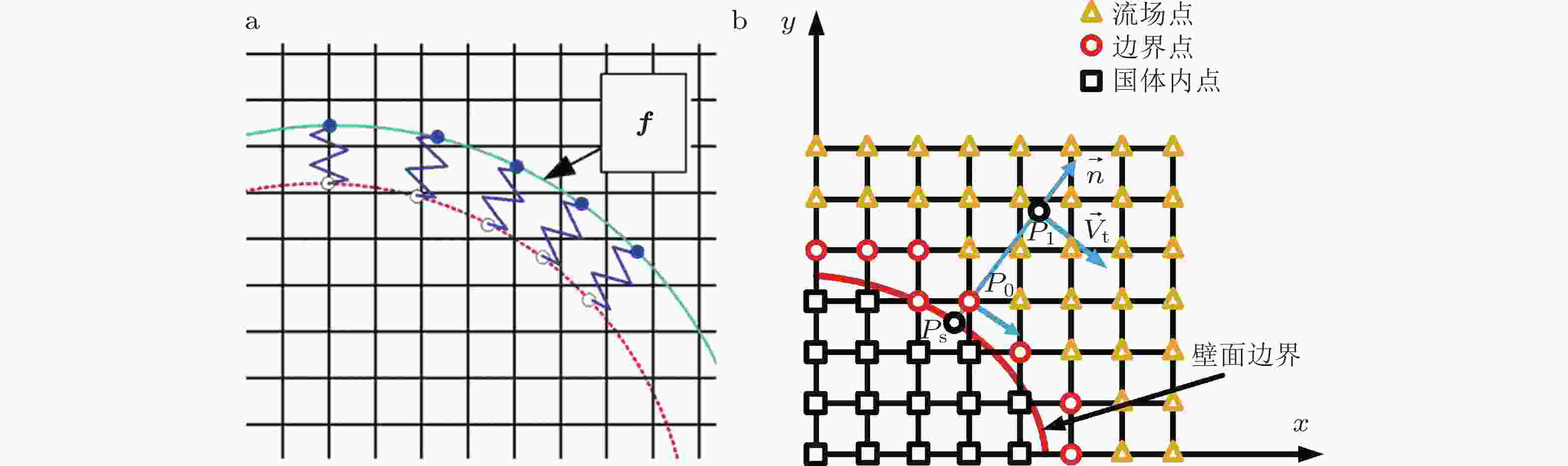
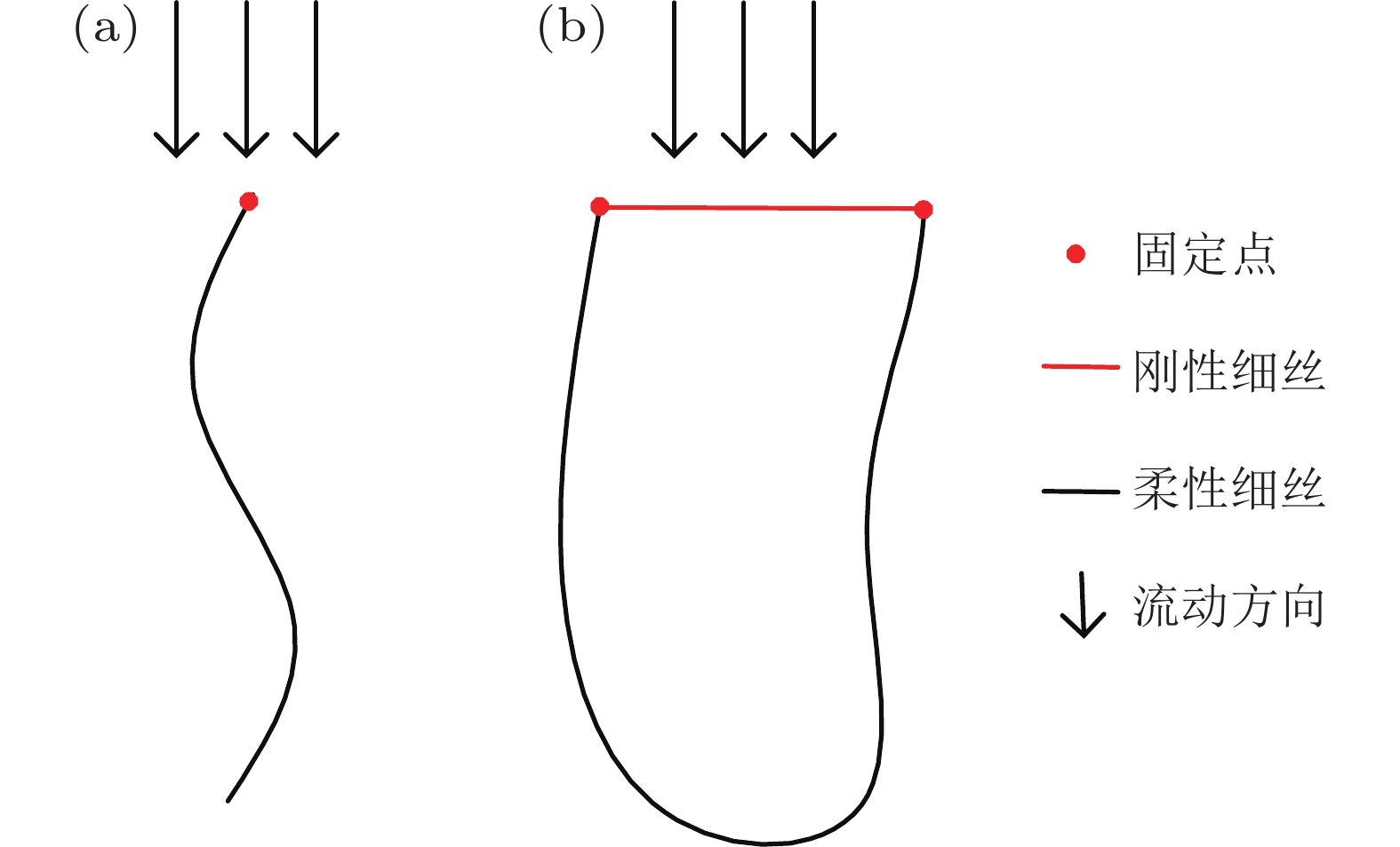
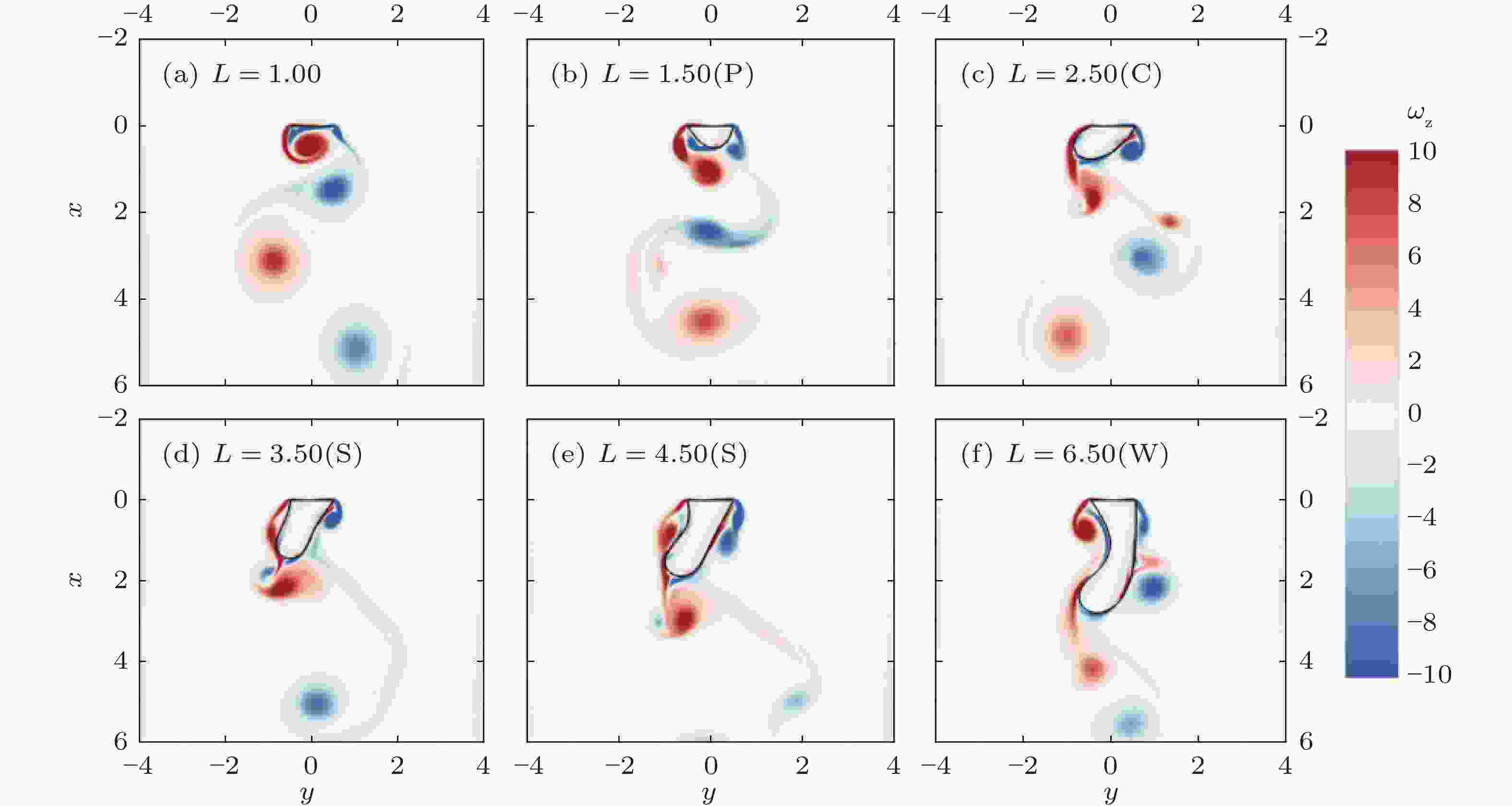
-
摘要: 本文总结了浸入式边界方法 (immersed bundary method, IB method) 中的力源建模研究进展, 并且对该方法在诸如生物体绕流及流固耦合等典型的复杂边界以及运动边界问题中的应用进行了介绍. 边界精度低是IB方法主要特征之一, 但该方法目前在计算气动声学等高精度计算中同样有所应用. 最后本文对IB方法在处理高雷诺数流动问题上所面临的挑战以及目前研究进展和未来发展方向进行了介绍.Abstract: This paper summarizes the advances in the modelling of force source for the immersed boundary (IB) method. Introductions have been given to the applications of this method in the fields of flow around biological structures and fluid-structure interaction, which are representatives of problems with complex and moving geometries, respectively. Although low accuracy at boundary is one main feature of the IB method, it has also been applied to these computational aeroacoustic problems which requires high-order accuracy. Finally, the challenges, advances and future expects of the IB method in dealing with high-Reynolds-number flow are also reviewed.
-
图 4 蝙蝠鱼示意图(Huang et al. 2020, Zhang et al. 2022b)
图 5 鱼类群体游泳数值模拟中不同个体的尾迹互相干涉(Peng et al. 2018)
图 6 基于IB方法的叶轮机械转静干涉计算. (a) 转静叶片排模型, (b) 流场瞬时涡量分布(Du et al, 2016a, 2016b)
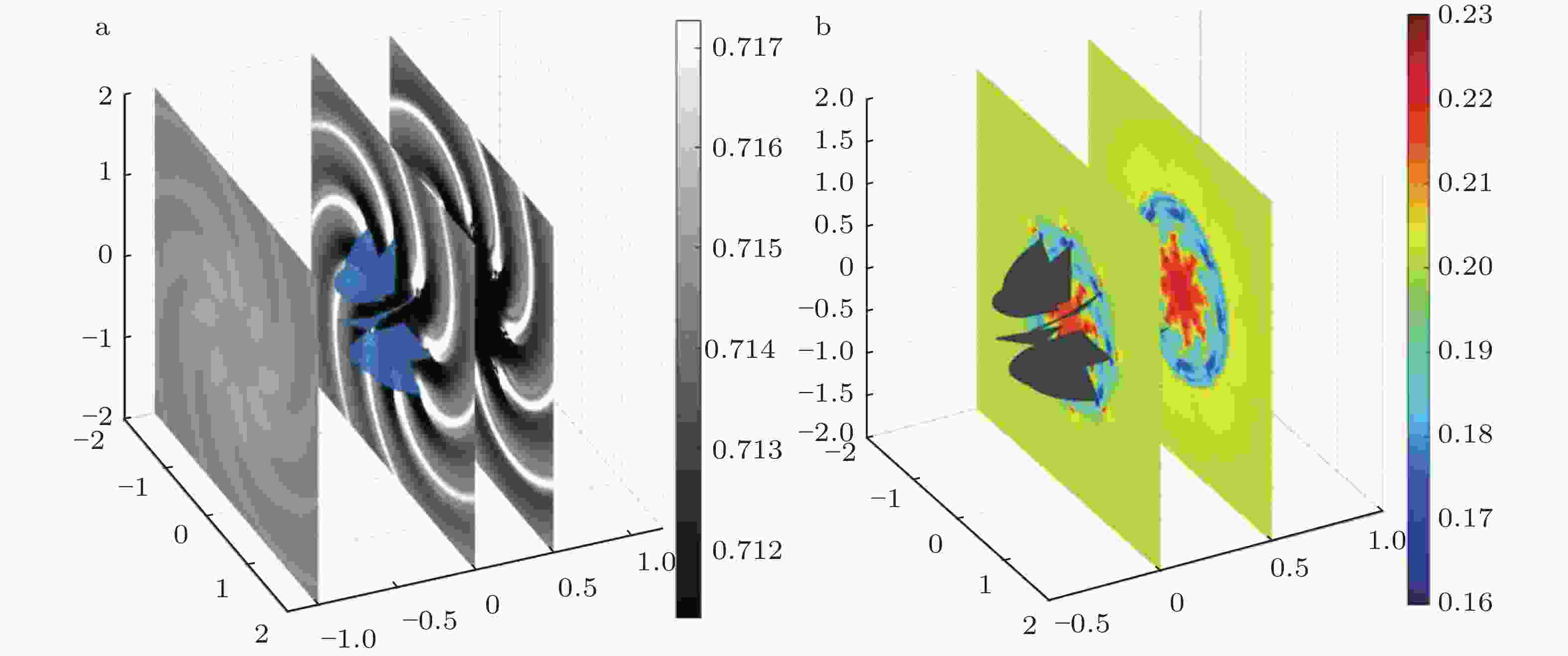
图 8 长度对刚性/柔性细丝组合体流固耦合响应及尾迹的影响(Ni et al. 2023)
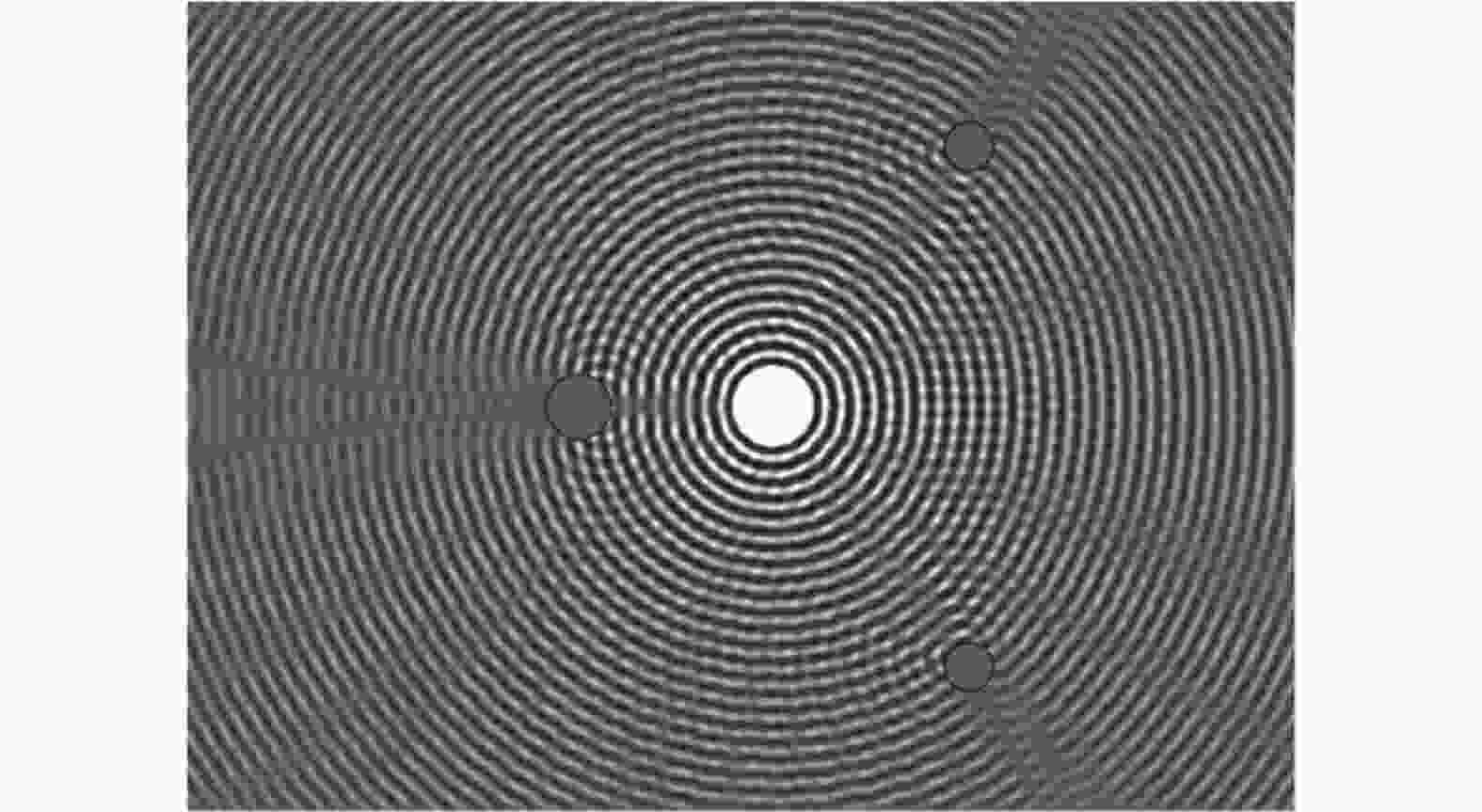
图 9 多个圆柱散射下的声场压力分布(Sun et al. 2012)
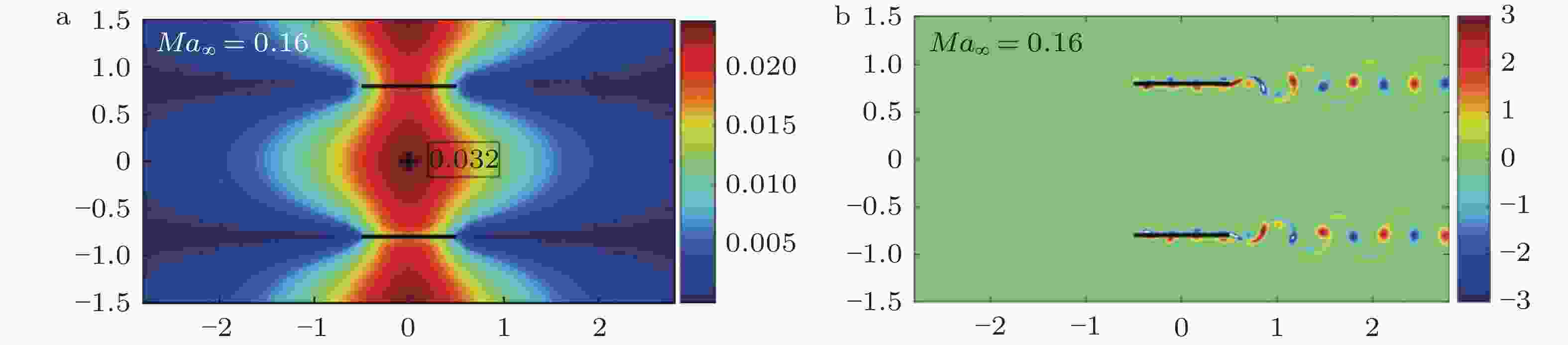
图 10 叶栅声共振所对应的流场特征. (a) 压力云图, (b) 涡量云图(Cheng et al. 2021a)
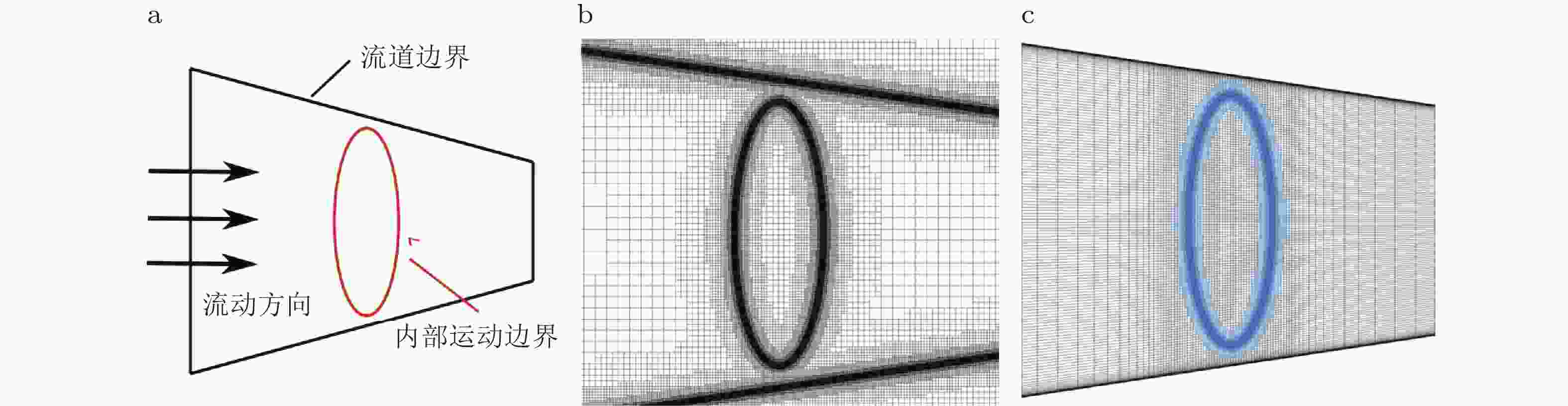
图 12 采用自适应网格加密生成的多层网格系统(Wang et al. 2020)
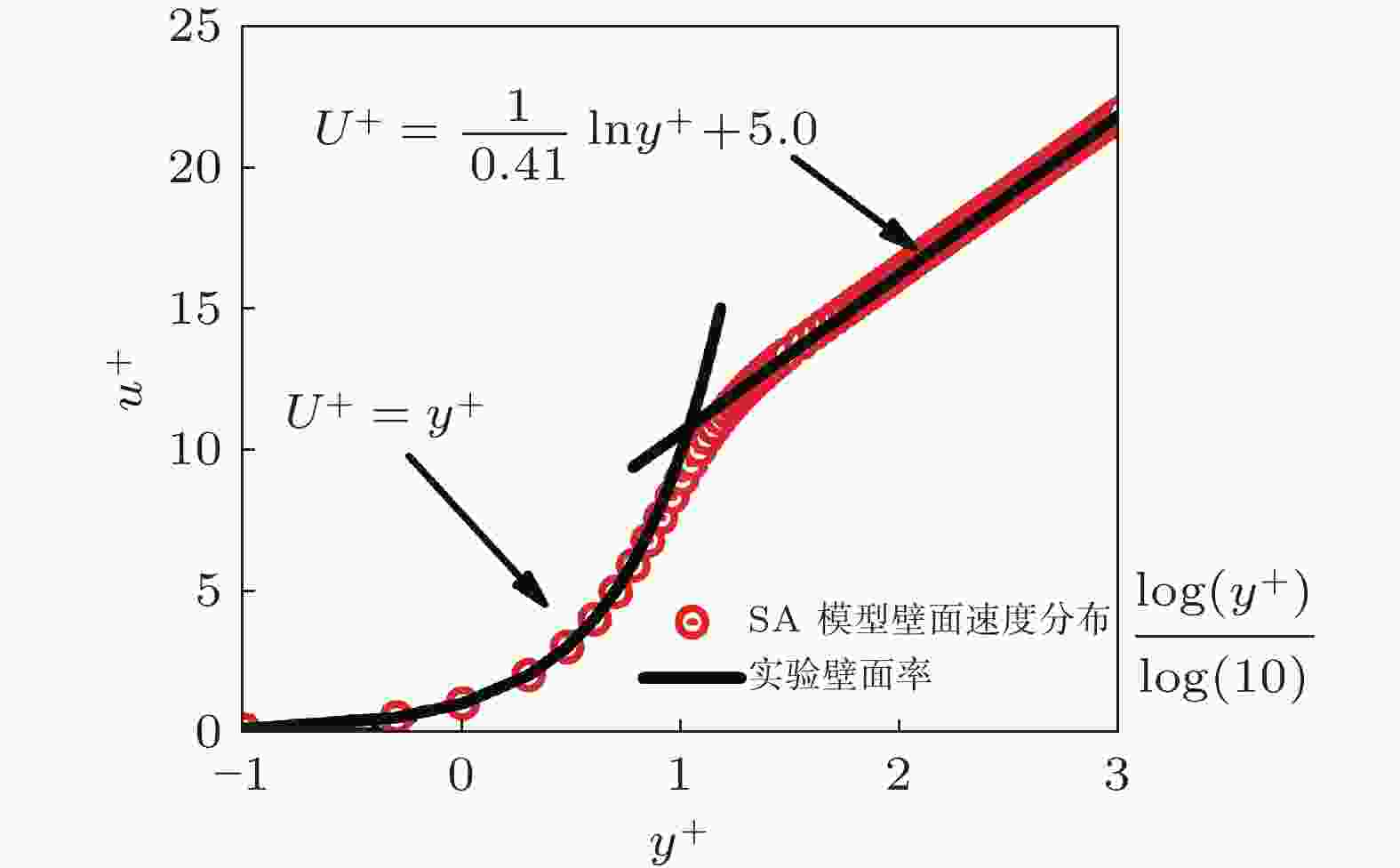
图 13 基于SA显式壁面模型的湍流边界层速度分布与壁面律对比(Chen et al. 2023)
图 14 (a) 内流问题示意图, (b) 采用笛卡尔网格结合自适应加密所生成的网格系统, (c) 流道贴体网格结合自适应加密生成的网格系统(Wang et al. 2023)
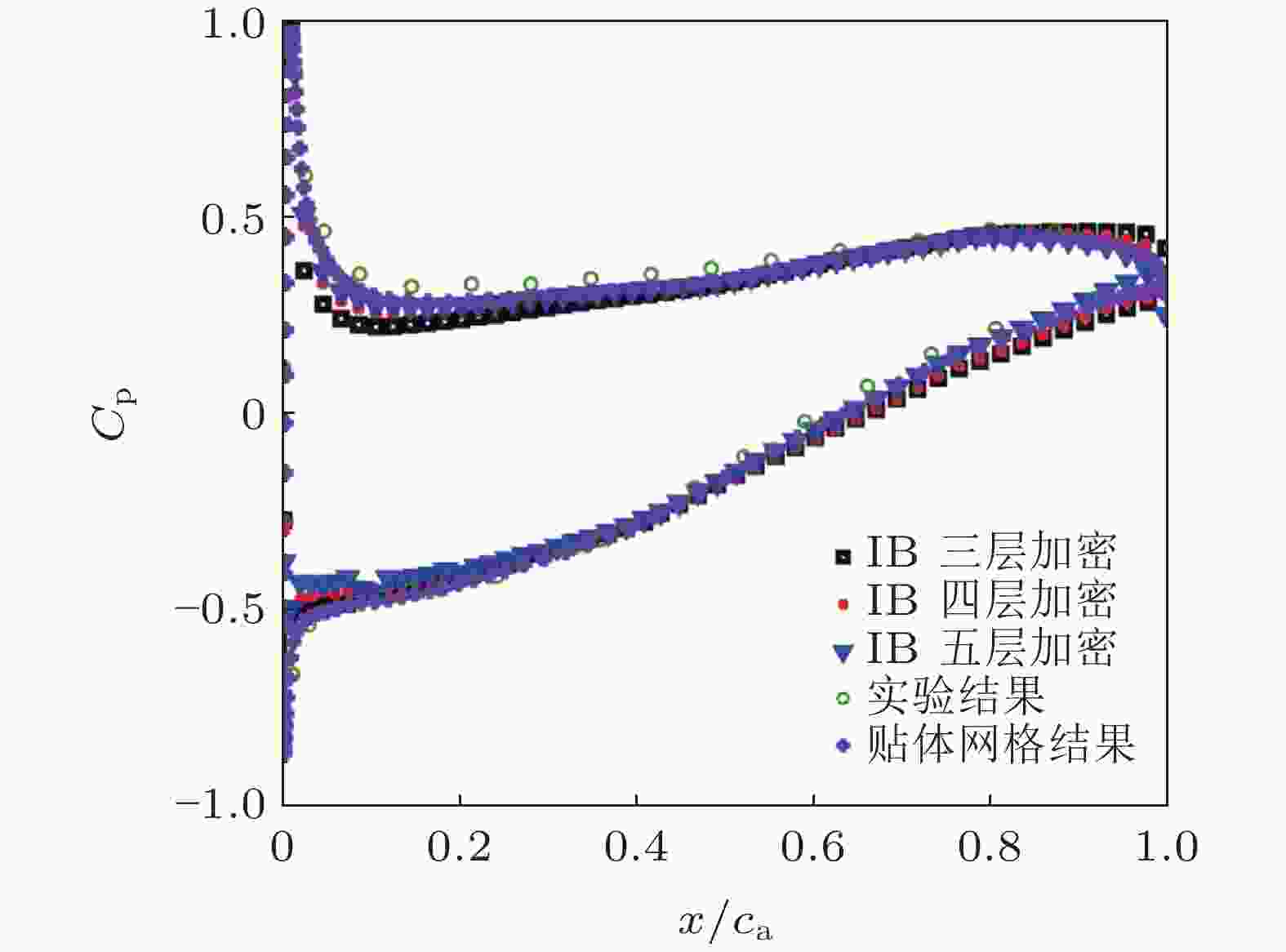
图 15 三维亚声速平面叶栅叶片表面压力分布数值模拟结果及其与实验的对比(Wang et al. 2023)
-
[1] 阎超, 于剑, 徐晶磊, 等. 2011. CFD模拟方法的发展成就与展望. 力学进展, 41: 562-589 (Yan C, Yu J, Xu J, et al. 2011. On the achievements and prospects for the methods of computational fluid dynamics. Advances in Mechanics, 41: 562-589).Yan C, Yu J, Xu J, et al. 2011. On the achievements and prospects for the methods of computational fluid dynamics. Advances in Mechanics, 41: 562-589. [2] Al M M, Samtaney R. 2017. A versatile embedded boundary adaptive mesh method for compressible flow in complex geometry. Journal of Computational Physics, 337: 339-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2017.02.044 [3] Angelidis D, Chawdhary S, Sotiropoulos F. 2016. Unstructured cartesian refinement with sharp interface immersed boundary method for 3D unsteady incompressible flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 325: 272-300. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2016.08.028 [4] Bao Y, Zhou D, Tao J, et al. 2017. Dynamic interference of two anti-phase flapping foils in side-by-side arrangement in an incompressible flow. Physics of Fluids, 29: 033601. doi: 10.1063/1.4978301 [5] Berger M J, Aftosmis M J. 2018. An ode-based wall model for turbulent flow simulations. AIAA Journal, 56: 700-714. doi: 10.2514/1.J056151 [6] Berger M J, Colella P. 1989. Local adaptive mesh refinement for shock hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 82: 64-84. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(89)90035-1 [7] Berger M J, Oliger J. 1984. Adaptive mesh refinement for hyperbolic partial differential equations. Journal of Computational Physics, 53: 484-512. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(84)90073-1 [8] Cai S G, Degrigny J, Boussuge J F, et al. 2021. Coupling of turbulence wall models and immersed boundaries on Cartesian grids. Journal of Computational Physics, 429: 109995. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109995 [9] Capizzano F. 2011. Turbulent wall model for immersed boundary methods. AIAA Journal, 49: 2367-2381. doi: 10.2514/1.J050466 [10] Capizzano F. 2016. Coupling a wall diffusion model with an immersed boundary technique. AIAA Journal, 54: 728-734. doi: 10.2514/1.J054197 [11] Chen C, Wang Y, Wang Z, et al. 2023. Application of immersed boundary method in turbomachines. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 36: 268-279. [12] Chen C, Wang Z, Du L, et al. 2021. Simulating unsteady flows in a compressor using immersed boundary method with turbulent wall model. Aerospace Science of Technology, 115: 106834. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.106834 [13] Chen W, Ji C, Williams J, et al. 2018. Vortex-induced vibrations of three tandem cylinders in laminar cross-flow: Vibration response and galloping mechanism. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 78: 215-238. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2017.12.017 [14] Cheng L, Du L, Wang X, et al. 2021a. Inviscid nonlinear modeling of vibration-induced acoustic resonance of a linear cascade. AIAA Journal, 59: 1849-1860. doi: 10.2514/1.J059501 [15] Cheng L, Du L, Wang X, et al. 2021b. A semi-implicit immersed boundary method for simulating viscous flow-induced sound with moving boundaries. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 373: 113438. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113438 [16] Cheng L, Du L, Wang X, et al. 2018. Influence of non-uniform mean flow on acoustic scattering from complex geometries. Computers and Fluids, 163: 20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2017.12.014 [17] Constant B, Péron S, Beaugendre H, et al. 2021. An improved immersed boundary method for turbulent flow simulations on Cartesian grids. Journal of Computational Physics, 435: 110240. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110240 [18] De Tullio M D, De Palma P, Iaccarino G, et al. 2007. An immersed boundary method for compressible flows using local grid refinement. Journal of Computational Physics, 225: 2098-2117. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.03.008 [19] Deng J, Caulfield C P. 2015. Three-dimensional transition after wake deflection behind a flapping foil. Physics Review E, 91: 043017. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.91.043017 [20] Deng J, Mao X, Xie F. 2019. Dynamics of two-dimensional flow around a circular cylinder with flexible filaments attached. Physics Review E, 100: 053107. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.100.053107 [21] Deng J, Sun L, Shao X. 2015. Dynamical features of the wake behind a pitching foil. Physics Review E, 92: 063013. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.063013 [22] Deng J, Sun L, Teng L, et al. 2016. The correlation between wake transition and propulsive efficiency of a flapping foil: A numerical study. Physics of Fluids, 28: 094101. doi: 10.1063/1.4961566 [23] Du L, Jing X, Sun X. 2014. Modes of vortex formation and transition to three-dimensionality in the wake of a freely vibrating cylinder. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 49: 554-573. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2014.05.012 [24] Du L, Sun X. 2015. Suppression of vortex-induced vibration using the rotary oscillation of a cylinder. Physics of Fluids, 27: 023603. doi: 10.1063/1.4913353 [25] Du L, Sun X, Yang V. 2016a. Generation of vortex lift through reduction of rotor/stator gap in turbomachinery. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 32: 472-485. doi: 10.2514/1.B35858 [26] Du L, Sun X, Yang V. 2016b. Vortex-lift mechanism in axial turbomachinery with periodically pitched stators. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 32: 486-499. doi: 10.2514/1.B35859 [27] Fadlun E A, Verzicco R, Orlandi P, et al. 2000. Combined immersed-boundary finite-difference methods for three-dimensional complex flow simulations. Journal of Computational Physics, 161: 35-60. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2000.6484 [28] Gabbard J, Gillis T, Chatelain P, et al. 2022. An immersed interface method for the 2D vorticity-velocity navier-stokes equations with multiple bodies. Journal of Computational Physics, 464: 111339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111339 [29] Gazzola M, Tchieu A A, Alexeev D, et al. 2016. Learning to school in the presence of hydrodynamic interactions. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 789: 726-749. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2015.686 [30] Ge L, Sotiropoulos F. 2007. A numerical method for solving the 3D unsteady incompressible navier–stokes equations in curvilinear domains with complex immersed boundaries. Journal of Computational Physics, 225: 1782-1809. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.02.017 [31] Gilmanov A, Sotiropoulos F. 2005. A hybrid cartesian/immersed boundary method for simulating flows with 3D, geometrically complex, moving bodies. Journal of Computational Physics, 207: 457-492. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2005.01.020 [32] Gilmanov A, Sotiropoulos F, Balaras E. 2003. A general reconstruction algorithm for simulating flows with complex 3D immersed boundaries on cartesian grids. Journal of Computational Physics, 191: 660-669. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00321-8 [33] Goldstein D, Handler R, Sirovich L. 1993. Modeling a no-slip flow boundary with an external force field. Journal of Computational Physics, 105: 354-366. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1993.1081 [34] Goldstine H H. 1980. The computer from pascal to von neumann. Princeton University Press. [35] Griffith M D, Leontini J S. 2017. Sharp interface immersed boundary methods and their application to vortex-induced vibration of a cylinder. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 72: 38-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2017.04.008 [36] Han P, Lauder G V, Dong H. 2020. Hydrodynamics of median-fin interactions in fish-like locomotion: effects of fin shape and movement. Physics of Fluids, 32: 011902. doi: 10.1063/1.5129274 [37] Holzinger F, Wartzek F, Schiffer H P, et al. 2016. Self-excited blade vibration experimentally investigated in transonic compressors: acoustic resonance. Journal of Turbomachinery, 138: 041001. doi: 10.1115/1.4032042 [38] Huang Q, Zhang D, Pan G. 2020. Computational model construction and analysis of the hydrodynamics of a rhinoptera javanica. IEEE Access, 8: 30410-30420. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2970942 [39] Huang W X, Shin S J, Sung H J. 2007. Simulation of flexible filaments in a uniform flow by the immersed boundary method. Journal of Computational Physics, 226: 2206-2228. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.07.002 [40] Huang W X, Sung H J. 2010. Three-dimensional simulation of a flapping flag in a uniform flow. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 653: 301-336. doi: 10.1017/S0022112010000248 [41] Lee C. 2003. Stability characteristics of the virtual boundary method in three-dimensional applications. Journal of Computational Physics, 184: 559-591. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(02)00038-4 [42] Shin S J, Huang W X, Sung H J. 2008. Assessment of regularized delta functions and feedback forcing schemes for an immersed boundary method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 58: 263-286. doi: 10.1002/fld.1706 [43] Huang W X, Chang C B, Sung H J. 2011. An improved penalty immersed boundary method for fluid–flexible body interaction. Journal of Computational Physics, 230: 5061-5079. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2011.03.027 [44] Jia L B, Li F, Yin X Z, et al. 2007. Coupling modes between two flapping filaments. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 581: 199-220. doi: 10.1017/S0022112007005563 [45] Kelly J, Menzer A. 2023. Hydrodynamics of body–body interactions in dense synchronous elongated fish schools. Physics of Fluids, 35: 041906. doi: 10.1063/5.0142950 [46] Kim S, Huang W X, Sung H J. 2010. Constructive and destructive interaction modes between two tandem flexible flags in viscous flow. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 661: 511-521. doi: 10.1017/S0022112010003514 [47] Kim Y, Peskin C S. 2007. Penalty immersed boundary method for an elastic boundary with mass. Physics of Fluids, 19: 053103. doi: 10.1063/1.2734674 [48] Komatsu R, Iwakami W, Hattori Y. 2016. Direct numerical simulation of aeroacoustic sound by volume penalization method. Computers and Fluids, 130: 24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2016.02.016 [49] Kurbatskii K A, Tam C K W. 1997. Cartesian boundary treatment of curved walls for high-order computational aeroacoustics schemes. AIAA Journal, 35: 133-140. doi: 10.2514/2.73 [50] Lai M C, Peskin C S. 2000. An immersed boundary method with formal second-order accuracy and reduced numerical viscosity. Journal of Computational Physics, 160: 705-719. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2000.6483 [51] Lee J, You D. 2013. An implicit ghost-cell immersed boundary method for simulations of moving body problems with control of spurious force oscillations. Journal of Computational Physics, 233: 295-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2012.08.044 [52] Leveque R J, Li Z. 1994. The immersed interface method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 31: 1019-1044. doi: 10.1137/0731054 [53] Li R, Xie C, Huang W X, et al. 2016. An efficient immersed boundary projection method for flow over complex/moving boundaries. Computers and Fluids, 140: 122-135. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2016.09.017 [54] Liang A, Jing X, Sun X. 2008. Constructing spectral schemes of the immersed interface method via a global description of discontinuous functions. Journal of Computational Physics, 227: 8341-8366. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2008.05.020 [55] Lima E Silva A L F, Silveira-Neto A, Damasceno J J R. 2003. Numerical simulation of two-dimensional flows over a circular cylinder using the immersed boundary method. Journal of Computational Physics, 189: 351-370. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00214-6 [56] Liu Q, Vasilyev O V. 2007. A brinkman penalization method for compressible flows in complex geometries. Journal of Computational Physics, 227: 946-966. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.07.037 [57] Ma M, Huang W X, Xu C, et al. 2021. A hybrid immersed boundary/wall-model approach for large-eddy simulation of high-reynolds-number turbulent flows. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 88: 108769. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2020.108769 [58] Ma M, Huang W X, Xu C. 2019. A dynamic wall model for large eddy simulation of turbulent flow over complex/moving boundaries based on the immersed boundary method. Physics of Fluids, 31: 115101. doi: 10.1063/1.5126853 [59] Mendelson L, Techet A H. 2021. Jumping archer fish exhibit multiple modes of fin–fin interaction. Bioinspiration and Biomimetics, 16: 016006. doi: 10.1088/1748-3190/abb78e [60] Mittal R, Dong H, Bozkurttas M, et al. 2008. A versatile sharp interface immersed boundary method for incompressible flows with complex boundaries. Journal of Computational Physics, 227: 4825-4852. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2008.01.028 [61] Mittal R, Iaccarino G. 2005. Immersed boundary methods. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 37: 239-261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.37.061903.175743 [62] Mochel L, Weiss P É, Deck S. 2014. Zonal immersed boundary conditions: application to a high-reynolds-number afterbody flow. AIAA Journal, 52: 2782-2794. doi: 10.2514/1.J052970 [63] Mohd Y J. 1997. Combined immersed-boundary/b-spline methods for simulations of flow in complex geometries. NASA ARS/Stanford University CTR, Stanford. [64] Ni J Y, Huang W X, Xu C X. 2023. Mode transition of a coupled rigid-flexible system in a uniform flow. Physics of Fluids, 35: 041706. doi: 10.1063/5.0147813 [65] Pan D, Deng J, Shao X, et al. 2016. On the propulsive performance of tandem flapping wings with a modified immersed boundary method. International Journal of Computational Methods, 13: 1650025. doi: 10.1142/S0219876216500250 [66] Park S G, Sung H J. 2018. Hydrodynamics of flexible fins propelled in tandem, diagonal, triangular and diamond configurations. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 840: 154-189. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2018.64 [67] Peng Z R, Huang H, Lu X Y. 2018. Hydrodynamic schooling of multiple self-propelled flapping plates. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 853: 587-600. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2018.634 [68] Peskin C S. 1972. Flow patterns around heart valves: a numerical method. Journal of Computational Physics, 10: 252-271. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(72)90065-4 [69] Peskin C S. 1977. Numerical analysis of blood flow in the heart. Journal of Computational Physics, 25: 220-252. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(77)90100-0 [70] Pu T M, Zhou C H. 2018. An immersed boundary/wall modeling method for RANS simulation of compressible turbulent flows. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 87: 217-238. doi: 10.1002/fld.4487 [71] Roma A M, Peskin C S, Berger M J. 1999. An adaptive version of the immersed boundary method. Journal of Computational Physics, 153: 509-534. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1999.6293 [72] Saiki E M, Biringen S. 1996. Numerical simulation of a cylinder in uniform flow: application of a virtual boundary method. Journal of Computational Physics, 123: 450-465. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1996.0036 [73] Seo J H, Mittal R. 2011. A high-order immersed boundary method for acoustic wave scattering and low-mach number flow-induced sound in complex geometries. Journal of Computational Physics, 230: 1000-1019. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2010.10.017 [74] Shi B, Yang X, Jin G, et al. 2019. Wall-modeling for large-eddy simulation of flows around an axisymmetric body using the diffuse-interface immersed boundary method. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 40: 305-320. doi: 10.1007/s10483-019-2425-6 [75] Sirovich L. 1967. Initial and boundary value problems in dissipative gas dynamics. Physics of Fluids, 10: 24. doi: 10.1063/1.1761987 [76] Slotnick J, Khodadoust A, Alonso J, et al. 2014. CFD vision 2030 study: a path to revolutionary computational aerosciences. NASA/CR: 218178. [77] Spalart P, Allmaras S. 1992. A one-equation turbulence model for aerodynamic flows. 30th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno: NV,USA. [78] Spalding D B. 1961. A single formula for the “law of the wall”. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 28: 455-458. doi: 10.1115/1.3641728 [79] Su S W, Lai M C, Lin C A. 2007. An immersed boundary technique for simulating complex flows with rigid boundary. Computers and Fluids, 36: 313-324. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2005.09.004 [80] Sun X, Jiang Y, Liang A, et al. 2012. An immersed boundary computational model for acoustic scattering problems with complex geometries. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 132: 3190-3199. doi: 10.1121/1.4757747 [81] Tamaki Y, Harada M, Imamura T. 2017. Near-wall modification of spalart–allmaras turbulence model for immersed boundary method. AIAA Journal, 55: 3027-3039. doi: 10.2514/1.J055824 [82] Taira K, Colonius T. 2007. The immersed boundary method: A projection approach. Journal of Computational Physics, 225: 2118-2137. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.03.005 [83] Tong W, Yang Y, Wang S. 2021. Estimating thrust from shedding vortex surfaces in the wake of a flapping plate. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 920: A10. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2021.434 [84] Trefethen L N. 1982. Group velocity in finite difference schemes. SIAM Review, 24: 113-136. doi: 10.1137/1024038 [85] Tseng Y H., Ferziger J H. 2003. A ghost-cell immersed boundary method for flow in complex geometry. Journal of Computational Physics, 192: 593-623. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2003.07.024 [86] Ubald B N, Watson R, Cui J, et al. 2021. Application of an immersed boundary method on an instrumented turbine blade with large eddy simulation. Journal of Turbomachinery, 143: 111005. doi: 10.1115/1.4051110 [87] Uddin E, Huang W X, Sung H J. 2015. Actively flapping tandem flexible flags in a viscous flow. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 780: 120-142. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2015.460 [88] Uhlmann M. 2005. An immersed boundary method with direct forcing for the simulation of particulate flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 209: 448-476. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2005.03.017 [89] Verzicco R. 2023. Immersed boundary methods: historical perspective and future outlook. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 55: 129-155. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-120720-022129 [90] Wang L, Xie C, Huang W X. 2020. A monolithic projection framework for constrained FSI problems with the immersed boundary method. Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering, 371: 113332. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113332 [91] Wang S, He G, Liu T. 2019. Estimating lift from wake velocity data in flapping flight. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 868: 501-537. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2019.181 [92] Wang S, Zhang X. 2011. An immersed boundary method based on discrete stream function formulation for two and three-dimensional incompressible flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 230: 3479-3499. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2011.01.045 [93] Wang S, Zhang X, He G, et al. 2014. Lift enhancement by dynamically changing wingspan in forward flapping flight. Physics of Fluids, 26: 061903. doi: 10.1063/1.4884130 [94] Wang W, Cao S. 2022. Numerical study of aerodynamic roles of bridge railings by immersed boundary method. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 228: 105111. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2022.105111 [95] Wang Z, Du L, Gao F, et al. 2023. Adaptive forcing distance in an immersed boundary method for internal flow simulation at high reynolds numbers. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 140: 44-63. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2023.03.020 [96] Wang Z, Du L, Sun X. 2020. Adaptive mesh refinement for simulating fluid-structure interaction using a sharp interface immersed boundary method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 92: 1890-1913. doi: 10.1002/fld.4853 [97] Wang Z J, Fidkowski K, Abgrall R, et al. 2013. High-order CFD methods: current status and perspective: high-order CFD methods. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 72: 811-845. doi: 10.1002/fld.3767 [98] Weihs D. 1973. Hydromechanics of fish schooling. Nature, 241: 290-291. doi: 10.1038/241290a0 [99] Weiss P É, Deck S. 2018. On the coupling of a zonal body-fitted/immersed boundary method with ZDES: application to the interactions on a realistic space launcher afterbody flow. Computers and Fluids, 176: 338-352. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2017.06.015 [100] Wong K W L, Zhao J, Lo J D, et al. 2018. Experimental investigation of flow-induced vibration of a sinusoidally rotating circular cylinder. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 848: 430-466. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2018.379 [101] Wu J, Shu C. 2009. Implicit velocity correction-based immersed boundary-lattice Boltzmann method and its applications. Journal of Computational Physics, 228: 1963-1979. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2008.11.019 [102] Xie F, Zheng H, Deng J, Zheng Y. 2019. Vortex induced vibration of a circular cylinder with a filament by using penalty immersed boundary method. Ocean Engineering, 186: 106078. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.05.060 [103] Xu S, Wang Z J. 2006a. Systematic derivation of jump conditions for the immersed interface method in three-dimensional flow simulation. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 27: 1948-1980. doi: 10.1137/040604960 [104] Xu S, Wang Z J. 2006b. An immersed interface method for simulating the interaction of a fluid with moving boundaries. Journal of Computational Physics, 216: 454-493. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2005.12.016 [105] Xu Y, Liu X. 2021. An immersed boundary method with y + adaptive wall function for smooth wall shear. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 93: 1929-1946. doi: 10.1002/fld.4960 [106] Yang L M, Shu C, Wang Y, et al. 2016. Development of discrete gas kinetic scheme for simulation of 3D viscous incompressible and compressible flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 319: 129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2016.05.018 [107] Yang L M, Shu C, Wu J. 2015. A three-dimensional explicit sphere function-based gas-kinetic flux solver for simulation of inviscid compressible flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 295: 322-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.03.058 [108] Yang L M, Shu C, Yang W M, et al. 2017. An immersed boundary-simplified sphere function-based gas kinetic scheme for simulation of 3D incompressible flows. Physics of Fluids, 29: 083605. doi: 10.1063/1.4997085 [109] Zhang D, Zhang J D, Huang W X. 2022a. Physical models and vortex dynamics of swimming and flying: a review. Acta Mechanica, 233: 1249-1288. doi: 10.1007/s00707-022-03192-9 [110] Zhang J D, Sung H J, Huang W X. 2022b. Hydrodynamic interaction of dorsal fin and caudal fin in swimming tuna. Bioinspiration and Biomimetics, 17: 066004. doi: 10.1088/1748-3190/ac84b8 [111] Zhang X, Gu X, Ma N. 2021. A ghost-cell immersed boundary method on preventing spurious oscillations for incompressible flows with a momentum interpolation method. Computers and Fluids, 220: 104871. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2021.104871 [112] Zhao E, Sun J, Tang Y, et al. 2020. Numerical investigation of tsunami wave impacts on different coastal bridge decks using immersed boundary method. Ocean Engineering, 201: 107132. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107132 [113] Zhong G, Sun X. 2009. New simulation strategy for an oscillating cascade in turbomachinery using immersed-boundary method. Journal Propulsion and Power, 25: 312-321. doi: 10.2514/1.35347 [114] Zhong X. 2007. A new high-order immersed interface method for solving elliptic equations with imbedded interface of discontinuity. Journal of Computational Physics, 225: 1066-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.01.017 -




 下载:
下载: