-
摘要: 数智力学意指可驾驭数智时代的力学. 本文将数智力学定义为: 探讨物理空间、信息空间、认知空间的自身与相互之间的作用机理, 并表达为因果性或关联性的规律. 文中列出了数智力学所面临的8个科学问题, 并给出在X-4范式四面体中探讨数智力学的7条方法论路径. 文中展述了当前可推动数智力学研究的5个研究方向, 分别为: 数智力学框架、智柔体力学、数智融合计算、交叉尺度力学、具身智能力学.Abstract: Digintel mechanics refers to the mechanics studies that would govern the scientific rules for the digintel era, with digintel abbreviates the combination of digital and intelligence. Digintel mechanics is defined herein as the exploration for the mechanisms concerning the interactions, both within and between, physical space, cyber space and cognition space, and as the revelation of causation or/and correlation laws. Eight basic scientific issues concerning digintel mechanics are listed. Attention is then focused on 7 routes of methodologies confined in the X-4 tetrahedron. Five research thrusts suitable for the preliminary development of digintel mechanics are enumerated, they are digintel mechanics formalism, mechanics of intelligent flexors, convergent digintel computation, cross-scale mechanics, and mechanics for embodied intelligence.
-
Key words:
- digintel mechanics /
- X-4 paradigm /
- intelligent flexors /
- digintel convergence
-
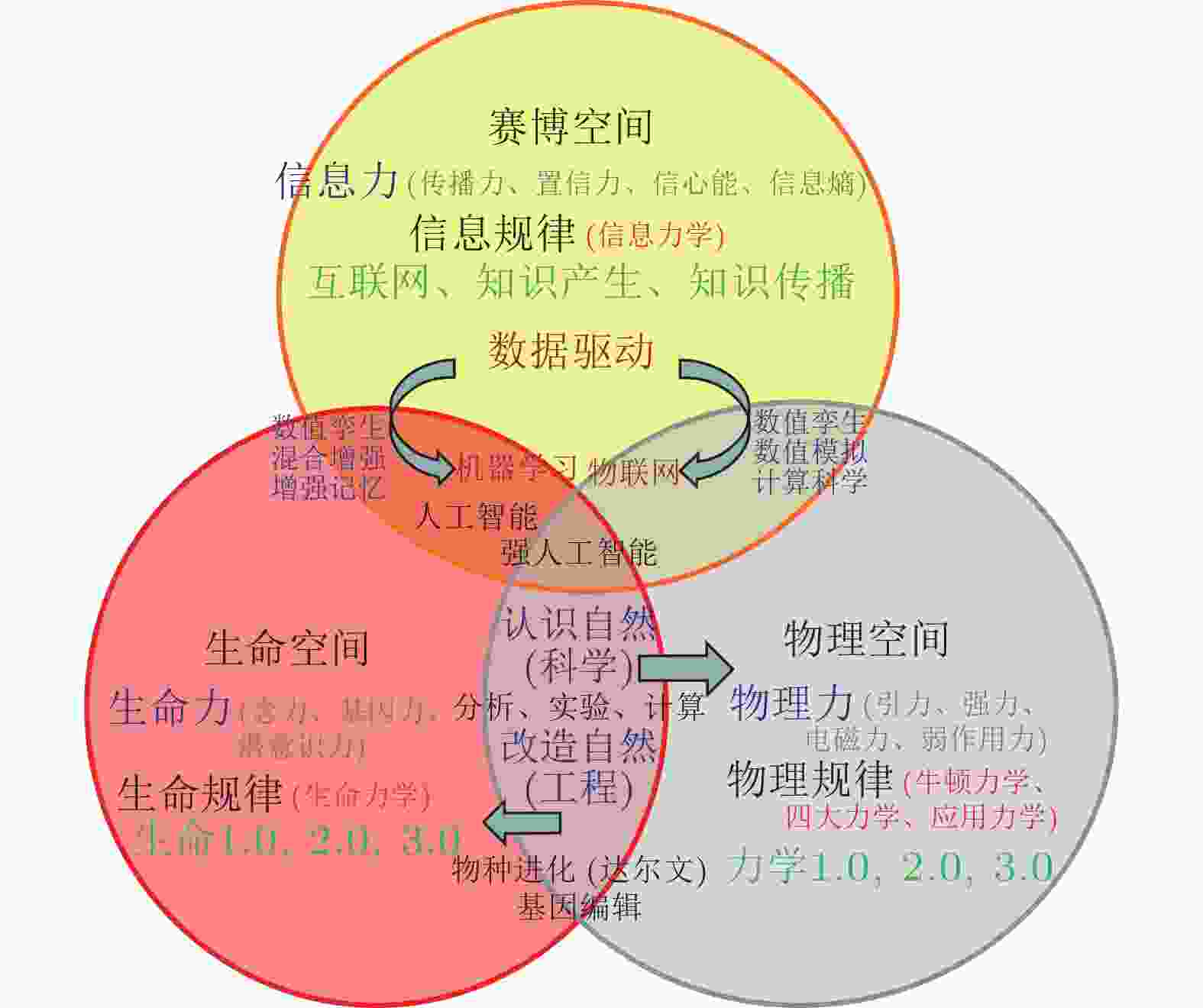
图 1 物理空间、信息空间与生命空间 (杨卫 2024)
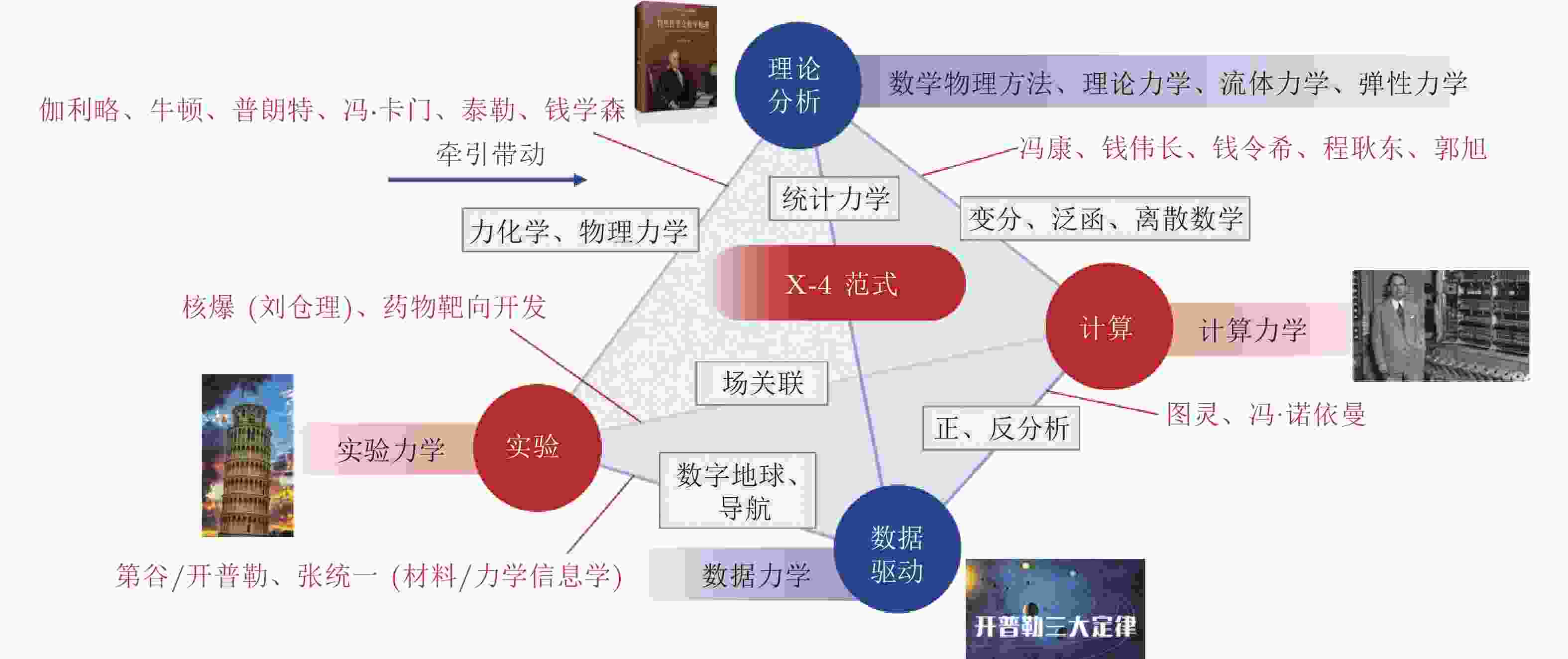
图 2 X-4范式(杨卫和赵沛 2024a)
-
[1] 牛顿. 2018. 自然哲学之数学原理 (王克迪译). 北京: 北京大学出版社 (原著出版于1687年).原著出版于1687年 [2] 托马斯·库恩. 2012. 科学革命的结构(伊安·哈金导读, 金吾伦和胡新和译). 北京: 北京大学出版社 (原著出版于1962年).原著出版于1962年 [3] 王鹏, 孙升, 张庆, 张统一. 2019. 力学信息学简介. 自然杂志, 40(5): 313-322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2019.05.001 [4] 杨卫. 2024. 力学基本问题. 北京: 科学出版社. [5] 杨卫, 赵沛. 2024a. 范式融合导向的数智时代力学专业核心课程. 力学与实践, doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-24-452. [6] 杨卫, 赵沛. 2024b. 基础学科领域本科教育教学改革试点工作—力学“101计划”. 力学与实践, doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-24-451. [7] Gao H, Ji B, Jager I L, et al. 2003. Materials become insensitive to flaws at nanoscale: Lessons from nature. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(10): 5597-5600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0631609100 [8] He G, Jin G, Yang Y. 2017. Space-time correlations and dynamic coupling in turbulent flows. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 49: 51-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-010816-060309 [9] Huang M C, Liu C, Guo Y L, et al. 2024. A mechanics-based data-free problem independent machine learning (PIML) model for large-scale structural analysis and design optimization. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 193: 105893. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2024.105893 [10] Jin Y B, Liu X W, Shao Y C, et al. 2022. High-speed quadrupedal locomotion by imitation-relaxation reinforcement learning. Nature Machine Intelligence, 4(12): 1198-1208. doi: 10.1038/s42256-022-00576-3 [11] Karapiperis K, Stainier L, Ortiz M, et al. 2021. Data-driven multiscale modeling in mechanics. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 147: 104239. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2020.104239 [12] Kepler J. 1622. Summary of copernican astronomy. Austria: Johann Planck. [13] Kepler J. 1997. The harmony of the world (Aiton E J, Duncan A M, Field J V Trans). Pennsylvania: American Philosophical Society. (Original work published 1619). [14] Meng Z Y, Zhong J R, Xu S B, et al. 2024. Simulating unsteady flows on a superconducting quantum processor. Communications Physics, 7(1): 349. doi: 10.1038/s42005-024-01845-w [15] Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis G E. 2019. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. Journal of Computational Physics, 378: 686-707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [16] Raissi M, Yazdani A, Karniadakis G E. 2020. Hidden fluid mechanics: Learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations. Science, 367(6481): 1026-1030. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw4741 [17] Shen W, Yao J, Yang Y. 2024. Designing turbulence with entangled vortices. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 121 (35): e2405351121. [18] Zhao Q, Zhu Q, Zhang Z, Yin B, Gao H, Zhou H. 2024. A machine learning–based framework for mapping hydrogen at the atomic scale. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 121 (39): e2410968121. -




 下载:
下载: