Progress in the analysis of debris cloud evolution: Fully based on probabilistic methods
-
摘要: 从碎片云的不确定性特征出发, 可以构建完全基于概率表征的碎片云演化分析方法. 用于对解体、演化和碰撞过程进行解析分析, 避免了数值方法计算效率低和结果鲁棒性差的问题.Abstract: In view of the intrinsic uncertainty of the debris cloud, a fully probabilistic framework of debris evolution is constructed. The breakup, evolution and collision of the debris cloud can be analyzed analytically, avoiding the problems of low computational efficiency and poor robustness of numerical methods.
-
Key words:
- space debris cloud /
- density /
- evolution
-
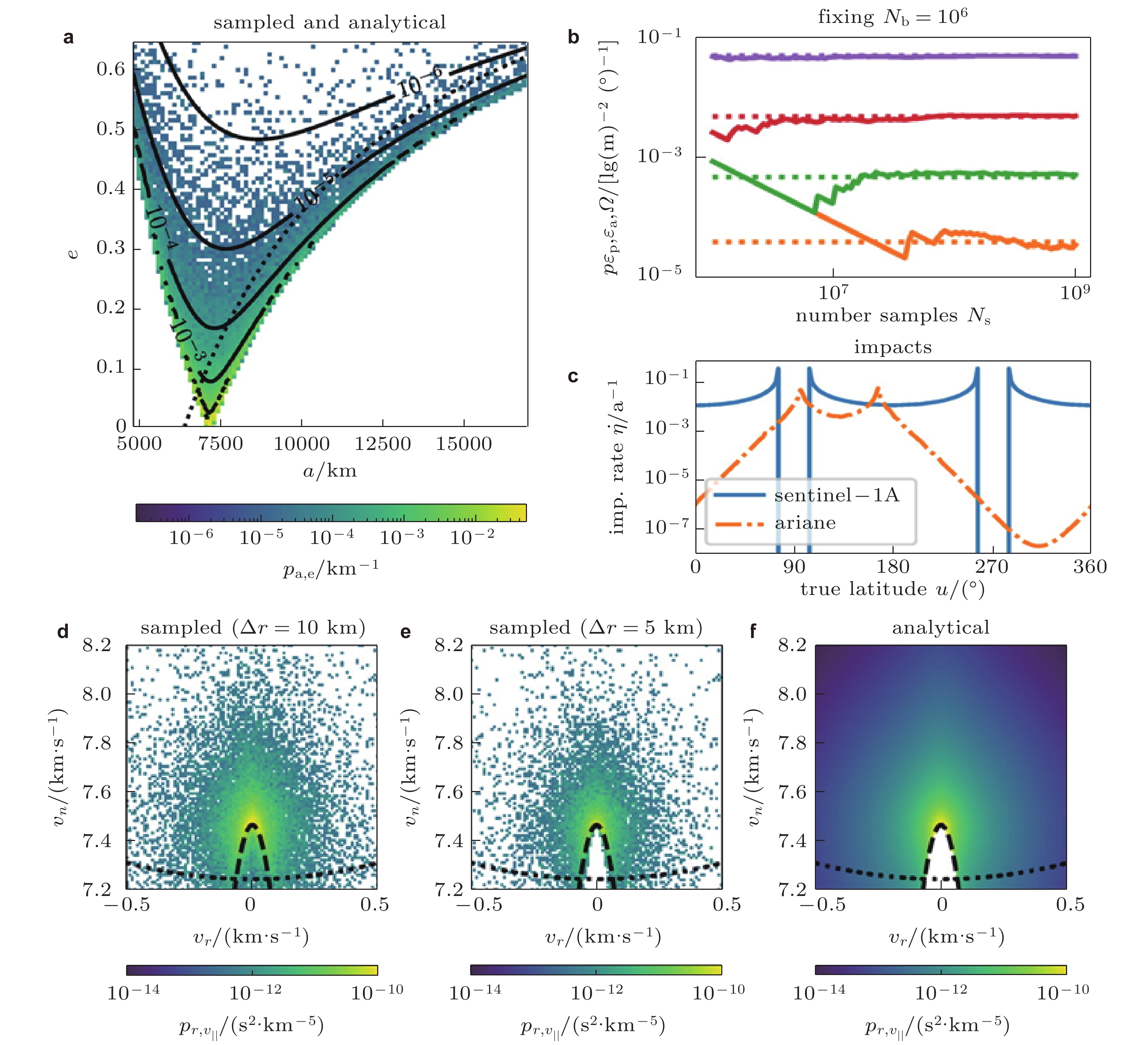
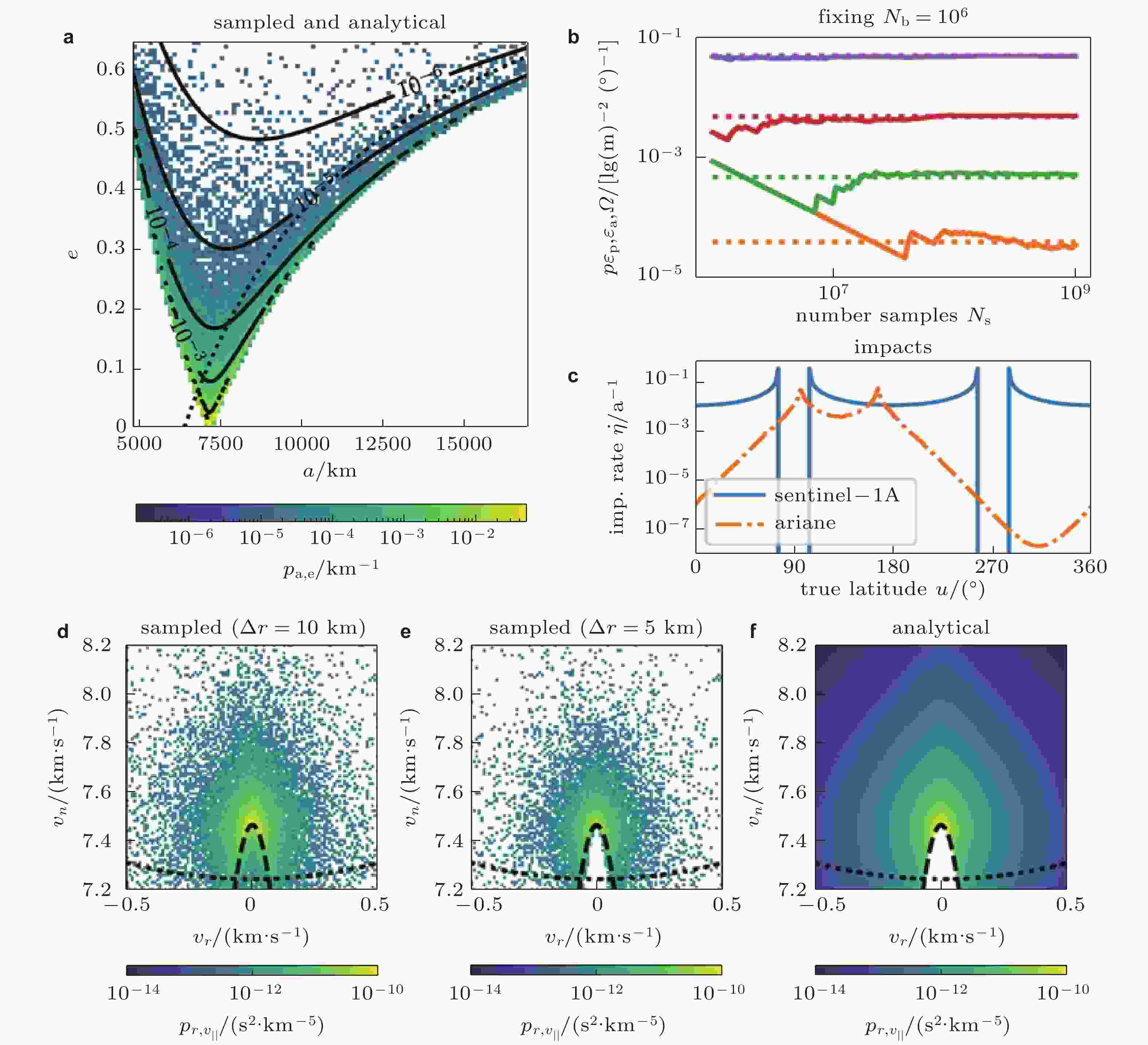
图 1 (a)分别通过采样法(颜色图)和解析法(等高线)得到的解体碎片半长轴与偏心率分布; (b)不同采样数量得到的概率密度(实线)与解析法(虚线)比较, 采样方法需要大量样本才能捕获小概率事件; (c)解体碎片云对空间目标的年碰撞率变化; (d) (e) (f) 碎片云在选定位置的速度分布 (Frey & Colombo 2021)
-
[1] Frey S, Colombo C. 2021. Transformation of satellite breakup distribution for probabilistic orbital collision hazard analysis. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 44: 88-105. doi: 10.2514/1.G004939 [2] Heard W B. 1976. Dispersion of ensembles of non-interacting particles. Astrophysics and Space Science, 43: 63-82. doi: 10.1007/BF00640556 [3] Jones B A, Doostan A, Born G H. 2013. Nonlinear propagation of orbit uncertainty using non-intrusive polynomial chaos. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 36: 430-444. doi: 10.2514/1.57599 [4] Letizia F. 2018. Extension of the density approach for debris cloud propagation. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 41: 2651-2657. doi: 10.2514/1.G003675 [5] Letizia F, Colombo C, Lewis H G. 2015. Analytical model for the propagation of small-debris-object clouds after fragmentations. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 38: 1478-1491. doi: 10.2514/1.G000695 [6] Letizia F, Colombo C, Lewis H G. 2016. Collision probability due to space debris clouds through a continuum approach. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 39: 2240-2249. doi: 10.2514/1.G001382 [7] Liou J-C. 2008. A statistical analysis of the future debris environment. Acta Astronautica, 62: 264-271. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2006.12.030 [8] Liou J-C, Hall D T, Krisko P H, et al. 2004. LEGEND – a three-dimensional LEO-to-GEO debris evolutionary model. Advances in Space Research, 34: 981-986. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.02.027 [9] Liou J-C, Johnson N L. 2006. Risks in space from orbiting debris. Science, 311: 340-341. doi: 10.1126/science.1121337 [10] Luo Y, Yang Z. 2017. A review of uncertainty propagation in orbital mechanics. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 89: 23-39. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2016.12.002 [11] Mcinnes C R. 1993. An analytical model for the catastrophic production of orbital debris. ESA Journal, 17: 293-305. [12] Walker R, Martin C E, Stokes P H, et al. 2001. Analysis of the effectiveness of space debris mitigation measures using the delta model. Advances in Space Research, 28: 1437-1445. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(01)00445-8 [13] Wittig A, Di Lizia P, Armellin R, et al. 2015. Propagation of large uncertainty sets in orbital dynamics by automatic domain splitting. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, 122: 239-261. doi: 10.1007/s10569-015-9618-3 [14] Yang Z, Luo Y-Z, Zhang J, et al. 2016. Uncertainty quantification for short rendezvous missions using a nonlinear covariance propagation method. Journal of Guidance Control and Dynamics, 39: 2170-2178. doi: 10.2514/1.G001712 -




 下载:
下载: