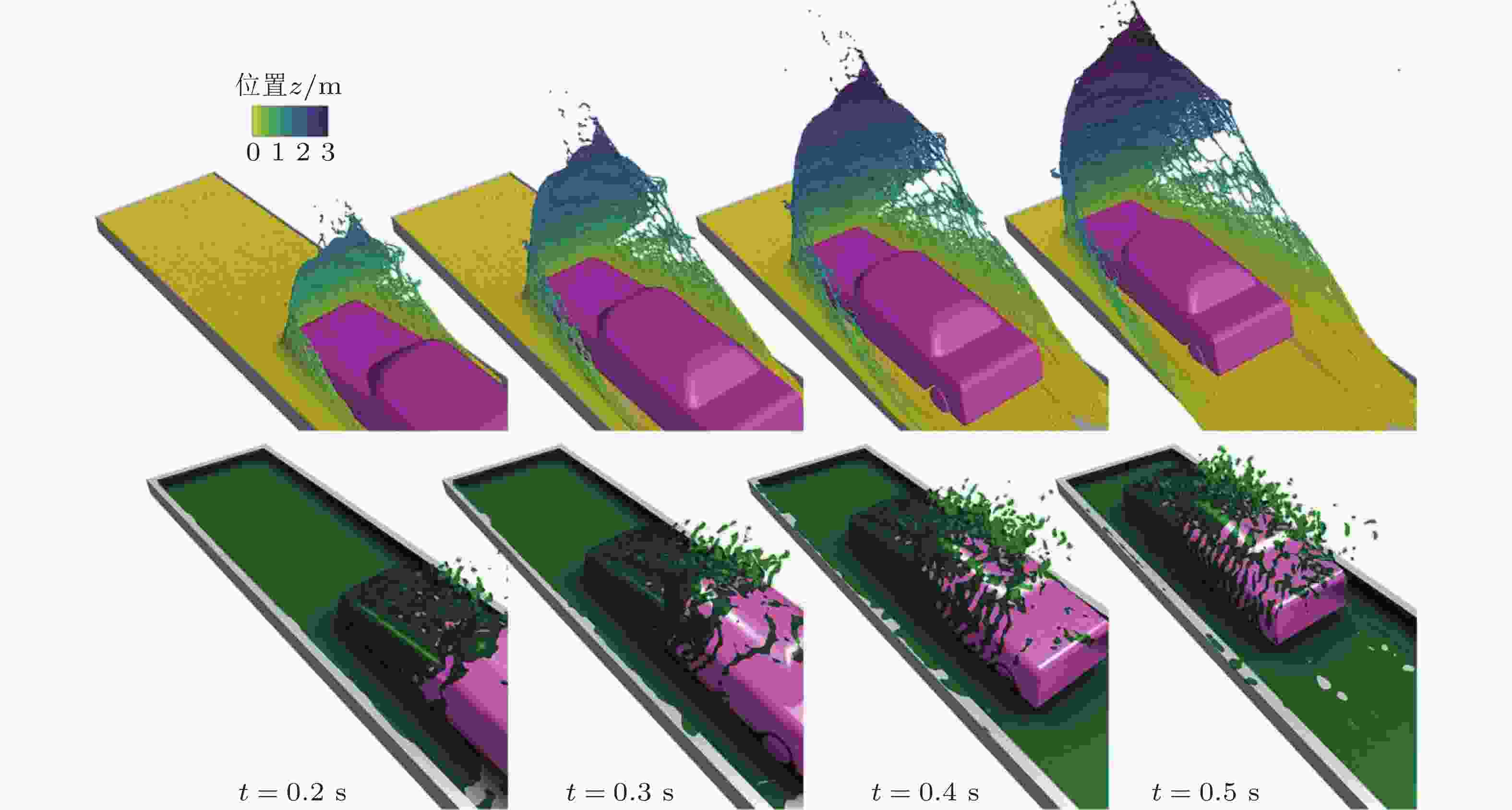
图 7 汽车涉水问题. 车辆运动速度为10 m/s时, 使用SPH (上) 和FVM (下) 求解器得到的不同时刻的自由表面演化结果 (Lyu et al. 2024)
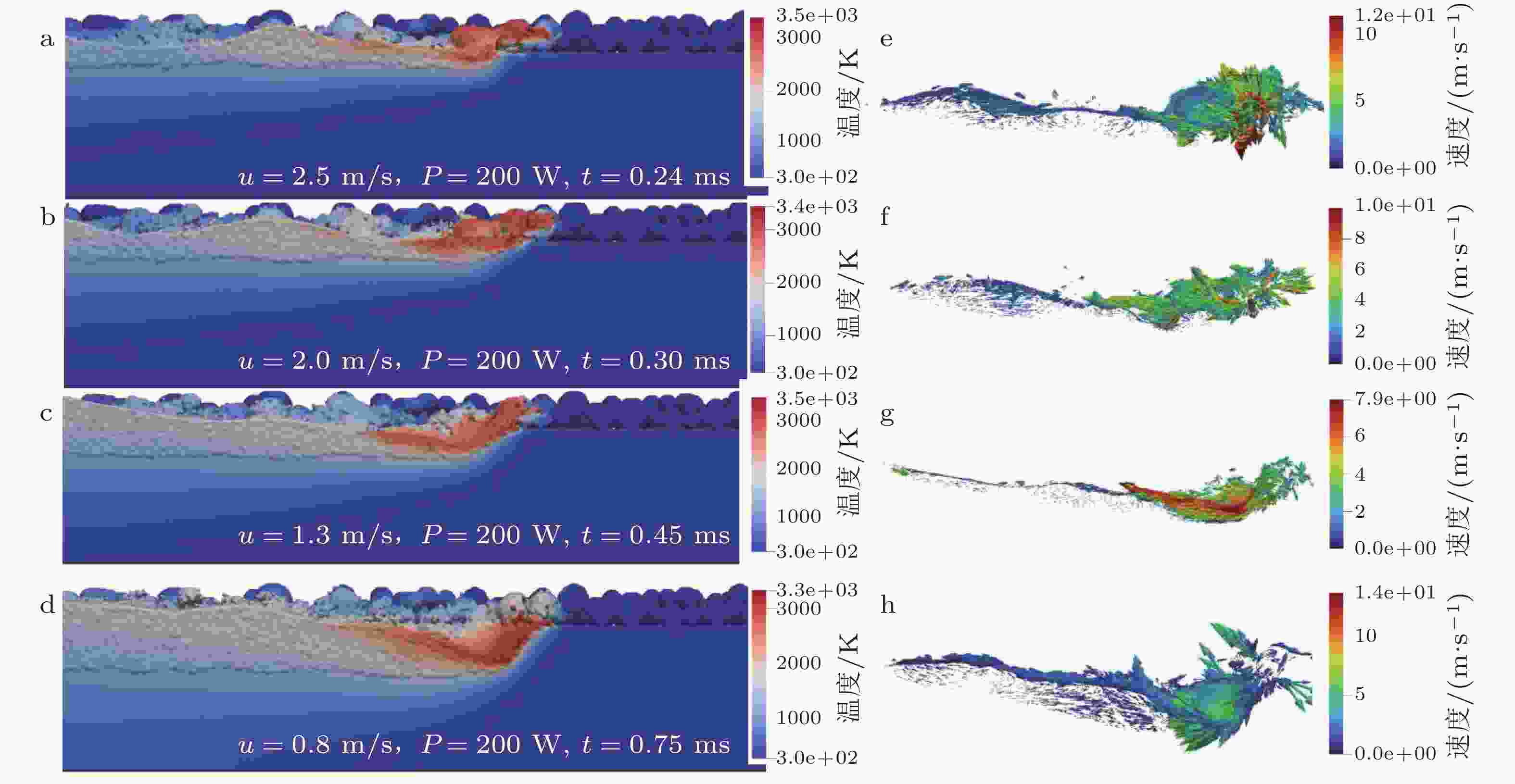
图 8 PBF过程的SPH模拟结果 (Ma et al. 2024). 不同激光功率与扫描速度下的熔池温度 (a) ~ (d) 和速度矢量 (e) ~ (h)
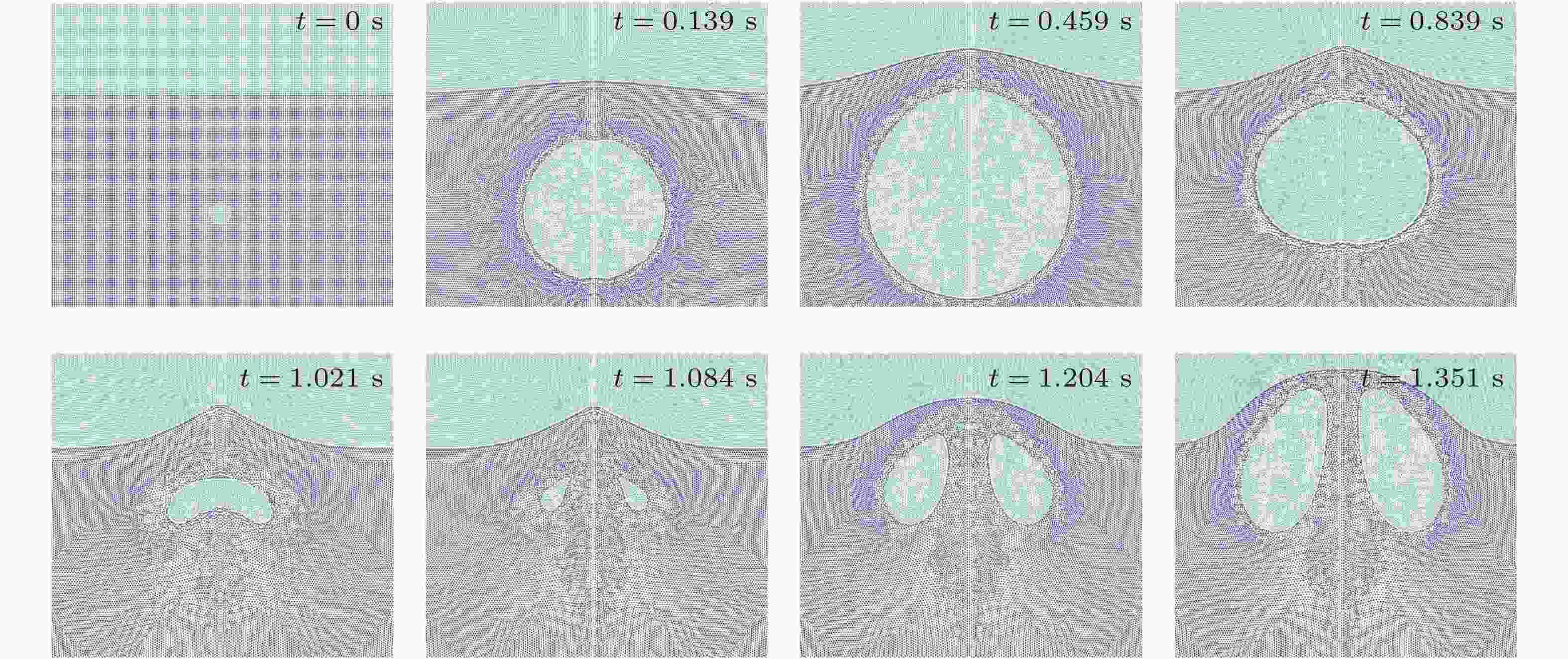
图 9 自由液面附近水下爆炸气泡脉动和射流的 SPH 模拟 (钟诗蕴 等 2022)
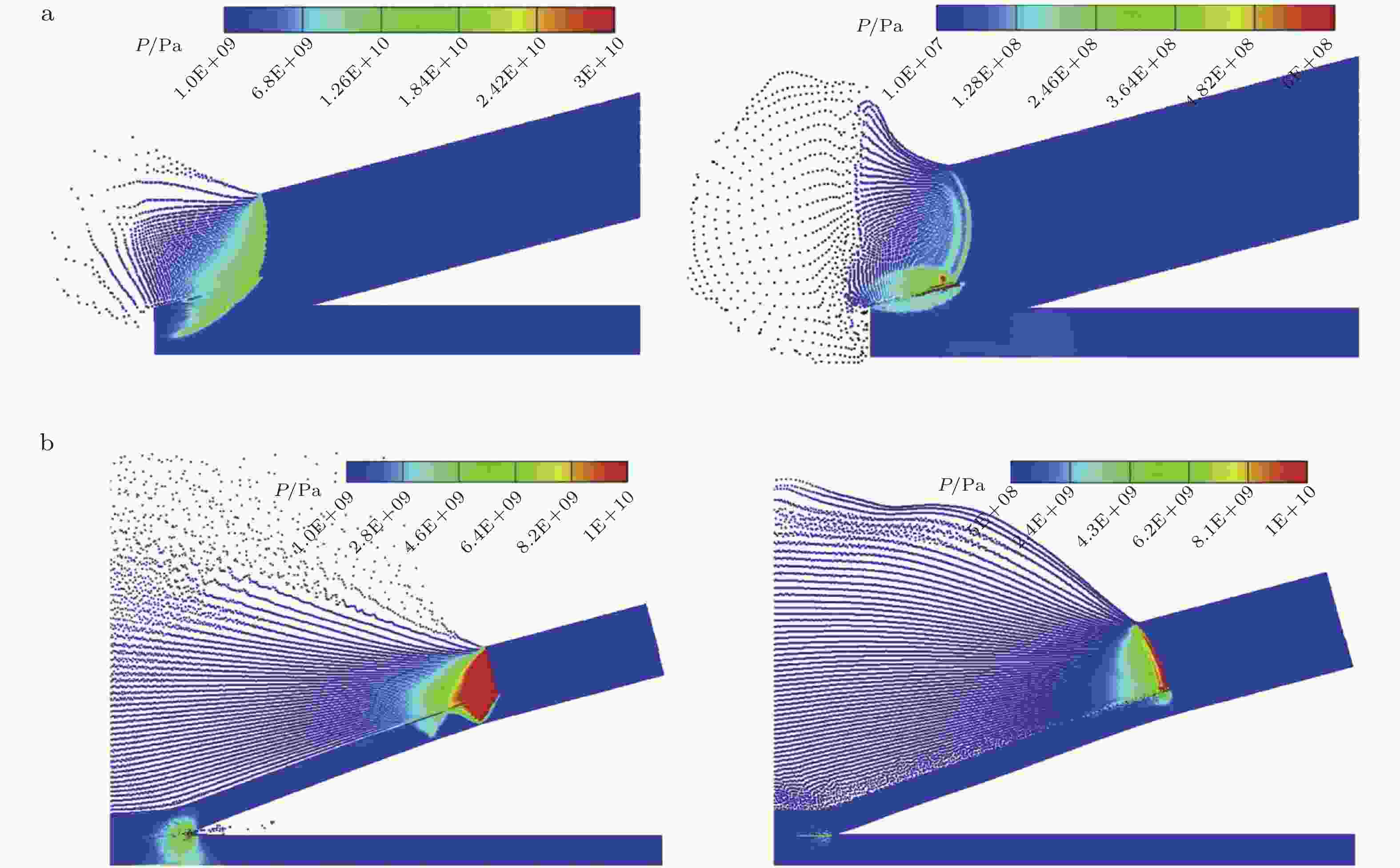
图 10 爆炸焊接的模拟结果. TNT (左) 和ANFO (右) 炸药爆炸初期 (a) 和后期 (b) 的压力分布 (Zhang & Liu 2019)
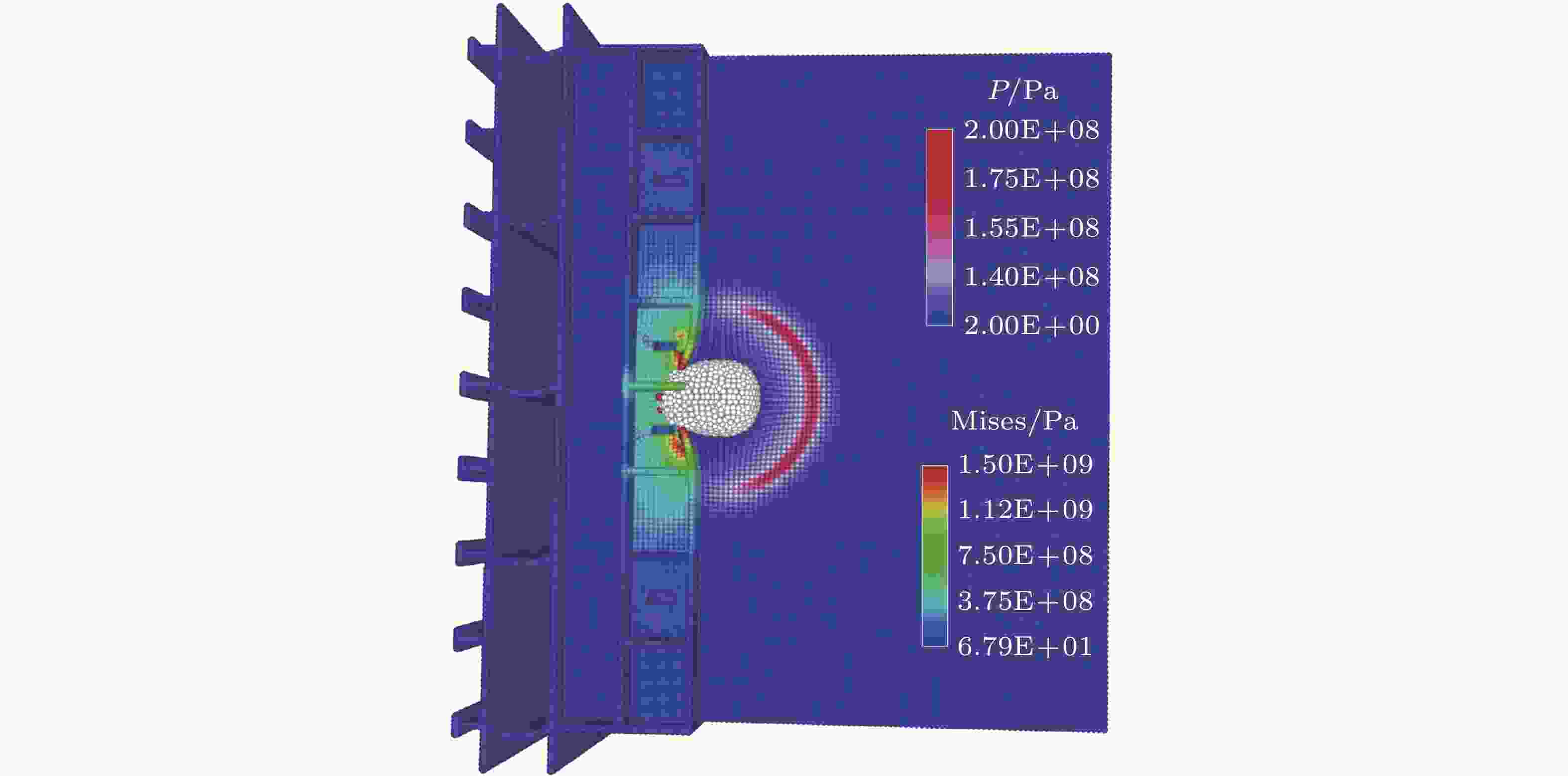
图 11 水下接触爆炸作用下舰船舷侧防护结构在0.25 ms时的流场压力云图以及结构的Mises应力云图 (王平平 等 2022)
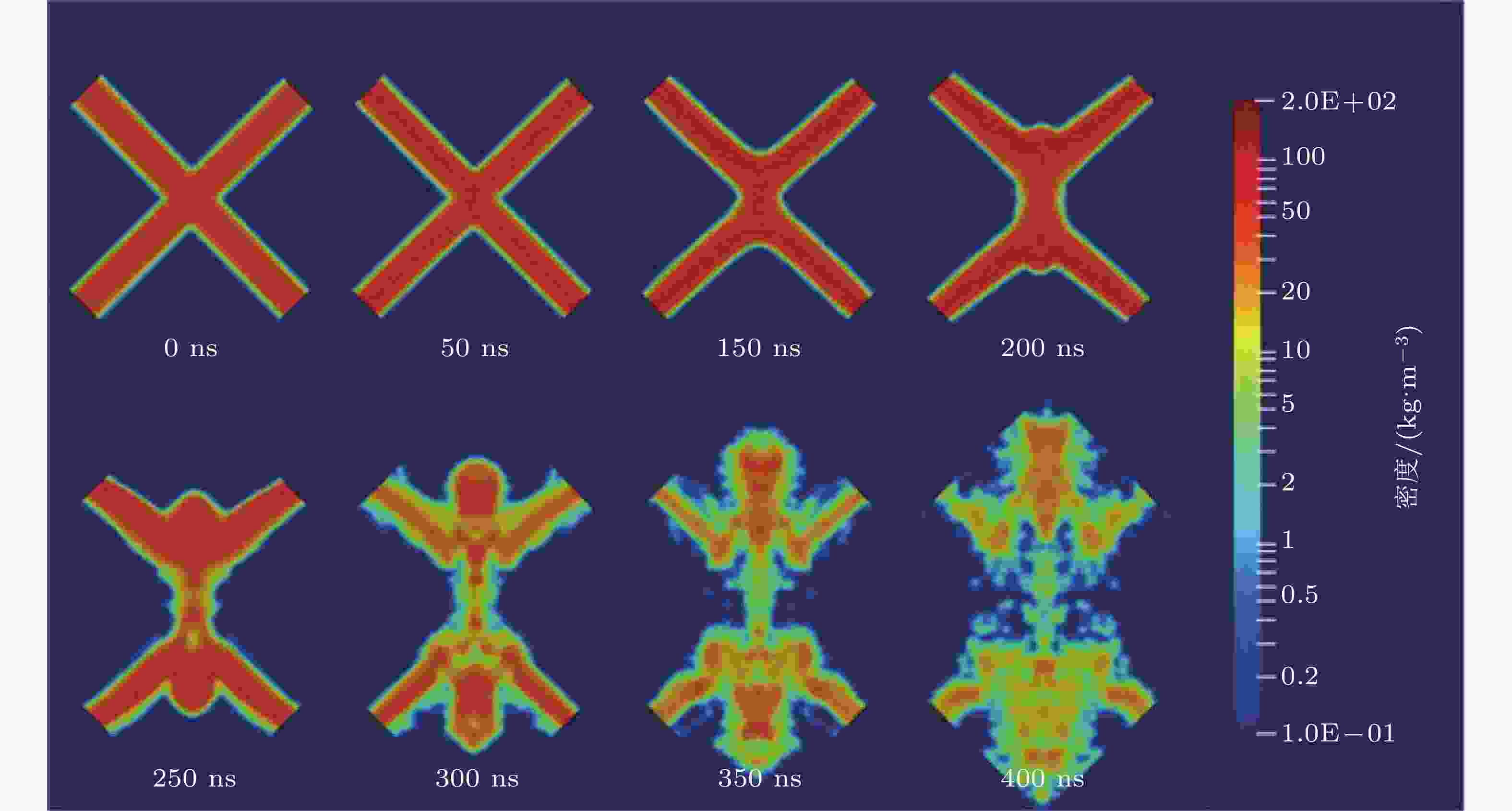
图 12 等粒子体X-pinch问题的SPH模拟. 密度分布的时间演化 (Park et al. 2024)
-
[1] 刘谋斌, 周冉, 邵家儒. 2014. 棱形液舱内液体晃荡问题的SPH数值模拟. 河海大学期刊部(自然科学版), 42(3): 257-261 (Liu M B, Zhou R, Shao J R. 2014. Numerical simulation of liquid sloshing in a prismatic tank with SPH method. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 42(3): 257-261).Liu M B, Zhou R, Shao J R. 2014. Numerical simulation of liquid sloshing in a prismatic tank with SPH method. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 42(3): 257-261 [2] 吴波, 韦汉, 徐世祥, 许杰, 黄宗辉. 2022. 基于SPH的椭圆双极线性聚能药包控制爆破数值模拟研究. 煤炭科学技术, 50(5): 135-142 (Wu B, Wei H, Xu S X, Xu J, Huang Z H. 2022. Numerical analysis of controlled blasting of elliptic bipolar linear shaped charge based on SPH. Coal Science and Technology, 50(5): 135-142).Wu B, Wei H, Xu S X, Xu J, Huang Z H. 2022. Numerical analysis of controlled blasting of elliptic bipolar linear shaped charge based on SPH. Coal Science and Technology, 50(5): 135-142. [3] 周建辉, 孙新利, 高巍然, 韩亚伟, 聂虎. 2009. 基于修正SPH方法的爆轰波绕射传播的数值模拟. 火炸药学报, 32(1): 66-69,73 (Zhou J H, Sun X L, Gao W R, Han Y W, Nie H. 2009. Numerical simulation of the diffraction detonation wave based on the modified SPH method. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 32(1): 66-69,73). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2009.01.018Zhou J H, Sun X L, Gao W R, Han Y W, Nie H. 2009. Numerical simulation of the diffraction detonation wave based on the modified SPH method. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 32(1): 66-69,73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2009.01.018 [4] 姚熊亮, 陈娟, 张阿漫, 冯观. 2010. 基于SPH方法的二维水下爆炸冲击载荷计算. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 31(10): 1303-1311 (Yao X L, Chen J, Zhang A M, Feng G. 2010. Computation of the blast loading of two-dimensional under water explosion using SPH method. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 31(10): 1303-1311). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2010.10.006Yao X L, Chen J, Zhang A M, Feng G. 2010. Computation of the blast loading of two-dimensional under water explosion using SPH method. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 31(10): 1303-1311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2010.10.006 [5] 张伟, 胡德安, 韩旭. 2010. 弹体侵彻运动陶瓷/金属复合装甲SPH模拟. 固体力学学报, S1: 70-75 (Zhang W, Hu D A, Han X. 2010. Simulation on projectile penetrating into moving ceramic/metal composite armor using SPH method. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, S1: 70-75).Zhang W, Hu D A, Han X. 2010. Simulation on projectile penetrating into moving ceramic/metal composite armor using SPH method. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, S1: 70-75. [6] 彭玉祥, 张阿漫, 薛冰, 礼绍博. 2021. 强冲击作用下舰船结构毁伤的三维无网格SPH-RKPM方法数值模拟. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 51(12): 150-163 (Peng Y X, Zhang A M, Xue B, Li S B. 2021. Numerical investigation of ship structure damage subject to strong impact using a 3D meshless SPH-RKPM method. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 51(12): 150-163).Peng Y X, Zhang A M, Xue B, Li S B. 2021. Numerical investigation of ship structure damage subject to strong impact using a 3D meshless SPH-RKPM method. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 51(12): 150-163 [7] 李林豪, 杨秀峰, SOHAG M A S M, 王晓亮, 刘青泉. 2022. 双液滴连续撞击高温壁面的SPH-ASR模拟研究. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 52(10): 37-49 (Li L H, Yang X F, SOHAG M A S M, Wang X L, Liu Q Q. 2022. Simulation of two successive drops impacting a heated wall by smoothed particle hydrodynamics with adaptivespatial resolution. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 52(10): 37-49).Li L H, Yang X F, SOHAG M A S M, Wang X L, Liu Q Q. 2022. Simulation of two successive drops impacting a heated wall by smoothed particle hydrodynamics with adaptivespatial resolution. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 52(10): 37-49 [8] 杨朋英, 张帆, 黄灿, 刘谋斌. 2022. 基于SPH方法的激光选区熔化数值模拟研究. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 52(10): 64-77 (Yang P Y, Zhang F, Huang C, Liu M B. 2022. Numerical simulation of selective laser melting based on SPH method. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 52(10): 64-77).Yang P Y, Zhang F, Huang C, Liu M B. 2022. Numerical simulation of selective laser melting based on SPH method. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 52(10): 64-77 [9] 查文舒, 李道伦, 沈路航, 张雯, 刘旭亮. 2022. 基于神经网络的偏微分方程求解方法研究综述. 力学学报, 54(3): 543-556 (Zha W S, Li D L, Shen L H, Zhang W, Liu X L. 2022. Review of neural network-based methods for solving partial differential equations. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 54(3): 543-556). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-617Zha W S, Li D L, Shen L H, Zhang W, Liu X L. 2022. Review of neural network-based methods for solving partial differential equations. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 54(3): 543-556. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-617 [10] 王平平, 张阿漫, 彭玉祥, 孟子飞. 2022. 近场水下爆炸瞬态强非线性流固耦合无网格数值模拟研究. 力学学报, 54(8): 2194-2209 (Wang P P, Zhang A M, Peng Y X, Meng Z F. 2022. Numerical simulation of transient strongly-nonlinear fluid-structure interaction in near-field underwater explosion based on meshless method. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 54(8): 2194-2209). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-271Wang P P, Zhang A M, Peng Y X, Meng Z F. 2022. Numerical simulation of transient strongly-nonlinear fluid-structure interaction in near-field underwater explosion based on meshless method. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 54(8): 2194-2209. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-271 [11] 缪广红, 胡昱, 艾九英, 祁俊翔, 马宏昊, 沈兆武. 2023. 炸药覆盖层对爆炸焊接影响的数值模拟. 焊接学报, 44(1): 40-48 (Miao G H, Hu Y, Ai J Y, Qi J X, Ma H H, Shen Z W. 2023. Numerical simulation research on the effect of explosive covering on explosive welding. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 44(1): 40-48). doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220121002Miao G H, Hu Y, Ai J Y, Qi J X, Ma H H, Shen Z W. 2023. Numerical simulation research on the effect of explosive covering on explosive welding. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 44(1): 40-48. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220121002 [12] 贾斌, 马志涛, 庞宝君. 2011. 填充泡沫铝防护结构的超高速撞击数值模拟. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 43(1): 16-20 (Jia B, Ma Z T, Pang B J. 2011. Numerical simulation investigation in hypervelocity impact on Al-foam stuffed shields. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 43(1): 16-20). doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2011.01.004Jia B, Ma Z T, Pang B J. 2011. Numerical simulation investigation in hypervelocity impact on Al-foam stuffed shields. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 43(1): 16-20. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2011.01.004 [13] 钟诗蕴, 孙鹏楠, 吕鸿冠, 彭玉祥, 张阿漫. 2022. SPH理论和方法在高速水动力学中的研究进展. 中国舰船研究, 17(3): 29-48 (Zhong S Y, Sun P N, Lyu H G, Peng Y X, Zhang A M. 2022. Research progress of smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications in high-speed hydrodynamic problems. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 17(3): 29-48).Zhong S Y, Sun P N, Lyu H G, Peng Y X, Zhang A M. 2022. Research progress of smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications in high-speed hydrodynamic problems. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 17(3): 29-48. [14] 钱志浩, 丁陈森, 许灵辰, 郭朝阳, 喻月, 罗词金, 刘谋斌. 2025. 一种高效高精度小样本的流固耦合代理模型. 力学学报 (Qian Z H, Ding C S, Xu L C, Guo C Y, Yu Y, Luo C J, Liu M B. 2025. A highly efficient and accurate surrogate model for fluid-structure interaction with limited data. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics).Qian Z H, Ding C S, Xu L C, Guo C Y, Yu Y, Luo C J, Liu M B. 2025. A highly efficient and accurate surrogate model for fluid-structure interaction with limited data. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics. [15] 高本兵, 尹建平, 陈杰, 王志军. 2018. 基于SPH方法的不同材质射流毁伤性能研究. 北京理工大学学报, 38(4): 353-358 (Gao B B, Yin J P, Chen J, Wang Z J. 2018. Study on damage characteristics of different jets based on SPH method. Transactions of Beijing institute of Technology, 38(4): 353-358).Gao B B, Yin J P, Chen J, Wang Z J. 2018. Study on damage characteristics of different jets based on SPH method. Transactions of Beijing institute of Technology, 38(4): 353-358. [16] 黄佳, 张昭, 张洪武. 2013. 聚能射流形成数值模拟. 计算力学学报, 30: 88-91 (Huang J, Zhang Z, Zhang H W. 2013. Numerical simulation of shaped charge formation. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 30: 88-91). doi: 10.7511/jslx201301015Huang J, Zhang Z, Zhang H W. 2013. Numerical simulation of shaped charge formation. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 30: 88-91. doi: 10.7511/jslx201301015 [17] 黄永辉, 李永杰, 杨阳, 熊卫国, 张智宇. 2024. 露天爆破中炸药单耗对岩石破碎块度的数值模拟研究. 工程科学学报, 46(6): 973-981 (Huang Y H, Li Y J, Yang Y, Xiong W G, Zhang Z Y. 2024. Effect of explosive powder factor on rock crushing block size in open-pit blasting. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 46(6): 973-981).Huang Y H, Li Y J, Yang Y, Xiong W G, Zhang Z Y. 2024. Effect of explosive powder factor on rock crushing block size in open-pit blasting. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 46(6): 973-981. [18] Abdoh D A, Ademiloye A S, Liew K M. 2020. Modeling glass cooling mechanism with down-flowing water film via the smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 362: 112839. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.112839 [19] Adami S, Hu X Y, Adams N A. 2012. A generalized wall boundary condition for smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 231(21): 7057-7075. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2012.05.005 [20] Afrasiabi M, Meier L, Röthlin M, Klippel H, Wegener K. 2020. GPU-accelerated meshfree simulations for parameter identification of a friction model in metal machining. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 176: 105571. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105571 [21] Afrasiabi M, Saelzer J, Berger S, Iovkov I, Klippel H, Röthlin M, Zabel A, Biermann D, Wegener K. 2021a. A numerical-experimental study on orthogonal cutting of AISI 1045 steel and Ti6Al4V alloy: SPH and FEM modeling with newly identified friction coefficients. Metals, 11(11): 1683. doi: 10.3390/met11111683 [22] Afrasiabi M, Klippel H, Roethlin M, Wegener K. 2021b. An improved thermal model for SPH metal cutting simulations on GPU. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 100: 728-750. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2021.08.010 [23] Alexiadis A, Ghraybeh S, Qiao G. 2018. Natural convection and solidification of phase-change materials in circular pipes: A SPH approach. Computational Materials Science, 150: 475-483. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2018.04.037 [24] Almasi F, Shadloo M S, Hadjadj A, Ozbulut M, Tofighi N, Yildiz M. 2021. Numerical simulations of multi-phase electro-hydrodynamics flows using a simple incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 81: 772-785. [25] Aly A M. 2016. Double-diffusive natural convection in an enclosure including/excluding sloshing rod using a stabilized ISPH method. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 73: 84-99. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.01.008 [26] Antoci C, Gallati M, Sibilla S. 2007. Numerical simulation of fluid–structure interaction by SPH. Computers & Structures, 85(11-14): 879-890. [27] Antonelli L, Francomano E, Gregoretti F. 2021. A CUDA-based implementation of an improved SPH method on GPU. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 409: 125482. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2020.125482 [28] Bai J, Zhou Y, Rathnayaka C M, Zhan H, Sauret E, Gu Y. 2021. A data-driven smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for fluids. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 132: 12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2021.06.029 [29] Bai J, Zhou Y, Ma Y, Jeong H, Zhan H, Rathnayaka C, Sauret E, Gu Y. 2022. A general neural particle method for hydrodynamics modeling. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 393: 114740. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2022.114740 [30] Basir S, Senocak I. 2022. Physics and equality constrained artificial neural networks: Application to forward and inverse problems with multi-fidelity data fusion. Journal of Computational Physics, 463: 111301. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111301 [31] Belytschko T, Krongauz Y, Organ D, Fleming M, Krysl P. 1996. Meshless methods: An overview and recent developments. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 139(1-4): 3-47. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(96)01078-X [32] Belytschko T, Guo Y, Liu W K, Xiao S P. 2000. A unified stability analysis of meshless particle methods. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 48(9): 1359-1400. doi: 10.1002/1097-0207(20000730)48:9<1359::AID-NME829>3.0.CO;2-U [33] Cao C, Gui N, Yang X, Tu J, Jiang S. 2024. Numerical simulation of safety injection and natural circulation in two containers by smoothed particle hydrodynamics on the effects of filling levels and thermal diffusivities. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 198: 110300. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2023.110300 [34] Chen H, Ming F R, Sun S L, Zhang A M. 2024. Study on the flooding characteristics of a deep-water submarine based on δ plus-smoothed particle hydrodynamics method and graphic processing units acceleration. Physics of Fluids, 36(1): 012132. doi: 10.1063/5.0179348 [35] Chen J Y, Feng D L, Liu J H, Yu S Y, Lu Y. 2023. Numerical modeling of the damage mechanism of concrete-soil multilayered medium subjected to underground explosion using the GPU-accelerated SPH. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 151: 265-274. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2023.03.003 [36] Chen J K, Beraun J E, Carney T C. 1999. A corrective smoothed particle method for boundary value problems in heat conduction. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 46(2): 231-252. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19990920)46:2<231::AID-NME672>3.0.CO;2-K [37] Chen J S, Pan C H, Wu C T, Liu W K. 1996. Reproducing kernel particle methods for large deformation analysis of non-linear structures. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 139(1-4): 195-22. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(96)01083-3 [38] Chen Z, Zong Z, Liu M B, Zou L, Li H T, Shu C. 2015. An SPH model for multiphase flows with complex interfaces and large density differences. Journal of Computational Physics, 283: 169-188. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2014.11.037 [39] Cheng Y G, Rabczuk T, Ding C S. 2024. Multi-DORGP for fast uncertainty quantification of multi-scale irregular defects in super large-scale fiber-reinforced composite. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 182: 108196. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2024.108196 [40] Cherfils J M, Pinon G, Rivoalen E. 2012. JOSEPHINE: A parallel SPH code for free-surface flows. Computer Physics Communications, 183(7): 1468-1480. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2012.02.007 [41] Cleary P W. 1998. Modelling confined multi-material heat and mass flows using SPH. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 22(12): 981-993. doi: 10.1016/S0307-904X(98)10031-8 [42] Cleary P W, Monaghan J J. 1999. Conduction modelling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 148(1): 227-264. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1998.6118 [43] Cleary P W, Ha J, Prakash M, Nguyen T. 2006. 3D SPH flow predictions and validation for high pressure die casting of automotive components. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 30(11): 1406-1427. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2006.03.012 [44] Colagrossi A, Landrini M. 2003. Numerical simulation of interfacial flows by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 191(2): 448-475. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00324-3 [45] Crespo A J C, Domínguez J M, Rogers B D, Gómez-Gesteira M, Longshaw S, Canelas R, Vacondio R, Barreiro A, García-Feal O. 2015. DualSPHysics: Open-source parallel CFD solver based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Computer Physics Communications, 187: 204-216. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2014.10.004 [46] Cross M M. 1965. Rheology of non-newtonian fluids: A new flow equation for pseudoplastic systems. Journal of Colloid Science, 20(5): 417-437. doi: 10.1016/0095-8522(65)90022-X [47] Dao M H, Lou J. 2022. Simulations of directed energy deposition additive manufacturing process by smoothed particle hydrodynamics methods. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 120(7): 4755-4774. [48] Dou W, Geng X, Xu Z. 2019. Experimental investigation and numerical simulation of the orthogonal cutting based on the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 44: 359-366. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.06.010 [49] Dyka C T, Ingel R P. 1995. An approach for tension instability in smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Computers & Structures, 57(4): 573-580. [50] Fang X L, Ming F R, Wang P P, Meng Z F, Zhang A M. 2022a. Application of multiphase Riemann-SPH in analysis of air-cushion effect and slamming load in water entry. Ocean Engineering, 248: 110789. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110789 [51] Fang X L, Ming F R, Wang P P, Sun P N, Zhang A M. 2022b. Application of SPH method in the study of ship capsizing induced by large-scale rising bubble. Ocean Engineering, 257: 111629. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111629 [52] Feng D L, Liu M B, Li H Q, Liu G R. 2013. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics modeling of linear shaped charge with jet formation and penetration effects. Computers & Fluids, 86: 77-85. [53] Fourey G, Hermange C, Le Touzé D, Oger G. 2017. An efficient FSI coupling strategy between smoothed particle hydrodynamics and finite element methods. Computer Physics Communications, 217: 66-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2017.04.005 [54] Fraser K, Kiss L I, St-Georges L. 2016. Adaptive thermal boundary conditions for smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Proceedings of the 14th Internation LS-DYNA Conference, 12–14. [55] Frissane H, Taddei L, Lebaal N, Roth S. 2019. 3D smooth particle hydrodynamics modeling for high velocity penetrating impact using GPU: Application to a blunt projectile penetrating thin steel plates. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 357: 112590. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2019.112590 [56] Fuchs S L, Praegla P M, Cyron C J, Wall W A, Meier C. 2022. A versatile SPH modeling framework for coupled microfluid-powder dynamics in additive manufacturing: Binder jetting, material jetting, directed energy deposition and powder bed fusion. Engineering with Computers, 38(6): 4853-4877. doi: 10.1007/s00366-022-01724-4 [57] Gingold R A, Monaghan J J. 1977. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics-theory and application to non-spherical stars. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 181(3): 375-389. doi: 10.1093/mnras/181.3.375 [58] Gray J P, Monaghan J J, Swift R P. 2001. SPH elastic dynamics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 190(49-50): 6641-6662. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(01)00254-7 [59] Grigoryev S Yu, Lakatosh B V, Krivokorytov M S, Zhakhovsky V V, Dyachkov S A, Ilnitsky D K, Migdal K P, Inogamov N A, Vinokhodov A Yu, Kompanets V O, Sidelnikov Yu V, Krivtsun V M, Koshelev K N, Medvedev V V. 2018. Expansion and fragmentation of a liquid-metal droplet by a short laser pulse. Physical Review Applied, 10(6): 064009. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.10.064009 [60] Gui N, Zhang X, Huang X, Yang X, Tu J, Jiang S. 2022. SPH simulation of natural convection in a modeled reactor core using a new combinatorial kernel. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 175: 109249. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2022.109249 [61] Guo C Y, Zhang H S, Qian Z H, Liu M B. 2024. Smoothed-Interface SPH model for multiphase fluid-structure interaction. Journal of Computational Physics, 113336. [62] Hammani I, Marrone S, Colagrossi A, Oger G, Le Touzé D. 2020. Detailed study on the extension of the δ-SPH model to multi-phase flow. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 368: 113189. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113189 [63] Hang N Z, Wang Z K, Liu M B. 2023. A novel data-driven dimensional analysis framework for predicting melt pool morphology and porosity evolution in powder bed fusion. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 315: 117929. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2023.117929 [64] Harisankar P C, Sil T. 2023. Drop-vapour coexistence in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 151: 56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2023.02.039 [65] Harmening J H, Pioch F, Fuhrig L, Peitzmann F J, Schramm D, El Moctar O. 2024. Data-assisted training of a physics-informed neural network to predict the separated Reynolds-averaged turbulent flow field around an airfoil under variable angles of attack. Neural Computing and Applications, 36(25): 15353-15371. doi: 10.1007/s00521-024-09883-9 [66] Hashemi H, Sliepcevich C. 1967. A numerical method for solving two-dimensional problems of heat conduction with change of phase. Chemical engineering progress symposium series, 63(79): 34-41. [67] He C F, Peng X, Ding C S. 2023. Dual order-reduced Gaussian process emulators (DORGP) for quantifying high-dimensional uncertain crack growth using limited and noisy data. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 417: 116394. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2023.116394 [68] He F, Zhang H S, Huang C, Liu M B. 2020. Numerical investigation of the solitary wave breaking over a slope by using the finite particle method. Coastal Engineering, 156: 103617. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2019.103617 [69] He F, Zhang H S, Huang C, Liu M B. 2022. A stable SPH model with large CFL numbers for multi-phase flows with large density ratios. Journal of Computational Physics, 453: 110944. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.110944 [70] He Y, Bayly A E, Hassanpour A, Muller F, Wu K, Yang D. 2018. A GPU-based coupled SPH-DEM method for particle-fluid flow with free surfaces. Powder Technology, 338: 548-562. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.07.043 [71] Hu D, Long T, Xiao Y, Han X, Gu Y. 2014. Fluid–structure interaction analysis by coupled FE–SPH model based on a novel searching algorithm. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 276: 266-286. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2014.04.001 [72] Hu M, Liu M B, Xie M W, Liu G R. 2015. Three-dimensional run-out analysis and prediction of flow-like landslides using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73: 1629-1640. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3513-1 [73] Huang C, Long T, Li S M, Liu M B. 2019. A kernel gradient-free SPH method with iterative particle shifting technology for modeling low-Reynolds flows around airfoils. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 106: 571-587. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.06.010 [74] Huang Z, Yu X. 2022. Numerical simulation study of expanding fracture of 45 steel cylindrical shell under different detonation pressure. Materials, 15(11): 3980. doi: 10.3390/ma15113980 [75] Ihmsen M, Akinci N, Becker M, Teschner M. 2011. A parallel SPH implementation on multi-core CPUs. Computer Graphics Forum, 30(1): 99-112. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2010.01832.x [76] Inutsuka S. 2002. Reformulation of smoothed particle hydrodynamics with Riemann solver. Journal of Computational Physics, 179(1): 238-267. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2002.7053 [77] Jagtap A D, Kharazmi E, Karniadakis G E. 2020. Conservative physics-informed neural networks on discrete domains for conservation laws: Applications to forward and inverse problems. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 365: 113028. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113028 [78] Jeong J H, Jhon M S, Halow J S, Van Osdol J. 2003. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: Applications to heat conduction. Computer Physics Communications, 153(1): 71-84. doi: 10.1016/S0010-4655(03)00155-3 [79] Ji Z, Xu F, Takahashi A, Sun Y. 2016. Large scale water entry simulation with smoothed particle hydrodynamics on single- and multi-GPU systems. Computer Physics Communications, 209: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2016.05.016 [80] Jiang F, Oliveira M S A, Sousa A C M. 2006. SPH simulation of transition to turbulence for planar shear flow subjected to a streamwise magnetic field. Journal of Computational Physics, 217(2): 485-501. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2006.01.009 [81] Katayama M, Kibe S, Yamamoto T. 2001. Numerical and experimental study on the shaped charge for space debris assessment. Acta Astronautica, 48(5-12): 363-372. doi: 10.1016/S0094-5765(01)00073-X [82] Khayyer A, Gotoh H, Falahaty H, Shimizu Y. 2018. An enhanced ISPH–SPH coupled method for simulation of incompressible fluid–elastic structure interactions. Computer Physics Communications, 232: 139-164. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2018.05.012 [83] Kirchdoerfer T, Ortiz M. 2016. Data-driven computational mechanics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 304: 81-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2016.02.001 [84] Kumaki R, Moriya T, Takahashi T. 2018. An expression model of blood drying process based on SPH method. 2018 International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT), 1–4. [85] Kyogoku H, Ikeshoji T T. 2020. A review of metal additive manufacturing technologies: Mechanism of defects formation and simulation of melting and solidification phenomena in laser powder bed fusion process. Mechanical Engineering Reviews, 7(1): 19-00182-19–00182. [86] Lai J, Yang H, Wang H, Zheng X, Wang Q. 2019. Penetration experiments and simulation of three-layer functionally graded cementitious composite subjected to multiple projectile impacts. Construction and Building Materials, 196: 499-511. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.154 [87] Li G Y, Ma X J, Zhang B W, Xu H W. 2021. An integrated smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for numerical simulation of the droplet impacting with heat transfer. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 124: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2020.12.003 [88] Li J, Lin J, Naceur H, Kong W, Ji S, Guan Y, Quan D, Chen J, Li Y. 2024. Symmetric SPH modeling of functionally graded nanocomposite plates subjected to low-velocity impact. Polymer Composites, 45(2): 1054-1066. doi: 10.1002/pc.27835 [89] Li M K, Zhang A M, Peng Y X, Ming F R. 2022. An improved model for compressible multiphase flows based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics with enhanced particle regeneration technique. Journal of Computational Physics, 458: 111106. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111106 [90] Libersky L D, Petschek A G. 1991. Smooth particle hydrodynamics with strength of materials. Advances in the Free-Lagrange Method Including Contributions on Adaptive Gridding and the Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics Method, 248–257. [91] Lin Y, Lüthi C, Afrasiabi M, Bambach M. 2023. Enhanced heat source modeling in particle-based laser manufacturing simulations with ray tracing. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 214: 124378. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2023.124378 [92] Liu C M, Gao H B, Li L Y, Wang J D, Guo C H, Jiang F C. 2021. A review on metal additive manufacturing: Modeling and application of numerical simulation for heat and mass transfer and microstructure evolution. China Foundry, 18: 317-334. doi: 10.1007/s41230-021-1119-2 [93] Liu G R, Liu M B. 2003. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: A meshfree particle method. World scientific. [94] Liu G R, Dai K Y, Nguyen T T. 2007. A smoothed finite element method for mechanics problems. Computational Mechanics, 39: 859-877. doi: 10.1007/s00466-006-0075-4 [95] Liu G R, Nguyen-Thoi T, Lam K Y. 2009. An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for static, free and forced vibration analyses of solids. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 320(4-5): 1100-1130. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2008.08.027 [96] Liu J, Yang X F, Zhang Z L, Liu M B. 2024. A massive MPI parallel framework of smoothed particle hydrodynamics with optimized memory management for extreme mechanics problems. Computer Physics Communications, 295: 108970. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2023.108970 [97] Liu M B, Liu G R. 2010. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH): An overview and recent developments. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 17: 25-76. doi: 10.1007/s11831-010-9040-7 [98] Liu M B, Liu G R. 2015. Particle methods for multi-scale and multi-physics. World Scientific. [99] Liu M B, Zhang Z L. 2019. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) for modeling fluid-structure interactions. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 62: 1-38. [100] Liu M B, Liu G R, Lam K Y. 2002. Investigations into water mitigation using a meshless particle method. Shock Waves, 12: 181-195. doi: 10.1007/s00193-002-0163-0 [101] Liu M B, Liu G R, Lam K Y, Zong Z. 2003. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics for numerical simulation of underwater explosion. Computational Mechanics, 30: 106-118. doi: 10.1007/s00466-002-0371-6 [102] Liu M B, Xie W P, Liu G R. 2005. Modeling incompressible flows using a finite particle method. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 29(12): 1252-1270. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2005.05.003 [103] Liu M B, Liu G R, Lam K Y. 2006. Adaptive smoothed particle hydrodynamics for high strain hydrodynamics with material strength. Shock Waves, 15(1): 21-29. doi: 10.1007/s00193-005-0002-1 [104] Liu M B, Shao J R, Chang J Z. 2012. On the treatment of solid boundary in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Science China Technological Sciences, 55: 244-254. doi: 10.1007/s11431-011-4663-y [105] Liu M B, Shao J R, Li H Q. 2013. Numerical simulation of hydro-elastic problems with smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 25(5): 673-682. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(13)60412-6 [106] Liu M B, Shao J R, Li H Q. 2014. An SPH model for free surface flows with moving rigid objects. Numerical Methods in Fluids, 74(9): 684-697. doi: 10.1002/fld.3868 [107] Liu M B, Zhang Z L, Feng D L. 2017. A density-adaptive SPH method with kernel gradient correction for modeling explosive welding. Computational Mechanics, 60: 513-529. doi: 10.1007/s00466-017-1420-5 [108] Liu S, Liu J, Chen J, Liu X. 2019. Influence of surface tension on the molten pool morphology in laser melting. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 146: 106075. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2019.106075 [109] Liu T G, Khoo B C, Xie W F. 2004. Isentropic one-fluid modelling of unsteady cavitating flow. Journal of Computational Physics, 201(1): 80-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2004.05.010 [110] Liu W K, Jun S, Zhang Y F. 1995. Reproducing kernel particle methods. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 20(8-9): 1081-1106. doi: 10.1002/fld.1650200824 [111] Liu Y P, Ren M K, Gu J F, Li Z, Ruan S L, Shen C Y. 2025. SPH simulation for 3D non-isothermal injection molding filling process using GPU acceleration. Computational Particle Mechanics, 1-15. [112] Liu Z, Li S, Pan X, Fang H. 2022. Mechanism study on spreading dynamics of nanofluids droplet coupled with thermal evaporation. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 183: 122172. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.122172 [113] Long T, Hu D, Wan D, Zhuang C, Yang G. 2017. An arbitrary boundary with ghost particles incorporated in coupled FEM–SPH model for FSI problems. Journal of Computational Physics, 350: 166-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2017.08.044 [114] Long T, Yang P, Liu M B. 2020. A novel coupling approach of smoothed finite element method with SPH for thermal fluid structure interaction problems. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 174: 105558. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105558 [115] Long T, Huang C, Hu D, Liu M B. 2021a. Coupling edge-based smoothed finite element method with smoothed particle hydrodynamics for fluid structure interaction problems. Ocean Engineering, 225: 108772. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108772 [116] Long T, Zhang Z L, Liu M B. 2021b. Multi-resolution technique integrated with smoothed particle element method (SPEM) for modeling fluid-structure interaction problems with free surfaces. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(8): 284711. [117] Lu Y, Chen J Y, Feng D L, Wang L, Liu M B. 2023. Numerical modeling of hypervelocity impacts on carbon fiber reinforced plastics using a GPU-accelerated SPH model. Computational Mechanics, 72(5): 907-926. doi: 10.1007/s00466-023-02318-7 [118] Lu Y, Wu P, Liu M B, Zhu C. 2024. A GPU-accelerated 3D ISPH-TLSPH framework for patient-specific simulations of cardiovascular fluid–structure interactions. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 428: 117110. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2024.117110 [119] Lucy L B. 1977. A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. The Astronomical Journal, 82: 1013. doi: 10.1086/112164 [120] Luo Z W, Wang Z K, Yan Z Y, Chen J, Li S G, Liu M B. 2022. Formation of defects in selective laser melted inconel 718 and its correlation with mechanical properties through dimensionless numbers. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 65(5): 254611. [121] Lüthi C, Afrasiabi M, Bambach M. 2023. An adaptive smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) scheme for efficient melt pool simulations in additive manufacturing. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 139: 7-27. [122] Lyu H G, Sun P N, Huang X T, Liu M B, Zha H Y, Zhang A M. 2024. Numerical investigation of vehicle wading based on an entirely particle-based three-dimensional SPH model. Computers & Fluids, 270: 106144. [123] Ma Y B, Zhou X, Zhang F, Weißenfels C, Liu M B. 2024. A novel smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for multi-physics simulation of laser powder bed fusion. Computational Mechanics, 74(5): 1009-1036. doi: 10.1007/s00466-024-02465-5 [124] Marrone S, Colagrossi A, Le Touzé D, Graziani G. 2010. Fast free-surface detection and level-set function definition in SPH solvers. Journal of Computational Physics, 229(10): 3652-3663. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2010.01.019 [125] Marrone S, Antuono M, Colagrossi A, Colicchio G, Le Touzé D, Graziani G. 2011. δ-SPH model for simulating violent impact flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 200(13-16): 1526-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2010.12.016 [126] Marrone S, Bouscasse B, Colagrossi A, Antuono M. 2012. Study of ship wave breaking patterns using 3D parallel SPH simulations. Computers & Fluids, 69: 54-66. [127] Meng Z F, Wang P P, Zhang A M, Ming F R, Sun P N. 2020. A multiphase SPH model based on Roe’s approximate Riemann solver for hydraulic flows with complex interface. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 365: 112999. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.112999 [128] Meng Z F, Zhang A M. Wang P P, Ming F R. 2021. A shock-capturing scheme with a novel limiter for compressible flows solved by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 386: 114082. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2021.114082 [129] Meng Z F, Zhang A M, Wang P P, Ming F R, Khoo B C. 2022a. A targeted essentially non-oscillatory (TENO) SPH method and its applications in hydrodynamics. Ocean Engineering, 243: 110100. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.110100 [130] Meng Z F, Zhang A M, Yan J L, Wang P P, Khayyer A. 2022b. A hydroelastic fluid–structure interaction solver based on the Riemann-SPH method. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 390: 114522. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2021.114522 [131] Mokos A, Rogers B D, Stansby P K, Domínguez J M. 2015. Multi-phase SPH modelling of violent hydrodynamics on GPUs. Computer Physics Communications, 196: 304-316. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2015.06.020 [132] Monaghan J J. 1992. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 30: 543-574. doi: 10.1146/annurev.aa.30.090192.002551 [133] Monaghan J J. 1994. Simulating free surface flows with SPH. Journal of Computational Physics, 110(2): 399-406. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1994.1034 [134] Monaghan J J. 1997. SPH and Riemann solvers. Journal of Computational Physics, 136(2): 298-307. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1997.5732 [135] Monaghan J J. 2005. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Reports on Progress in Physics, 68(8): 1703-1759. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/68/8/R01 [136] Monaghan J J, Gingold R A. 1983. Shock simulation by the particle method SPH. Journal of Computational Physics, 52(2): 374-389. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(83)90036-0 [137] Morikawa D, Senadheera H, Asai M. 2021. Explicit incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics in a multi-GPU environment for large-scale simulations. Computational Particle Mechanics, 8(3): 493-510. doi: 10.1007/s40571-020-00347-0 [138] Morris J P, Fox P J, Zhu Y. 1997. Modeling low Reynolds number incompressible flows using SPH. Journal of Computational Physics, 136(1): 214-226. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1997.5776 [139] Mostafaei A, Ghiaasiaan R, Ho I T, Strayer S, Chang K C, Shamsaei N, Shao S, Paul S, Yeh A C, Tin S, To A C. 2023. Additive manufacturing of nickel-based superalloys: A state-of-the-art review on process-structure-defect-property relationship. Progress in Materials Science, 136: 101108. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2023.101108 [140] Ng K C, Ng Y L, Sheu T W H, Alexiadis A. 2020. Assessment of smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) models for predicting wall heat transfer rate at complex boundary. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 111: 195-205. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.10.017 [141] Nguyen M T, Aly A M, Lee S W. 2018. ISPH modeling of natural convection heat transfer with an analytical kernel renormalization factor. Meccanica, 53: 2299-2318. doi: 10.1007/s11012-018-0825-3 [142] Nishiura D, Furuichi M, Sakaguchi H. 2015. Computational performance of a smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulation for shared-memory parallel computing. Computer Physics Communications, 194: 18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2015.04.006 [143] Niu X, Zhao J, Wang B. 2019. Application of smooth particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method in gravity casting shrinkage cavity prediction. Computational Particle Mechanics, 6: 803-810. doi: 10.1007/s40571-019-00263-y [144] Oger G, Le Touzé D, Guibert D, De Leffe M, Biddiscombe J, Soumagne J, Piccinali J G. 2016. On distributed memory MPI-based parallelization of SPH codes in massive HPC context. Computer Physics Communications, 200: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2015.08.021 [145] Pan W, Bao J, Tartakovsky A M. 2014. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics continuous boundary force method for Navier–Stokes equations subject to a Robin boundary condition. Journal of Computational Physics, 259: 242-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2013.12.014 [146] Papazoglou E L, Karkalos N E, Karmiris-Obratański P, Markopoulos A P. 2022. On the modeling and simulation of SLM and SLS for metal and polymer powders: A review. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 1-33. [147] Park S S, Kim D K, Kim J H, Kim E S. 2023. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for pinch plasma simulation with non-ideal MHD model. Physics of Plasmas, 30(5): 053901. doi: 10.1063/5.0138221 [148] Park S S, Kim D K, Ham S, Chung K J, Na Y S, Kim E S. 2024. SPH code development for X-pinch plasma simulation. Physics of Plasmas, 31(3): 033901. doi: 10.1063/5.0182654 [149] Peng C, Wang S, Wu W, Yu H S, Wang C, Chen J Y. 2019. LOQUAT: An open-source GPU-accelerated SPH solver for geotechnical modeling. Acta Geotechnica, 14: 1269-1287. doi: 10.1007/s11440-019-00839-1 [150] Peng Y X, Zhang A M, Ming F R. 2021a. Particle regeneration technique for smoothed particle hydrodynamics in simulation of compressible multiphase flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 376: 113653. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113653 [151] Peng Y X, Zhang A M, Ming F R. 2021b. Numerical simulation of structural damage subjected to the near-field underwater explosion based on SPH and RKPM. Ocean Engineering, 222: 108576. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108576 [152] Peng Y X, Zhang A M, Wang S P. 2021c. Coupling of WCSPH and RKPM for the simulation of incompressible fluid–structure interactions. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 102: 103254. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2021.103254 [153] Price D J, Wurster J, Tricco T S, Nixon C, Toupin S, Pettitt A, Chan C, Mentiplay D, Laibe G, Glover S, Dobbs C, Nealon R, Liptai D, Worpel H, Bonnerot C, Dipierro G, Ballabio G, Ragusa E, Federrath C, Iaconi R, Reichardt T, Forgan D, Hutchison M, Constantino T, Ayliffe B, Hirsh K, Lodato G. 2018. Phantom: A smoothed particle hydrodynamics and magnetohydrodynamics code for astrophysics. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 35: e031. doi: 10.1017/pasa.2018.25 [154] Qiu Y, Niu X, Song T, Shen M, Li W, Xu W. 2021. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of selective laser melting process based on SPH method. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 71: 224-236. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.09.018 [155] Quarteroni A, Manzoni A, Vergara C. 2017. The cardiovascular system: Mathematical modelling, numerical algorithms and clinical applications. Acta Numerica, 26: 365-590. doi: 10.1017/S0962492917000046 [156] Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis G E. 2017a. Physics informed deep learning (Part I): Data-driven solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1711.10561. [157] Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis G E. 2017b. Physics informed deep learning (Part II): Data-driven discovery of nonlinear partial differential equations. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1711.10566. [158] Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis G E. 2019. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. Journal of Computational Physics, 378: 686-707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [159] Raizah Z A S. 2020. Natural convection from cross blade inside a nanofluid-filled cavity using ISPH method. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 30(10): 4629-4648. [160] Ray M, Yang X F, Kong S C, Bravo L, Kweon C B M. 2017. High-fidelity simulation of drop collision and vapor–liquid equilibrium of van der Waals fluids. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 36(2): 2385-2392. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2016.06.018 [161] Ren M K, Gu J F, Li Z, Ruan S L, Shen C Y. 2022. A multiscale simulation of polymer melt injection molding filling flow using SPH method with slip-link model. Polymers, 14(20): 4334. doi: 10.3390/polym14204334 [162] Rezavand M, Zhang C, Hu X Y. 2020. A weakly compressible SPH method for violent multi-phase flows with high density ratio. Journal of Computational Physics, 402: 109092. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.109092 [163] Rodríguez Prieto J M, Larsson S, Afrasiabi M. 2023. Thermomechanical simulation of orthogonal metal cutting with PFEM and SPH using a temperature-dependent friction coefficient: A comparative study. Materials, 16(10): 3702. doi: 10.3390/ma16103702 [164] Roe P L. 1981. Approximate Riemann solvers, parameter vectors, and difference schemes. Journal of Computational Physics, 43(2): 357-372. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(81)90128-5 [165] Rogersm B D, Mokos A, Fourtakas G, Crespo A J C, Domínguez J M, Altomare C, Canelas R. 2015. Developing SPH simulations for coastal applications accelerated on GPUs using dualsphysics. Hydrolink, 3(3): 81-84. [166] Russell M A, Souto-Iglesias A, Zohdi T I. 2018. Numerical simulation of laser fusion additive manufacturing processes using the SPH method. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 341: 163-187. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2018.06.033 [167] Rustico E, Bilotta G, Gallo G, Herault A, Del Negro C, Dalrymple R A. 2012. A journey from single-GPU to optimized multi-GPU SPH with CUDA. 7th SPHERIC Workshop, 56. [168] Shao J R, Li H Q, Liu G R, Liu M B. 2012. An improved SPH method for modeling liquid sloshing dynamics. Computers & Structures, 100: 18-26. [169] Shao J R, Yang Y, Gong H F, Liu M B. 2019. Numerical simulation of water entry with improved SPH method. International Journal of Computational Methods, 16(02): 1846004. doi: 10.1142/S0219876218460040 [170] Sohag Md M A, Chausalkar A, Li L, Yang X F. 2022. Numerical study of drop spread and rebound on heated surfaces with consideration of high pressure. Physics of Fluids, 34(11): 113319. doi: 10.1063/5.0124794 [171] Sollich D, Reinheimer E N, Wagner J, Berger P, Eberhard P. 2022. An improved recoil pressure boundary condition for the simulation of deep penetration laser beam welding using the SPH method. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 96: 26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechflu.2022.06.001 [172] Springel V. 2005. The cosmological simulation code gadget-2. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 364(4): 1105-1134. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09655.x [173] Sun P N, Colagrossi A, Marrone S, Antuono M, Zhang A M. 2018. Multi-resolution delta-plus-SPH with tensile instability control: Towards high Reynolds number flows. Computer Physics Communications, 224: 63-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2017.11.016 [174] Sun P N, Le Touzé D, Oger G, Zhang A M. 2021a. An accurate SPH volume adaptive scheme for modeling strongly-compressible multiphase flows. Part 1: Numerical scheme and validations with basic 1D and 2D benchmarks. Journal of Computational Physics, 426: 109937. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109937 [175] Sun P N, Le Touzé D, Oger G, Zhang A M. 2021b. An accurate FSI-SPH modeling of challenging fluid-structure interaction problems in two and three dimensions. Ocean Engineering, 221: 108552. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108552 [176] Tang X, Zhang, C, Haidn O, Hu X Y. 2023. An integrative SPH method for heat transfer problems involving fluid-structure interaction. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 39(2): 722248. doi: 10.1007/s10409-022-22248-x [177] Tokunaga H, Motoyama Y, Okane T. 2023. Particle method simulation of direct-chill casting process including breakout. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 129(9): 4407-4418. [178] Toro E F. 2009. Riemann solvers and numerical methods for fluid dynamics: A practical introduction. 3rd ed. Springer, Dordrecht ; New York. [179] Tricco T S, Price D J. 2012. Constrained hyperbolic divergence cleaning for smoothed particle magnetohydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 231(21): 7214-7236. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2012.06.039 [180] Troconis J, Sánchez-Silva F, Carvajal-Mariscal I, Peña-Polo F, Sigalotti L D G, Klapp J. 2023. Simulation of van der Waals liquid droplets within a hot air atmosphere using the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 202: 123749. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2022.123749 [181] Tsuzuki S, Aoki T. 2016. Effective dynamic load balance using space-filling curves for large-scale SPH simulations on GPU-rich supercomputers. 2016 7th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA), Salt Lake, UT, USA, IEEE, 1–8. [182] Valdez-Balderas D, Domínguez J M, Rogers B D, Crespo A J C. 2013. Towards accelerating smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations for free-surface flows on multi-GPU clusters. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 73(11): 1483-1493. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2012.07.010 [183] Van Leer B. 1979. Towards the ultimate conservative difference scheme. V. A second-order sequel to Godunov’s method. Journal of Computational Physics, 32(1): 101-136. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(79)90145-1 [184] Verbeeten W M H, Peters G W M, Baaijens F P T. 2001. Differential constitutive equations for polymer melts: The extended Pom–Pom model. Journal of Rheology, 45(4): 823-843. doi: 10.1122/1.1380426 [185] Verma K, Szewc K, Wille R. 2017. Advanced load balancing for SPH simulations on multi-GPU architectures. 2017 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC), IEEE, 1–7. [186] Vishwakarma V, Das A K, Das P K. 2011. Steady state conduction through 2D irregular bodies by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 54(1-3): 314-325. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.09.040 [187] Walayat K, Wang Z, Usman K, Liu M B. 2018. An efficient multi-grid finite element fictitious boundary method for particulate flows with thermal convection. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 126: 452-465. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.05.007 [188] Wang F, Zhai Z, Zhao Z, Di Y, Chen X. 2024a. Physics-informed neural network for lithium-ion battery degradation stable modeling and prognosis. Nature Communications, 15(1): 4332. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48779-z [189] Wang G, Liu G R, Peng Q, De S, Feng D L, Liu M B. 2015. A 3D smoothed particle hydrodynamics method with reactive flow model for the simulation of ANFO. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 40(4): 566-575. doi: 10.1002/prep.201400244 [190] Wang P P, Zhang A M, Meng Z F, Ming F R, Fang X L. 2021. A new type of WENO scheme in SPH for compressible flows with discontinuities. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 381: 113770. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2021.113770 [191] Wang P P, Zhang A M, Fang X L, Khayyer A, Meng Z F. 2022. Axisymmetric Riemann–smoothed particle hydrodynamics modeling of high-pressure bubble dynamics with a simple shifting scheme. Physics of Fluids, 34(11): 112122. doi: 10.1063/5.0123106 [192] Wang T, He X, Li M, Li Y, Bi R, Wang Y, Cheng C, Shen X, Meng J, Zhang H, Liu H, Wang Z, Li S, Shao B, Liu T Y. 2024b. Ab initio characterization of protein molecular dynamics with AI2BMD. Nature, 635: 1019-1027. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08127-z [193] Wang Z, Liu M B. 2019. Dimensionless analysis on selective laser melting to predict porosity and track morphology. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 273: 116238. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.05.019 [194] Wang Z, Yan W T, Liu W K, Liu M B. 2019. Powder-scale multi-physics modeling of multi-layer multi-track selective laser melting with sharp interface capturing method. Computational Mechanics, 63: 649-661. doi: 10.1007/s00466-018-1614-5 [195] Weirather J, Rozov V, Wille M, Schuler P, Seidel C, Adams N A, Zaeh M F. 2019. A smoothed particle hydrodynamics model for laser beam melting of Ni-based alloy 718. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 78(7): 2377-2394. [196] Wessels H, Bode T, Weißenfels C, Wriggers P, Zohdi T I. 2019. Investigation of heat source modeling for selective laser melting. Computational Mechanics, 63: 949-970. doi: 10.1007/s00466-018-1631-4 [197] Wessels H, Weißenfels C, Wriggers P. 2020. The neural particle method–An updated Lagrangian physics informed neural network for computational fluid dynamics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 368: 113127. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113127 [198] Wilson dhileep kumar C, Saravanan S, Raghukandan K. 2022. Numerical and experimental investigation on aluminum 6061-V-grooved stainless steel 304 explosive cladding. Defence Technology, 18(2): 249-260. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2020.11.010 [199] Wyen C F. 2011. Rounded cutting edges and their influence in machining titanium [Doctoral Thesis]. ETH Zurich. [200] Xia X L, Liang Q H. 2016. A GPU-accelerated smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) model for the shallow water equations. Environmental Modelling & Software, 75: 28-43. [201] Xiao S, Bai J, Jeong H, Alzubaidi L, Gu Y. 2025. A meshless Runge-Kutta-based physics-Informed neural network framework for structural vibration analysis. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 170: 106054. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2024.106054 [202] Xiao X, Zhou Y, Wang H, Yang X. 2020. A novel CNN-based poisson solver for fluid simulation. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26(3): 1454-1465. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2018.2873375 [203] Xiao X, Ma X, Kari T, Xu Q, Fan M. 2023. Numerical simulation of droplet evaporation based on the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Thermal Science, 27: 3745-3756. doi: 10.2298/TSCI230311101X [204] Xiao Y, Dong H, Zhou J, Wang J. 2017. Studying normal perforation of monolithic and layered steel targets by conical projectiles with SPH simulation and analytical method. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 75: 12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2016.11.004 [205] Xue B, Wang S P, Peng Y X, Zhang A M. 2022. A novel coupled Riemann SPH–RKPM model for the simulation of weakly compressible fluid–structure interaction problems. Ocean Engineering, 266: 112447. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112447 [206] Xue B, Zhang A M, Peng Y X, Zhang Q, Li S. 2024. A meshfree orthotropic laminated shell model for geometrically nonlinear static and dynamic analysis. Computational Mechanics, 73(5): 1033-1051. doi: 10.1007/s00466-023-02399-4 [207] Yang E, Bui H H, De Sterck H, Nguyen G D, Bouazza A. 2020. A scalable parallel computing SPH framework for predictions of geophysical granular flows. Computers and Geotechnics, 121: 103474. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103474 [208] Yang E, Bui H H, Nguyen G D, Choi C E, Ng C W W, De Sterck H, Bouazza A. 2021a. Numerical investigation of the mechanism of granular flow impact on rigid control structures. Acta Geotechnica, 16: 2505-2527. doi: 10.1007/s11440-021-01162-4 [209] Yang P Y, Huang C, Zhang Z L, Long T, Liu M B. 2021b. Simulating natural convection with high Rayleigh numbers using the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 166: 120758. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120758 [210] Yang Q, Xu F, Yang Y, Dai Z, Wang J. 2023. A GPU-accelerated adaptive particle refinement for multi-phase flow and fluid-structure coupling SPH. Ocean Engineering, 279: 114514. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114514 [211] Yang X F, Liu M B. 2013. Numerical modeling of oil spill containment by boom using SPH. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 56: 315-321. doi: 10.1007/s11433-012-4980-6 [212] Yang X F, Liu M B. 2016. Bending modes and transition criteria for a flexible fiber in viscous flows. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 28(6): 1043-1048. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60709-6 [213] Yang X F, Kong S C. 2017. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for evaporating multiphase flows. Physical Review E, 96(3): 033309. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.96.033309 [214] Yang X F, Liu M B. 2017a. Particle-based modeling of asymmetric flexible fibers in viscous flows. Communications in Computational Physics, 22(4): 1015-1027. doi: 10.4208/cicp.OA-2016-0208 [215] Yang X F, Peng S, Liu M B, Shao J R. 2012. Numerical simulation of ballast water by SPH method. International Journal of Computational Methods, 09: 1240002. doi: 10.1142/S0219876212400026 [216] Yang X F, Liu M B, Peng S. 2014. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and element bending group modeling of flexible fibers interacting with viscous fluids. Physical Review E, 90(6): 063011. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.90.063011 [217] Yang X F, Liu M B, Peng S, Huang C. 2016. Numerical modeling of dam-break flow impacting on flexible structures using an improved SPH–EBG method. Coastal Engineering, 108: 56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2015.11.007 [218] Yang X F, Ray M, Kong S C, Kweon C B M. 2019. SPH simulation of fuel drop impact on heated surfaces. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 37(3): 3279-3286. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.07.078 [219] Yang X F, Kong S C, Liu M B, Liu Q. 2021c. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics with adaptive spatial resolution (SPH-ASR) for free surface flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 443: 110539. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110539 [220] Yang X F, Liu M B. 2017b. Numerical study of Rayleigh-Taylor instability by using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Acta Physica Sinica, 66(16): 164701. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.164701 [221] Yin M, Charon N, Brody R, Lu L, Trayanova N, Maggioni M. 2024. A scalable framework for learning the geometry-dependent solution operators of partial differential equations. Nature Computational Science, 4(12): 928-940. doi: 10.1038/s43588-024-00732-2 [222] Yuan B, Wang H, Heitor A, Chen X. 2024. A physics-informed convolutional neural network for partial differential equations with space-time domain. Journal of Computational Physics, 515: 113284. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2024.113284 [223] Zhang A M, Sun P N, Ming F R. 2015. An SPH modeling of bubble rising and coalescing in three dimensions. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 294: 189-209. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2015.05.014 [224] Zhang C, Hu X Y, Adams N A. 2017a. A weakly compressible SPH method based on a low-dissipation Riemann solver. Journal of Computational Physics, 335: 605-620. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2017.01.027 [225] Zhang C, Hu X Y, Adams N A. 2017b. A generalized transport-velocity formulation for smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 337: 216-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2017.02.016 [226] Zhang C, Zhu Y, Hu X Y. 2023a. An efficient multi-resolution SPH framework for multi-phase fluid-structure interactions. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 66(10): 104712. [227] Zhang F, Huang C, Zhang H S, Liu T G, Liu M B. 2022a. A finite particle method based on a Riemann solver for modeling incompressible flows. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 124: 74-88. [228] Zhang F, Yang P, Liu M B. 2023b. An improved continuum surface tension model in SPH for simulating free-surface flows and heat transfer problems. Journal of Computational Physics, 490: 112322. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112322 [229] Zhang H S, Zhang Z L, He F, Liu M B. 2022b. Numerical investigation on the water entry of a 3D circular cylinder based on a GPU-accelerated SPH method. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 94: 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechflu.2022.01.007 [230] Zhang H S, Li X X, Feng K W, Liu M B. 2023c. 3D large-scale SPH modeling of vehicle wading with GPU acceleration. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 66(10): 104711. [231] Zhang N, Klippel H, Afrasiabi M, Röthlin M, Kuffa M, Bambach M, Wegener K. 2023d. Hybrid SPH-FEM solver for metal cutting simulations on the GPU including thermal contact modeling. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 41: 311-327. doi: 10.1016/j.cirpj.2022.12.012 [232] Zhang N, Klippel H, Kneubühler F, Afrasiabi M, Kuffa M, Wegener K. 2024a. Investigation of friction modeling on numerical Ti6Al4V cutting simulations. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 274: 109231. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2024.109231 [233] Zhang Y Y, Ma Y, Qiu M X, Liu X H, Deng F P, Jin L J. 2024b. Numerical simulation of micro-explosion of cathode micro-protrusion based on smoothed particle magnetohydrodynamics. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 31(2): 738-746. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2023.3324900 [234] Zhang Z L, Liu M B. 2017. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics with kernel gradient correction for modeling high velocity impact in two- and three-dimensional spaces. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 83: 141-157. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2017.07.015 [235] Zhang Z L, Liu M B. 2018. A decoupled finite particle method for modeling incompressible flows with free surfaces. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 60: 606-633. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2018.03.043 [236] Zhang Z L, Liu M B. 2019. Numerical studies on explosive welding with ANFO by using a density adaptive SPH method. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 41: 208-220. [237] Zhang Z L, Feng D L, Liu M B. 2018a. Investigation of explosive welding through whole process modeling using a density adaptive SPH method. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 35: 169-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.08.004 [238] Zhang Z L, Walayat K, Chang J Z, Liu M B. 2018b. Meshfree modeling of a fluid-particle two-phase flow with an improved SPH method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 116: 530-569. doi: 10.1002/nme.5935 [239] Zhang Z L, Feng D L, Ma T, Liu M B. 2019a. Predicting the damage on a target plate produced by hypervelocity impact using a decoupled finite particle method. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 98: 110-125. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2018.10.012 [240] Zhang Z L, Long T, Chang J Z, Liu M B. 2019b. A smoothed particle element method (SPEM) for modeling fluid–structure interaction problems with large fluid deformations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 356: 261-293. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2019.07.024 [241] Zhang Z L, Walayat K, Huang C, Chang J Z, Liu M B. 2019c. A finite particle method with particle shifting technique for modeling particulate flows with thermal convection. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 128: 1245-1262. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.09.074 [242] Zhang Z L, Khalid M S U, Long T, Chang J Z, Liu M B. 2020a. Investigations on sloshing mitigation using elastic baffles by coupling smoothed finite element method and decoupled finite particle method. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 94: 102942. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2020.102942 [243] Zhang Z L, Ma T, Feng D L, Liu M B. 2020b. A new formula for predicting the crater size of a target plate produced by hypervelocity impact. International Journal of Computational Methods, 17(01): 1844004. doi: 10.1142/S0219876218440048 [244] Zhang Z L, Khalid M S U, Long T, Liu M B, Shu C. 2021. Improved element-particle coupling strategy with δ-SPH and particle shifting for modeling sloshing with rigid or deformable structures. Applied Ocean Research, 114: 102774. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2021.102774 [245] Zhao Z X, Bilotta G, Yuan Q E, Gong Z X, Liu H. 2023. Multi-GPU multi-resolution SPH framework towards massive hydrodynamics simulations and its applications in high-speed water entry. Journal of Computational Physics, 490: 112339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112339 [246] Zhou X, Wang Z K, Hu P, Liu M B. 2023. Discrepancies between Gaussian surface heat source model and ray tracing heat source model for numerical simulation of selective laser melting. Computational Mechanics, 71(3): 599-613. doi: 10.1007/s00466-022-02235-1 [247] Zhou X, Hu P, Ma Y B, Zhang J, Liu M B. 2024. Numerical simulation of metal sheet damage under high-speed tangential airflow and laser irradiation. Computational Mechanics, 1–20. [248] Zhu G X, Hughes J, Zheng S M, Greaves D. 2023a. A novel MPI-based parallel smoothed particle hydrodynamics framework with dynamic load balancing for free surface flow. Computer Physics Communications, 284: 108608. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2022.108608 [249] Zhu G X, Zou L, Chen Z, Wang A M, Liu M B. 2018. An improved SPH model for multiphase flows with large density ratios. Numerical Methods in Fluids, 86(2): 167-184. doi: 10.1002/fld.4412 [250] Zhu S Q, Yu T, Xu T, Chen H Y, Dustdar S, Gigan S, Gunduz D, Hossain E, Jin Y, Lin F, Liu B, Wan Z, Zhang J, Zhao Z, Zhu W, Chen Z, Durrani T S, Wang H, Wu J, Zhang T, Pan Y. 2023b. Intelligent computing: The latest advances, challenges, and future. Intelligent Computing, 2: 0006. doi: 10.34133/icomputing.0006 [251] Zoller P, Fakhreddine Y A. 1994. Pressure—volume—temperature studies of semi-crystalline polymers. Thermochimica Acta, 238: 397-415. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6031(94)85221-9 -




 下载:
下载: