-
摘要: 细胞膜是细胞与外部环境进行物质与能量交换的界面, 是调节细胞正常生命活动的重要结构基础. 细胞膜上力敏感受体可通过力学作用方式参与并影响细胞的力信号转导等功能. 整合素和钙黏素是细胞膜上典型的力敏感受体, 可介导细胞与细胞周围基质或邻近细胞发生力学作用, 并将力学刺激信号转导为生化信号, 进而激活细胞内一系列应答反应, 最终影响细胞生长、分化、增殖、凋亡和迁移等功能. 力敏感受体介导细胞功能调控研究已成为探索细胞主动响应外界复杂力学微环境的力学生物学机制的关键, 为进一步深入认识生理和病理状态下细胞功能变化规律, 为揭示疾病的发生、发展机制提供重要的力学生物学理论与实验依据. 本文总结了力敏感受体介导细胞功能调控的国内外研究进展; 介绍了黏附界面处典型力敏感受体的结构和功能; 总结了这些力敏感受体参与的细胞力信号感知与响应的数理模型; 概述了细胞通过力敏感受体进行力学信号转导的过程; 介绍了黏附介导细胞功能调控的力学生物学过程和机制; 简述了体外构建模拟细胞力学微环境中细胞−细胞外基质和细胞−细胞力学相互作用的技术; 指出了力敏感受体介导细胞功能调控的力学生物学研究发展趋势和未来方向.Abstract: As the interface between cells and their external environment for materials and energy exchange, the cell membrane is an important structure that regulates cellular activities. Representative transmembrane force-sensitive receptors, such as integrins and cadherins, are found to play key roles in mediating cellular interactions with the ECM or adjacent cells. These interactions will then transduce mechanical stimuli into biochemical signals, which in turn activate a series of intracellular signaling cascade, and ultimately affect cell growth, differentiation, proliferation, migration and apoptosis etc. The investigation of cellular mechanobiology regulated by force-sensitive adhesion receptors has thus become the key to explore the mechanobiological mechanisms of cellular actively in response to complex mechanical microenvironments. This provides valuable theoretical and experimental basis for further understanding of the changes in cell functions under physiological and pathological conditions, as well as for revealing the mechanism of disease development. This review summarizes the cutting-edge progresses in cellular mechanobiology regulated force-sensitive adhesion receptors. This review begins by introducing the structure and function of force-sensitive receptors at the adhesion interface, and followed by elaborating systematic mathematical models of how cells sense and respond to mechanical signals mediated by these receptors. It also outlines the processes of mechanical signal transduction through force-sensitive receptors, and the mechanobiological mechanism of adhesion-mediated changes in cell functions. In addition, the techniques for constructing of in vitro mechanical microenvironment that mimic cell-ECM (via integrin ligation) and cell-cell (via cadherin ligation) interactions are described. Finally, we identify the future directions of mechanobiology in terms of force-sensitive receptors regulated cell functions.
-
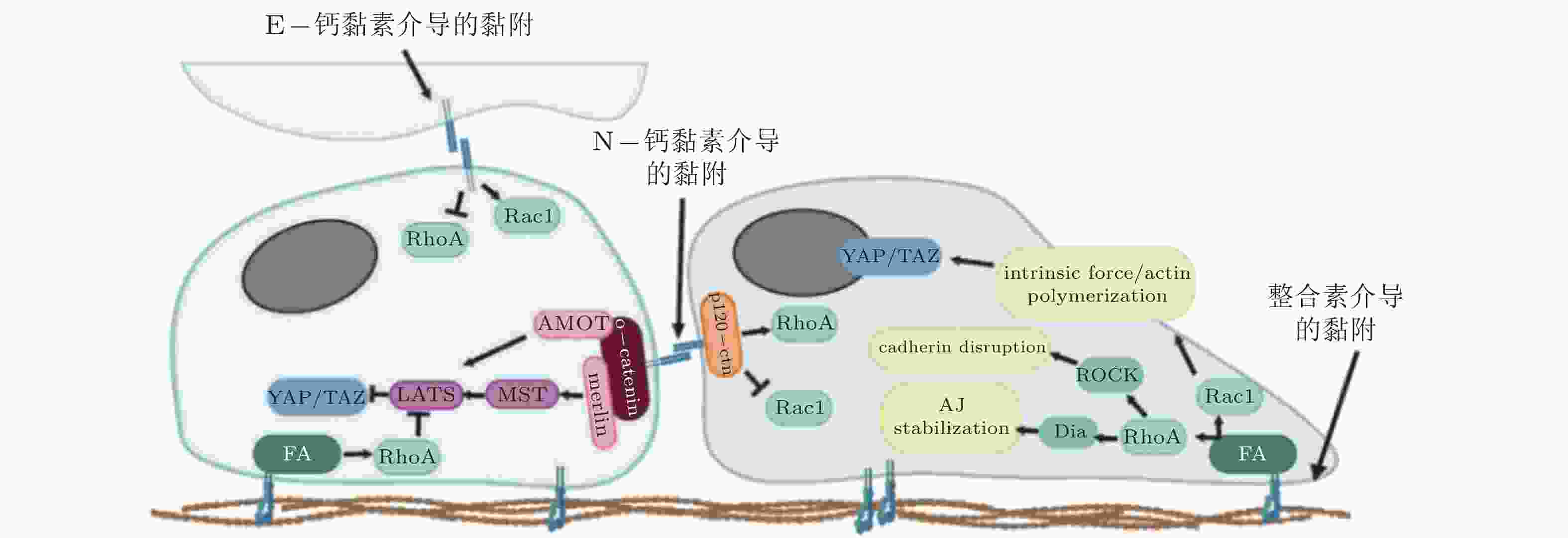
图 3 整合素和钙黏素介导的黏附相互作用之间的串扰(Barcelona-Estaje et al. 2021)
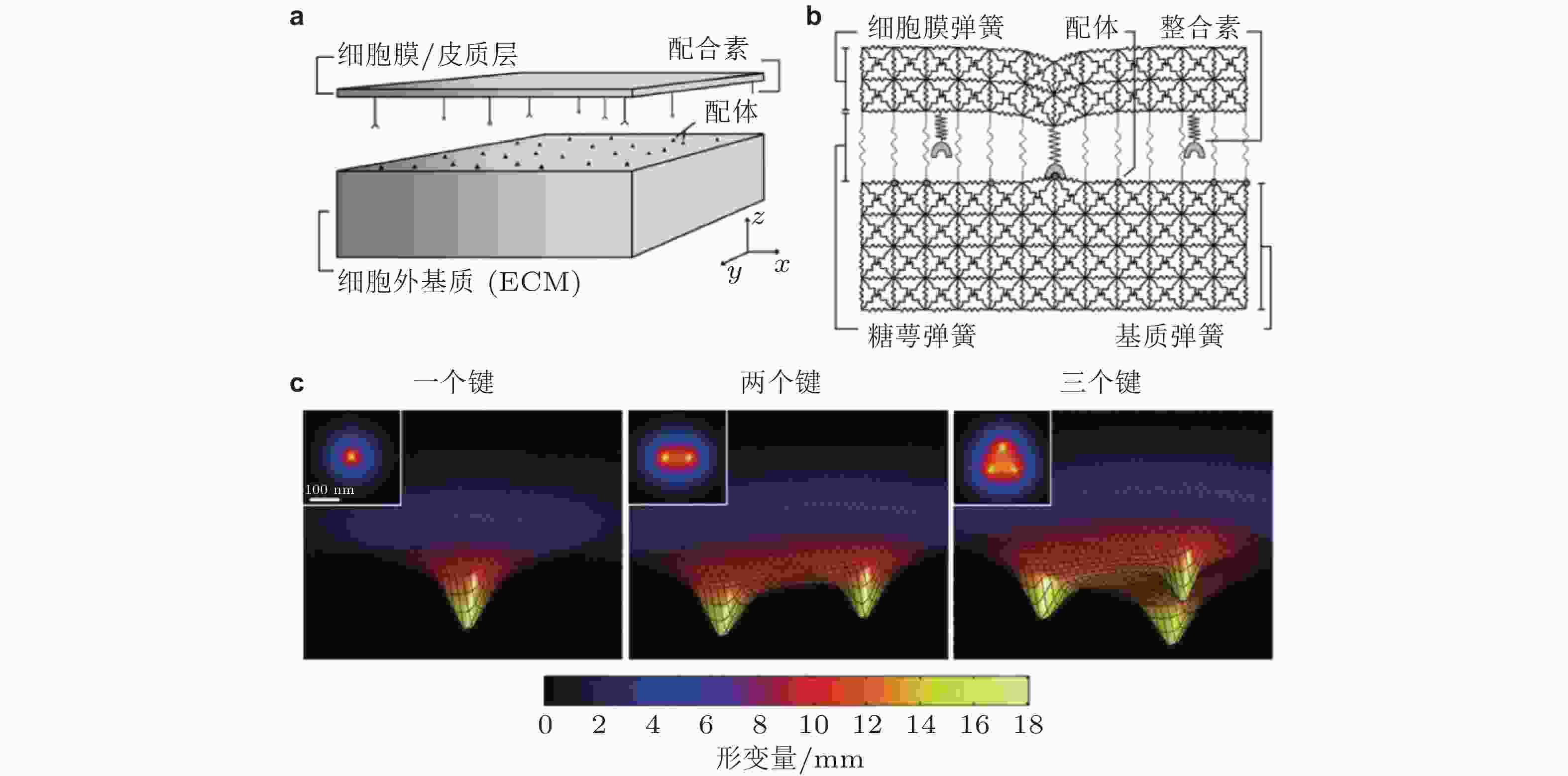
图 4 整合素-配体结合的LSM模型示意图(Paszek et al. 2009). (a) Cell-ECM界面. 整合素和配体分别分布在代表细胞膜和ECM的两平板表面; (b) 格子弹簧模型 (LSM) , 整合素-配体键由弹簧连接来表示; (c) 形成1,2,3个整合素-配体键引起的膜变形云图, 插图为对应的俯视图; 当更多的键形成时, 膜与ECM表面将更为接近
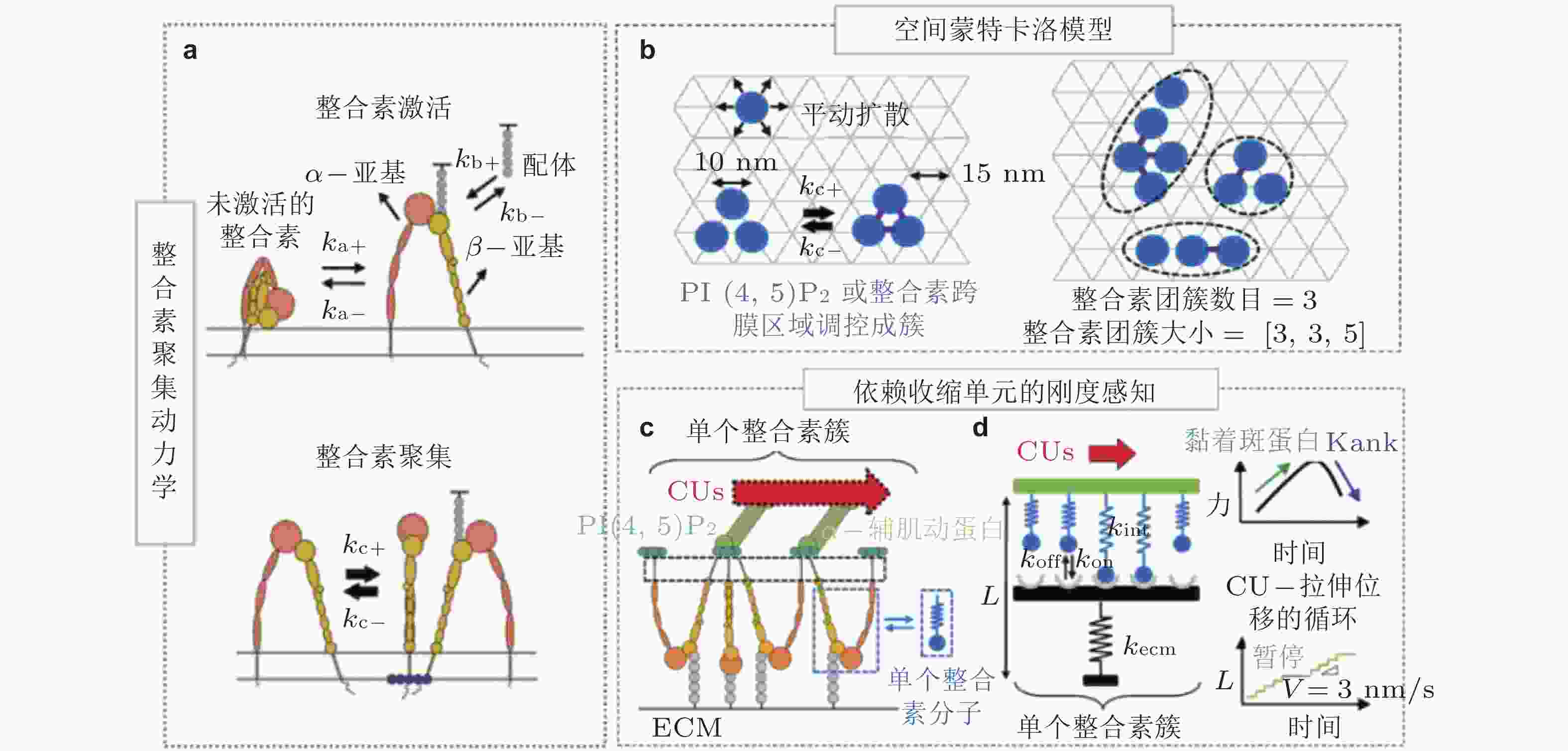
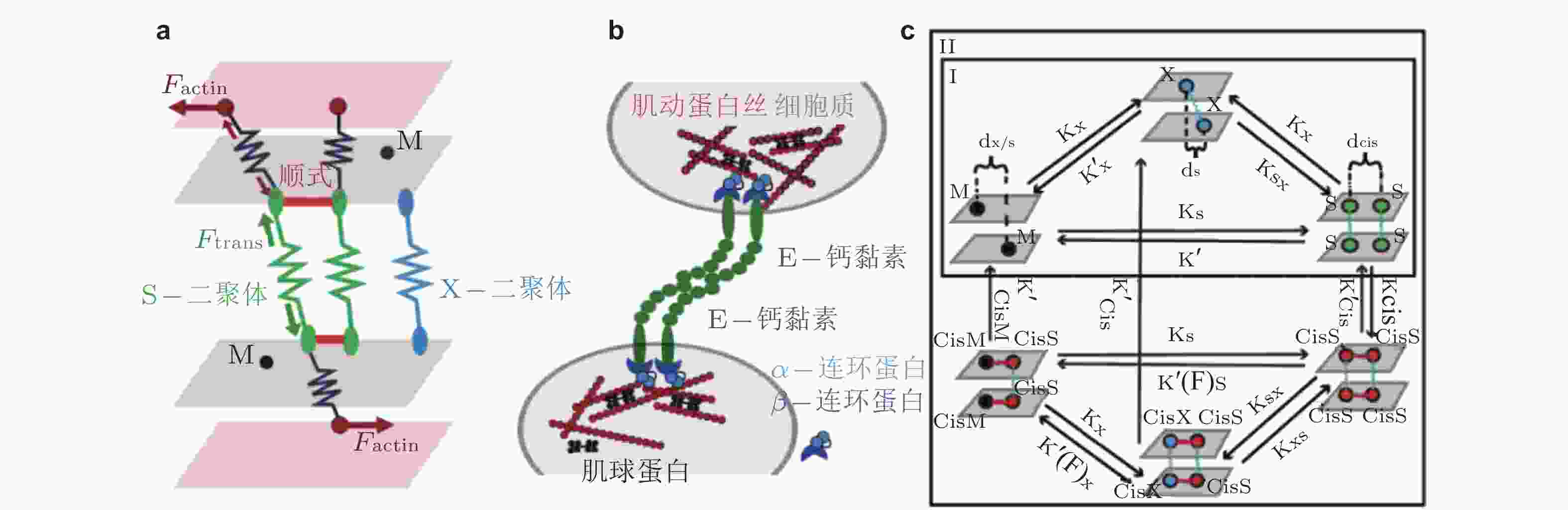
图 5 整合素聚集与力致解离模型(Cheng et al. 2020). (a) 细胞膜上的整合素聚集动力学, 整合素具有激活/失活两种状态. 踝蛋白头部域可促进整合素的激活, 激活的整合素可以通过PI(4,5)P2或整合素跨膜区域产生聚集, (b) 整合素聚集的二维空间蒙特卡洛模型, 考虑了整合素在质膜上的激活和失活、扩散和聚集, (c) 整合素可以结合胞外ECM和细胞内基于肌球蛋白的类肌节收缩单位(CUs), (d) 将整合素聚集体所黏附的ECM建模为弹簧, 将整合素聚集体-ECM的力学作用建模为CU在位移边界条件下拉伸的逆锁/滑移键为滑移键断裂速率;
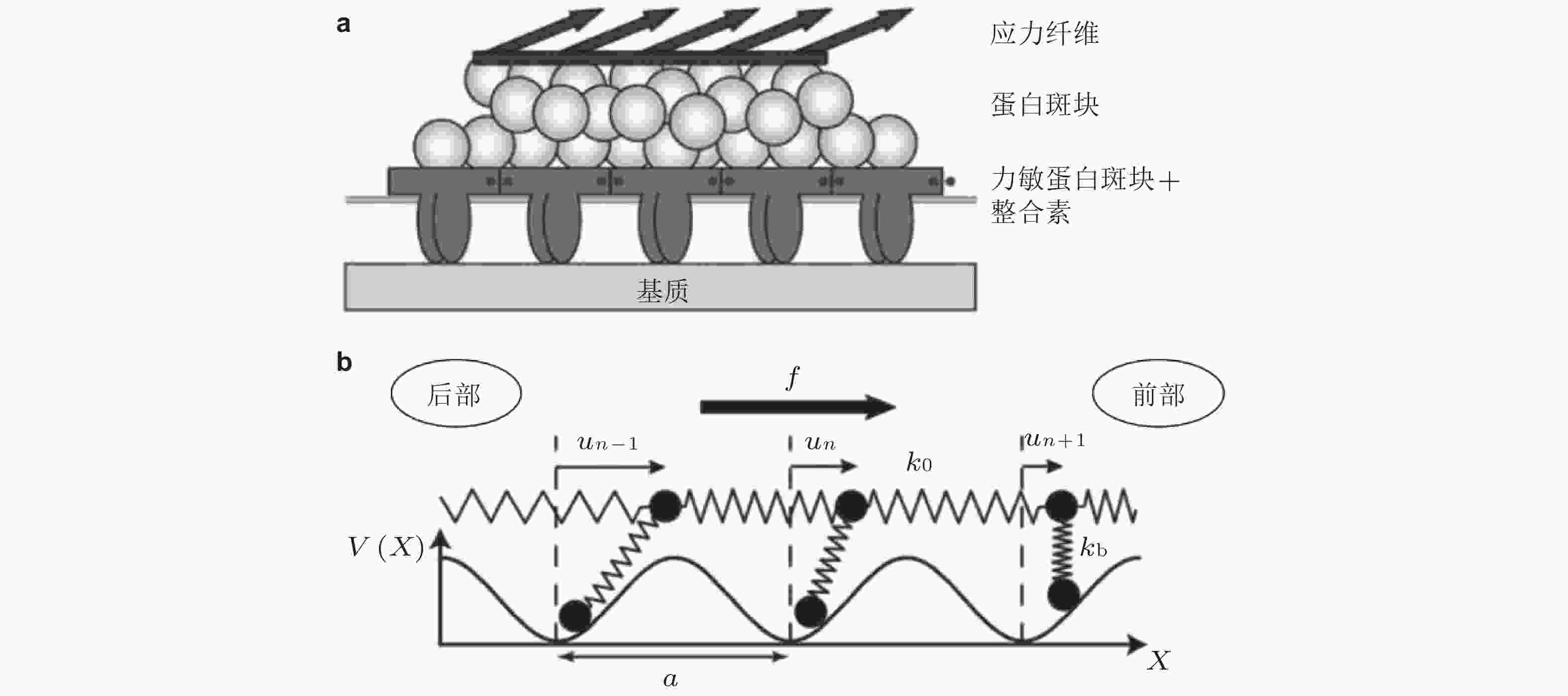
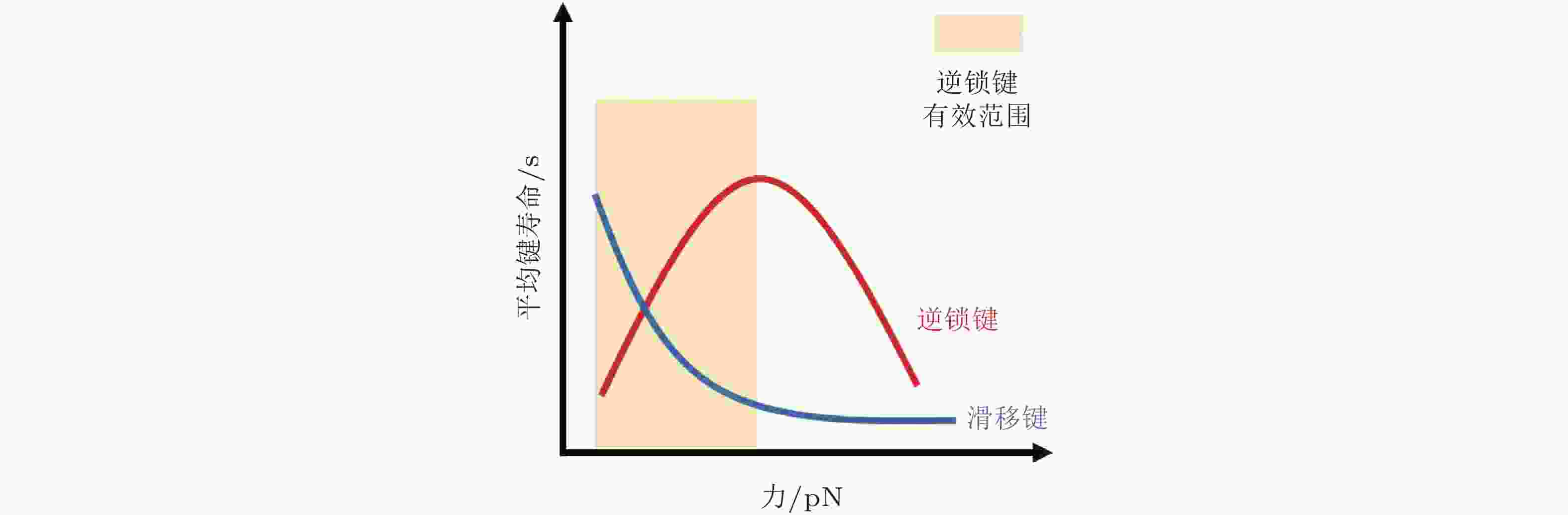
$ {k}_{b} $ (s−1) 为逆锁键断裂速率;$ {F}_{a} $ (pN) 为滑移键特征断裂力;$ {F}_{b} $ (pN) 为逆锁键特征断裂力. 在较低的分子键张力范围内 (小于20 pN) , 逆锁键占主导地位, 解离速率随力的增加而降低; 而在较大的分子键张力范围内 (大于25 pN) , 滑移键占主导地位, 解离速率随力的增加而增加图 6 黏着斑各向异性生长的线性弹簧链模型. (a) 黏着斑(FAs)的结构示意图. 上层、中层、下层分别为相连的应力纤维, 蛋白斑块以及力敏感的斑块蛋白与整合素结合体(Besser & Safran 2006), (b) 一维黏附弹簧链模型(Nicolas et al. 2004). 力敏蛋白与ECM的锚定连接用正弦势函数V(x)表示, 锚点之间的距离a (nm) 为整合素间距, un (nm) 为第n个粒子在无力情况下的位移
图 7 二维黏附分子模型示意图(Walcott et al. 2011). 每个分子可以与其相邻分子形成四个横向键, 可以通过柔性域与表面结合, 并且可以以两种状态存在
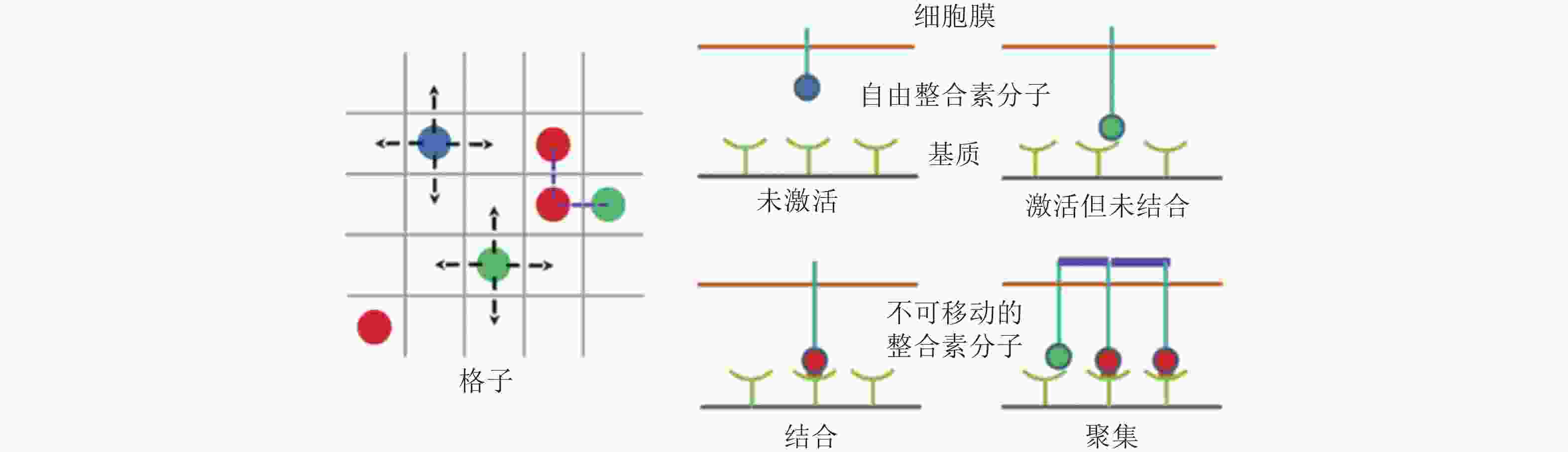
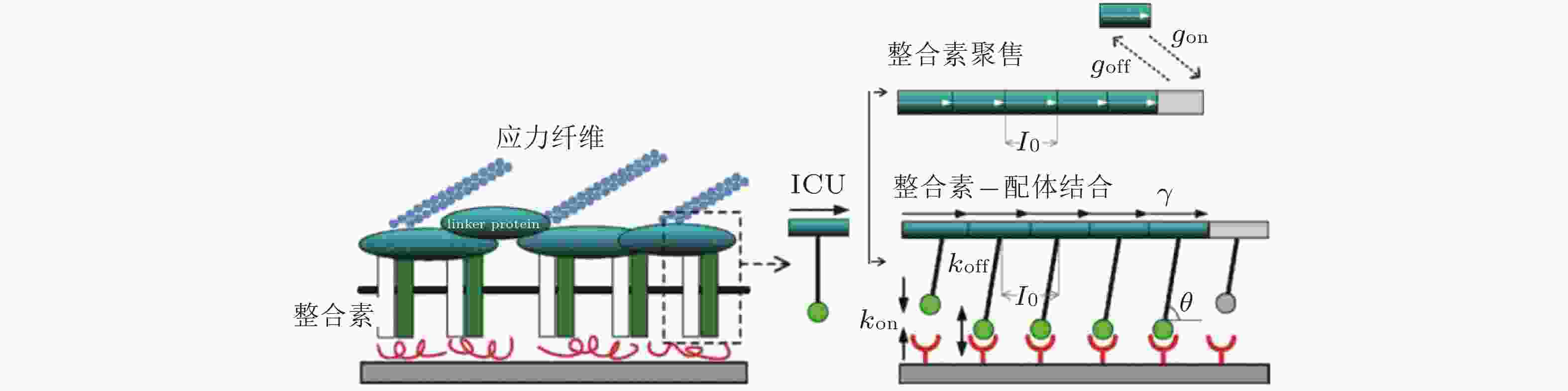
图 8 整合素聚集过程的4种状态示意图(Peng et al. 2012). 用蓝色、绿色、红色的实心圆分别表示未激活、激活但未结合配体和已结合配体的整合素分子; 左图为俯视图, 箭头所指为自由的整合素分子可能扩散的位置, 而已结合的整合素则固定在原位; 右图为整合素在聚集过程中的4种状态, 聚集的整合素由踝蛋白 (紫色短线) 连接
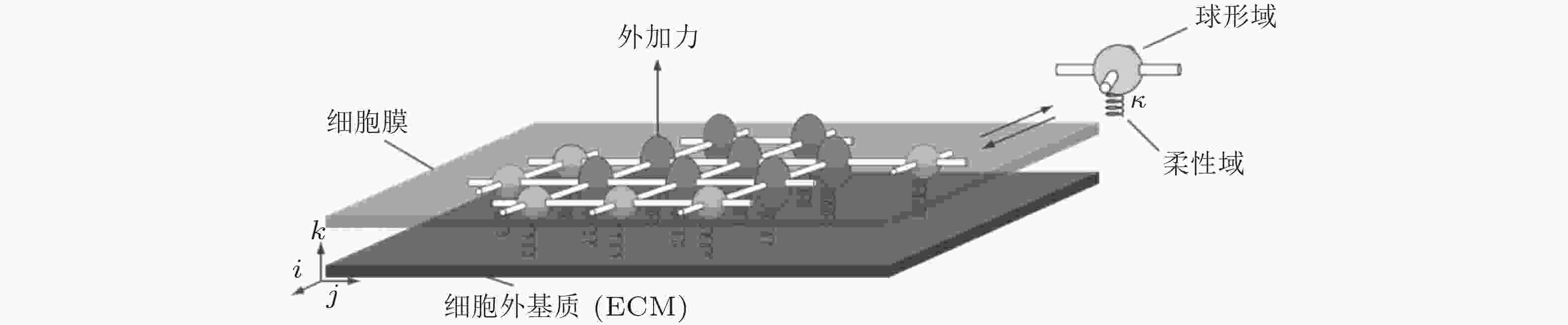
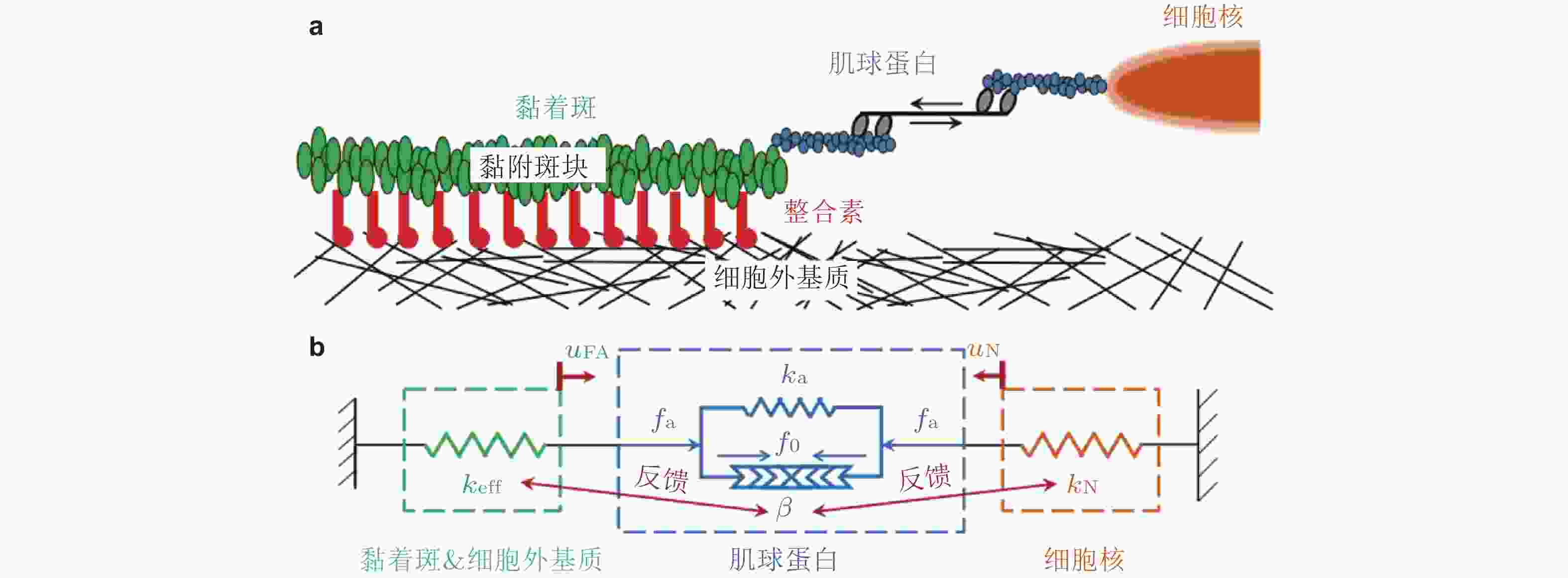
图 9 基质/核刚度调节黏着斑尺寸的力-化耦合模型(Cao et al. 2015). (a) 细胞-ECM黏附示意图, (b) ECM&黏着斑-肌球蛋白-细胞核结构的简化模型
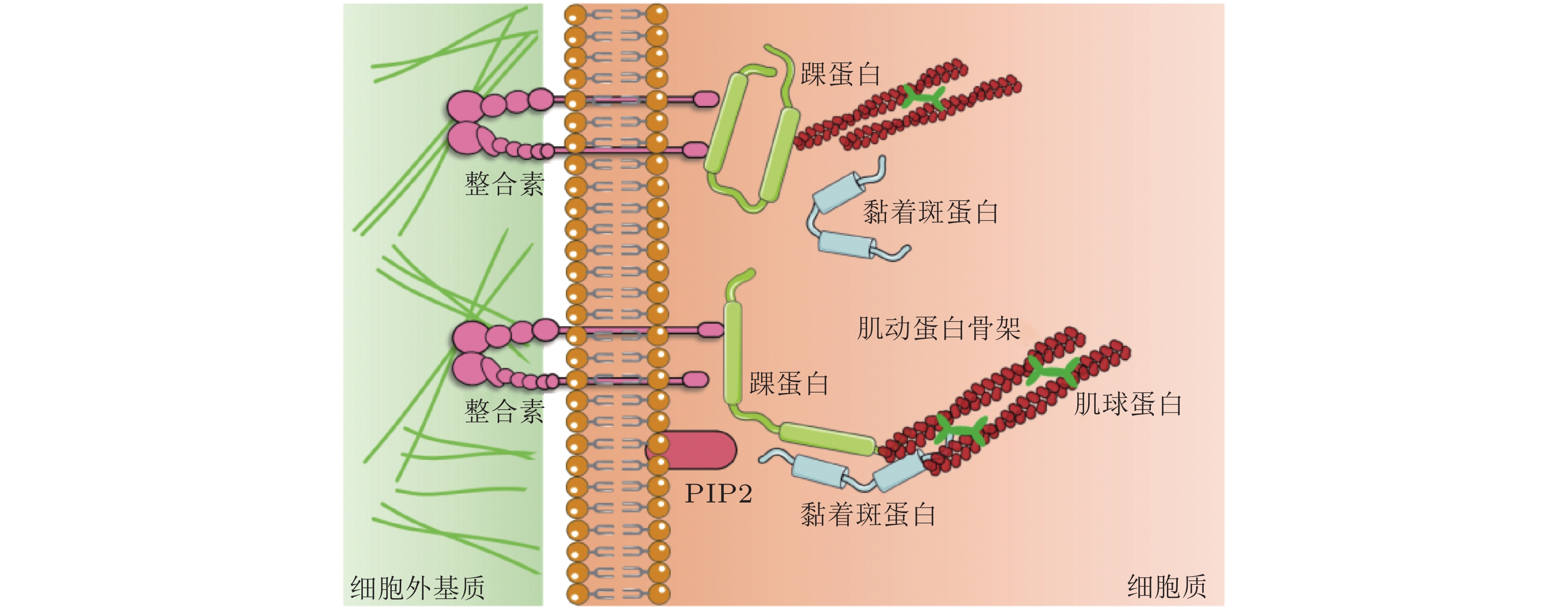
图 10 黏着斑的微观结构示意图(Kong et al. 2010). 整合素的内部结构域通过衔接蛋白(如黏着斑蛋白和踝蛋白)黏附在肌动蛋白应力纤维上, 而外部结构域与配体结合, 在细胞和基质之间形成整合素-配体分子键. 虚线矩形表示与相关衔接蛋白结合的整合素, 将其整体建模为整合素复合单元(ICU); 右上为ICU与黏着斑的结合或分离示意图; 右下为整合素-配体键的形成和断裂示意图
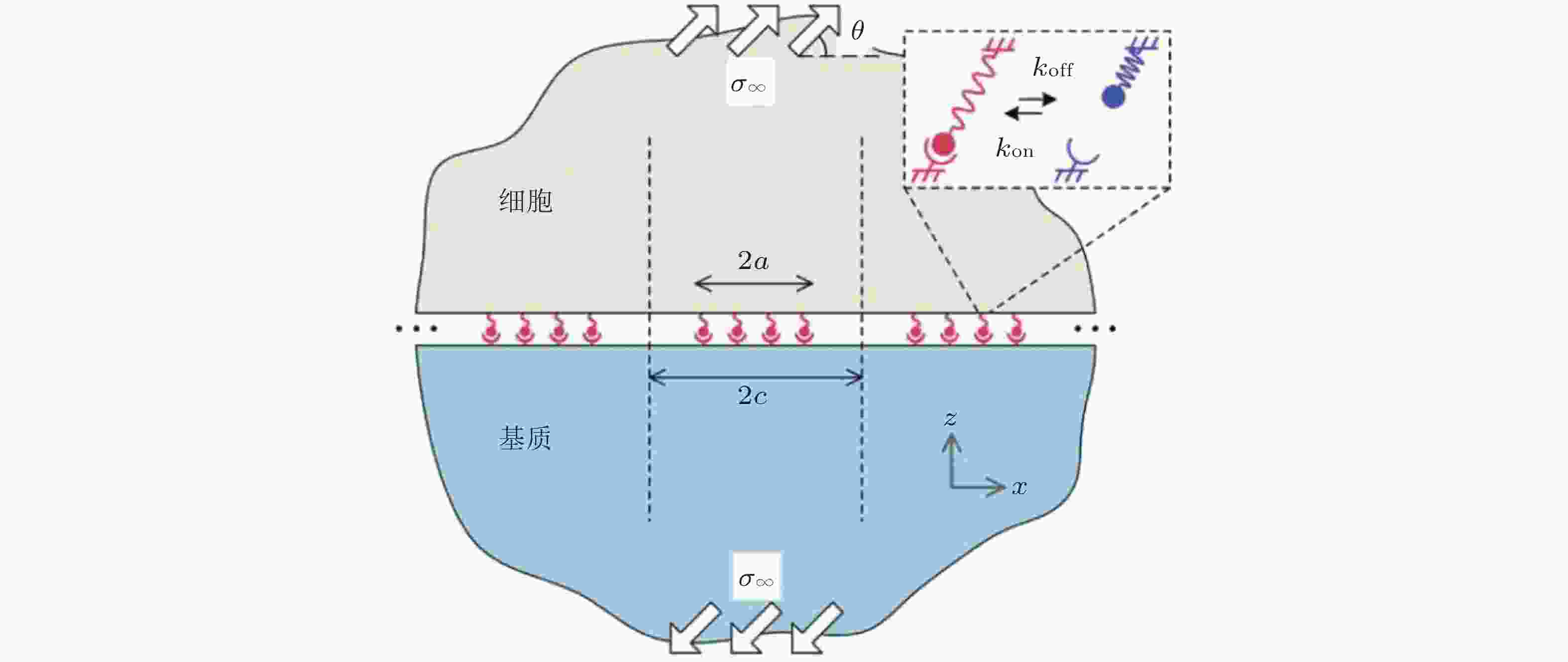
图 11 在倾斜牵拉应力作用下, 两种不同弹性介质间黏附分子键的周期性排列示意图(Qian et al. 2008)
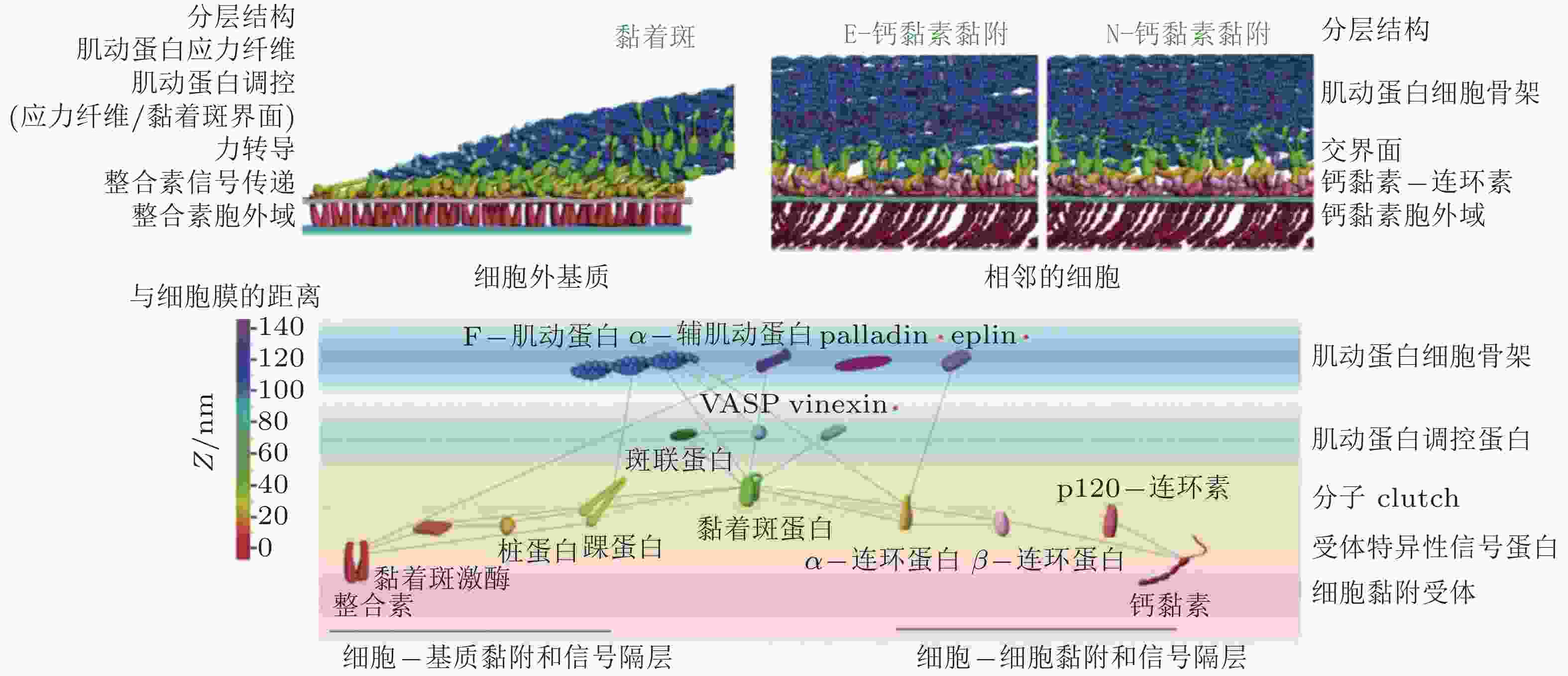
图 12 细胞黏附复合物的纳米尺度结构(Xia & Kanchanawong 2017)
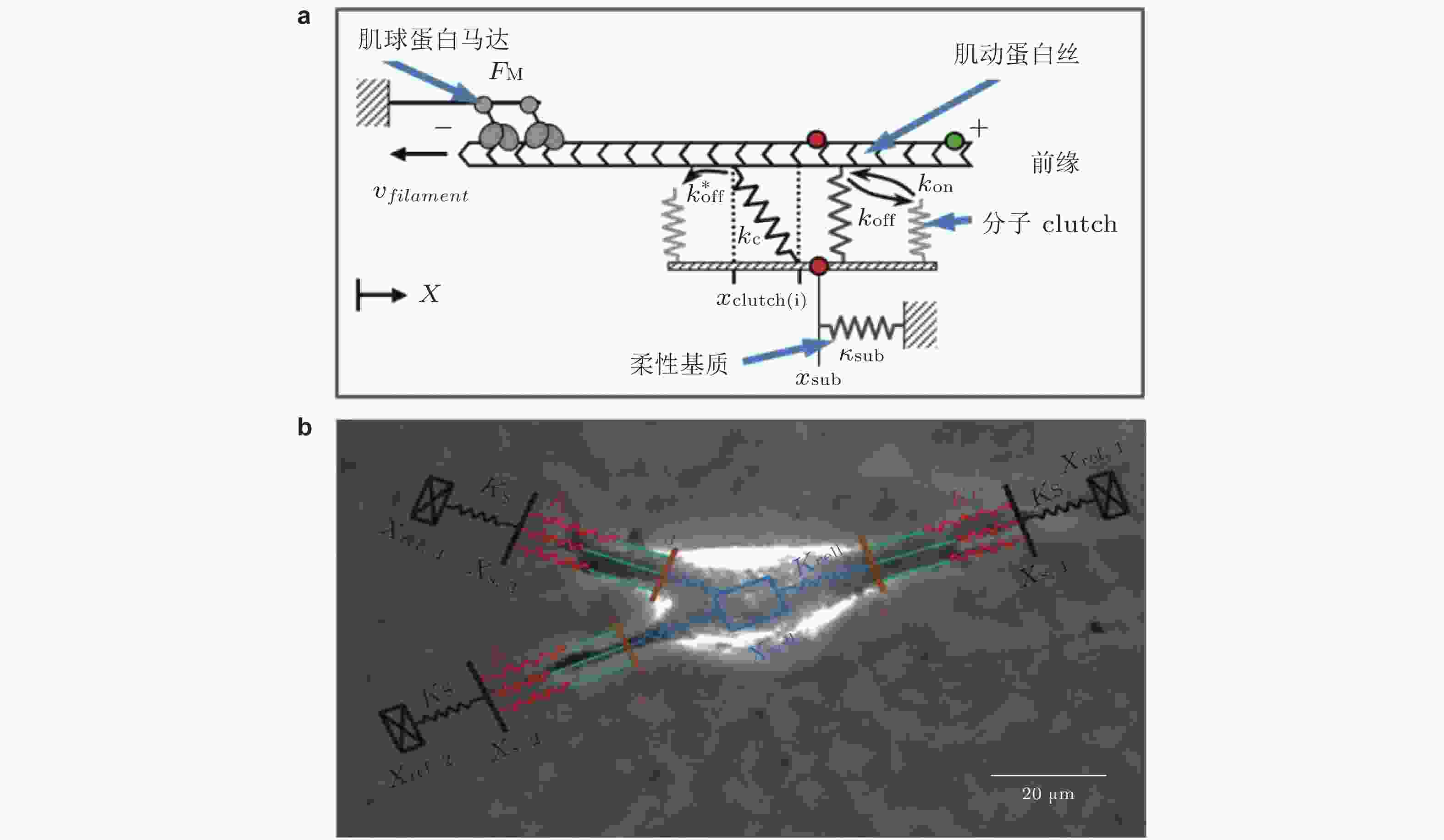
图 13 Motor-Clutch模型. (a) 弹性基质上黏附细胞的刚度感知机制示意图模型(Chan & Odde 2008). 肌球蛋白马达以相当的速度和力将肌动蛋白丝 (F-actin) 拉向左侧 (细胞中心) ; Clutch可逆地与肌动蛋白丝结合/解离, 以抑制向细胞中心方向的回退流, (b) 细胞迁移模型的示意图(Bangasser et al. 2017). 用“Motor-Clutch”模块来等效细胞伪足的功能, 多个模块共同作用以实现迁移行为
图 14 考虑黏附增强的“Motor-Clutch”模型(Elosegui-Artola et al. 2016). (a)当Clutch以速率
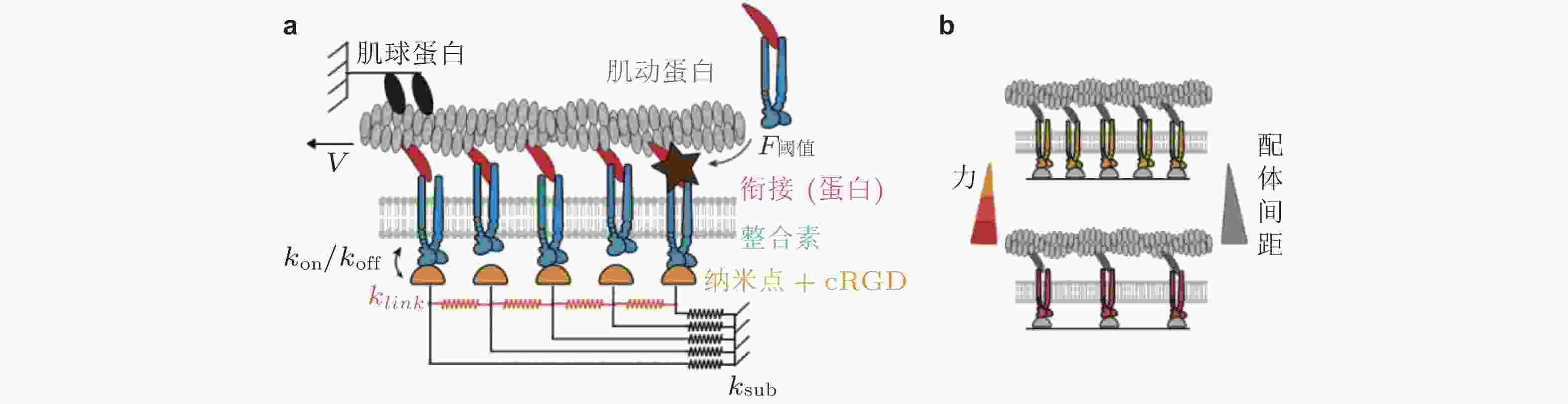
$ {k}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}} $ (s−1) 与基质结合, 随着肌球蛋白收缩, 力逐渐加载到踝蛋白, 打开了其隐藏的黏着斑蛋白结合位点, 并导致其招募黏着斑蛋白, 从而实现黏附增强, (b)顶部为踝蛋白结构是否解折叠而决定两种力-刚度关系的机制示意图, 下部为对应的数据结果: 实验结果 (点) 与有/无踝蛋白展开的模型预测结果对比(实线); 蓝/红线表示有/无黏附增强时, 模型预测的牵张力-刚度关系图 15 配体间距与黏附增强的Motor-Clutch模型(Oria et al. 2017). (a) 通过在每个Clutch中设置张力阈值来引入力学敏感性, 当分子键张力超过阈值时, 会触发进一步的整合素招募 (暗棕星) . 弹性基质由连接配体到基质的弹簧 (
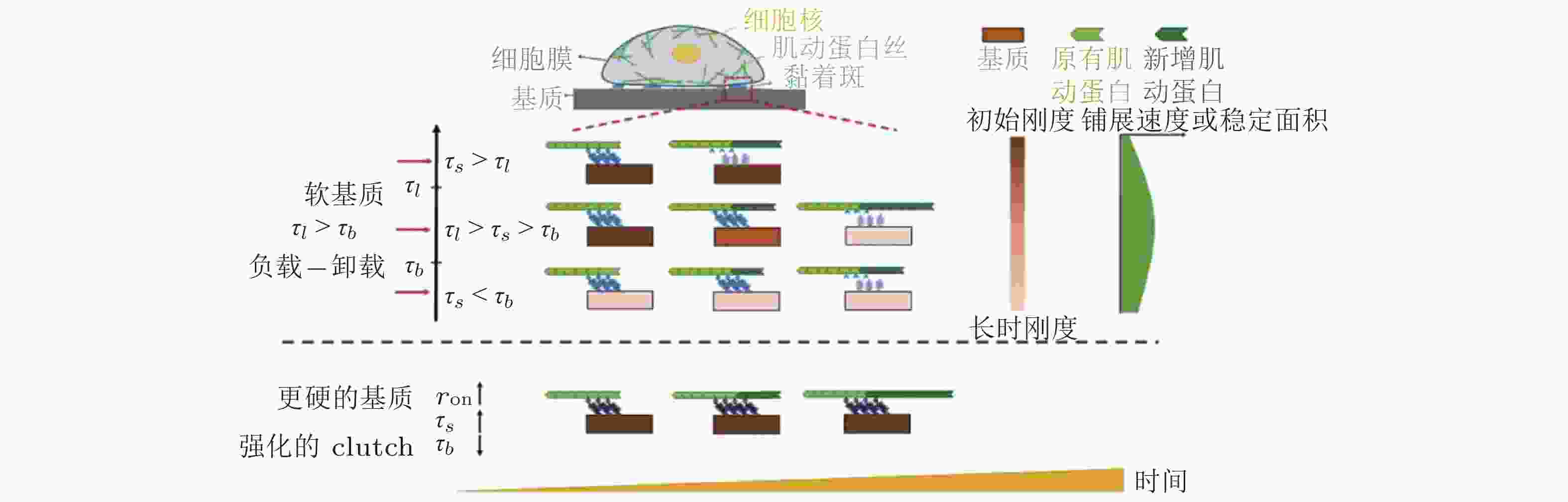
$ {k}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{b}} $ , 黑色) 和相互连接的弹簧 ($ {k}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{k}} $ , 橙色) 表示, (b) 随着配体间距的减小, 每个独立分子键上的张力载荷也减小图 16 ECM粘弹性对细胞行为的影响示意图(Gong et al. 2018)
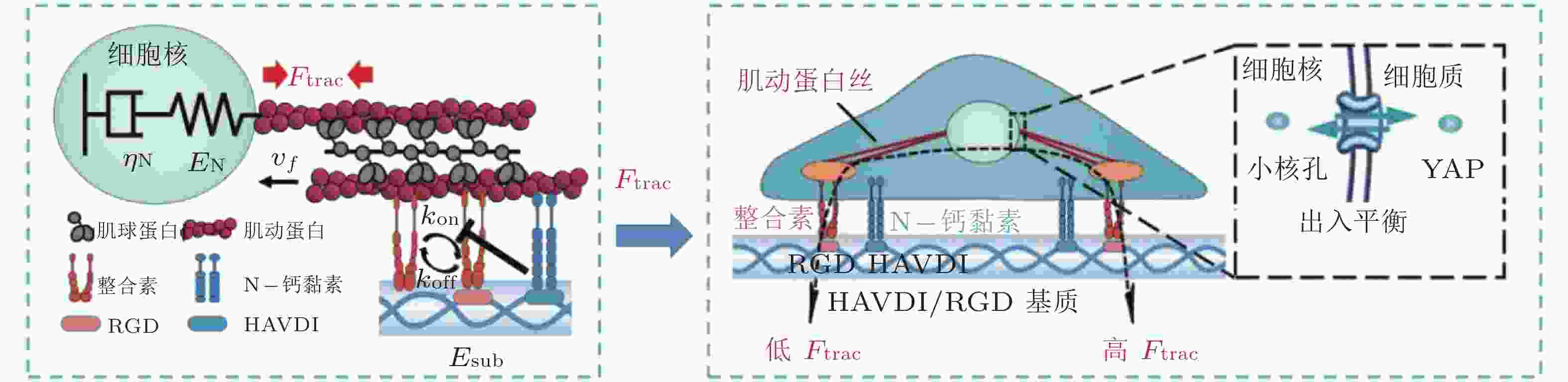
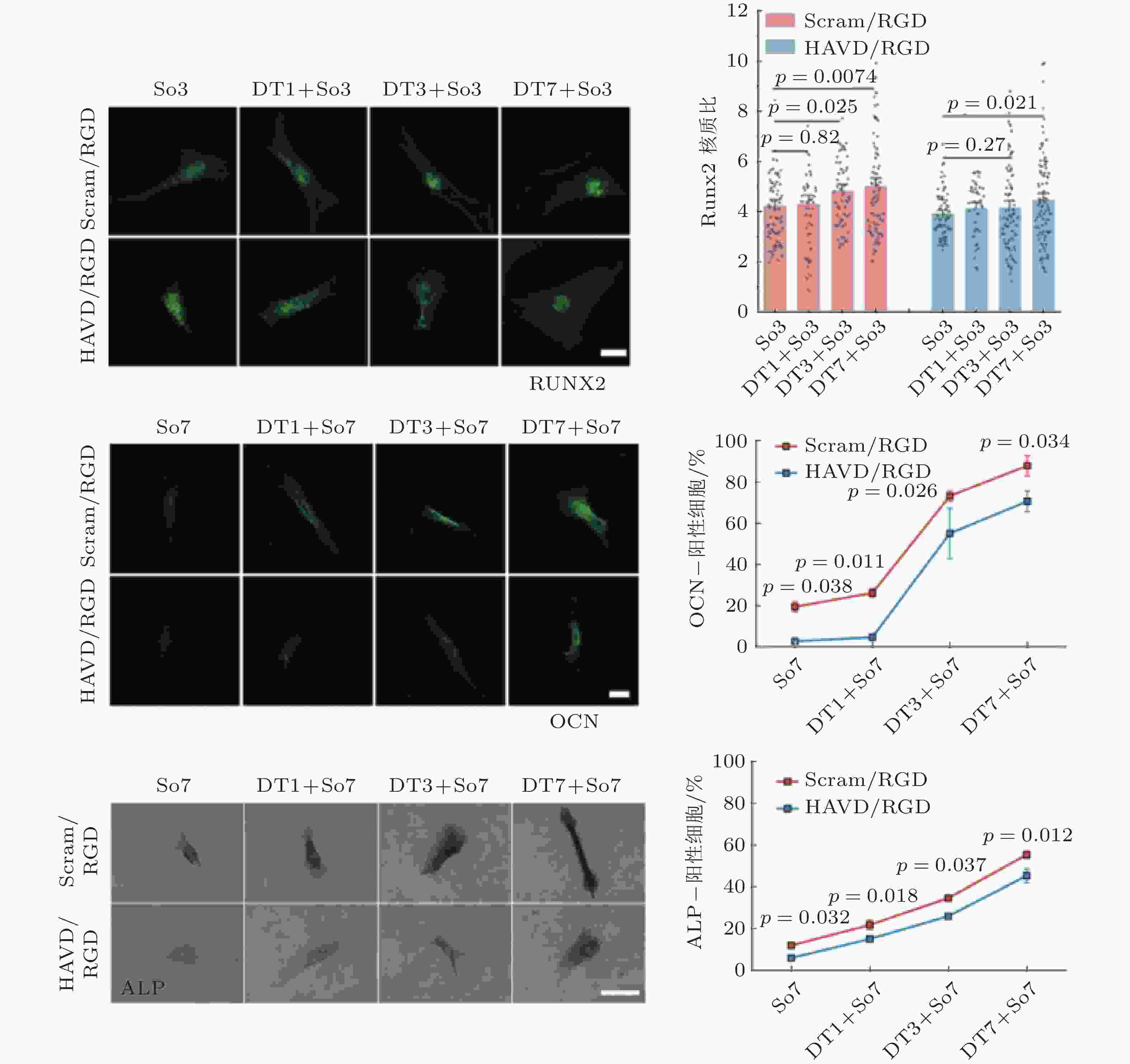
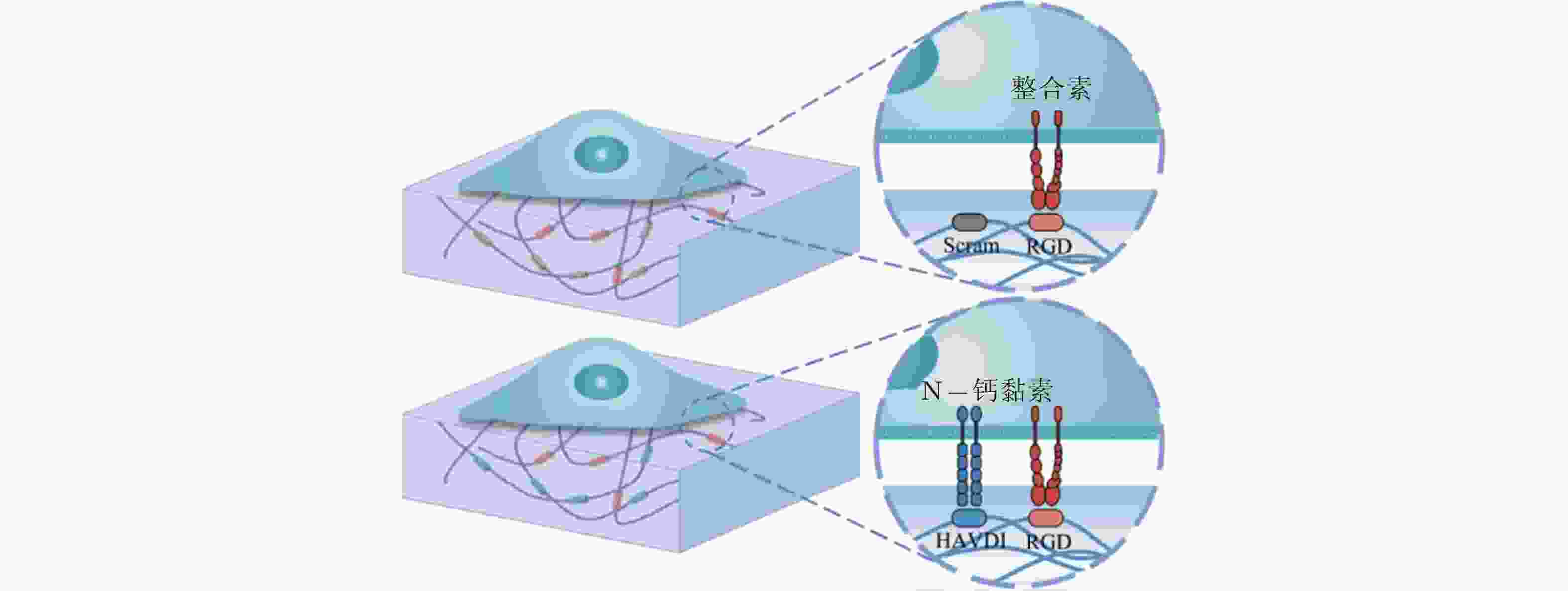
图 17 基于Motor-Clutch的转录因子重定位模型(Zhang et al. 2021). 模型解释了HAVDI连接在MSCs中改变YAP核定位中的作用; HAVDI的连接 (N-钙黏素为基础的黏附连接) 扰乱了整合素的聚集, 降低了整合素与RGD结合的
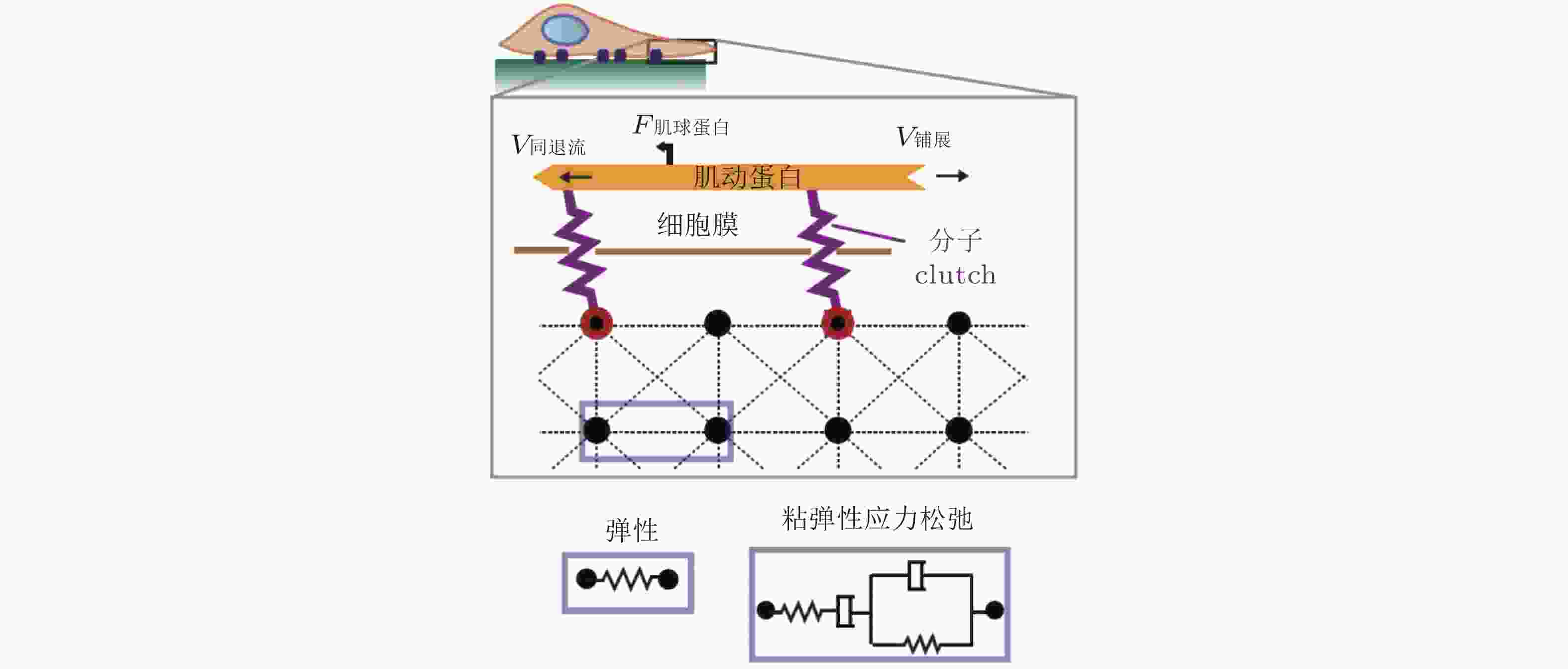
$ {k}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}} $ (s−1) 值, 由此降低肌动蛋白丝中的$ {F}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{c}} $ (pN) , 导致粘弹性核的变形改变影响了核孔尺寸、YAP在核内外的转运速率, 最终导致在HAVDI/RGD基质上的YAP 核/质比改变图 18 细胞在弹性或粘弹性基质上铺展的模型示意图(Chaudhuri et al. 2015a). 细胞前缘的肌动蛋白丝通过形成分子键的方式与基质结合, 这些分子键通过负载减缓了肌球蛋白马达驱动的肌动蛋白丝回退流; 将基质等效为由Hookean弹簧 (代表弹性基质) 或Burgers模型单元 (代表应力松弛的粘弹性基质) 连接的节点阵列
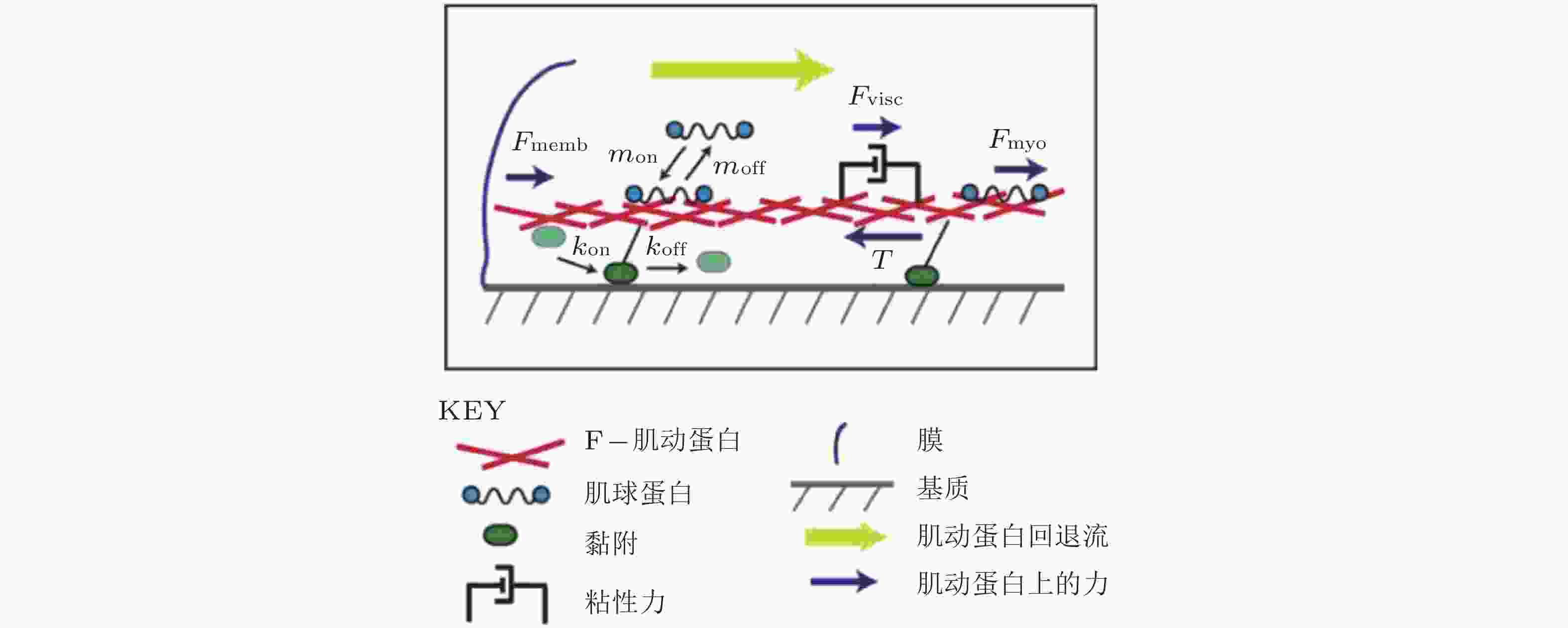
图 19 细胞铺展前缘的受力示意图(Craig et al. 2015). 肌动蛋白网络粘性力、黏着斑-基质牵张力与肌球蛋白收缩力之间的平衡, 其中肌球蛋白和黏附都以一定的速率与肌动蛋白网络相结合/分离
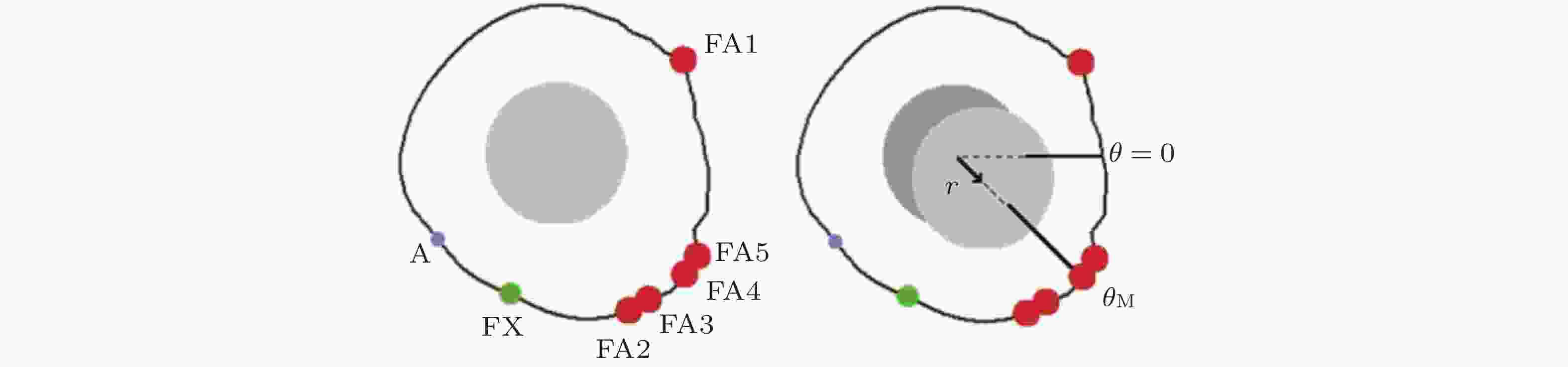
图 20 细胞迁移的模拟示意图(Stephanou et al. 2008). 细胞周围形成的各种黏附类型 (A: 黏附点; FX: 黏附复合物; FA: 黏着斑) . 只有黏着斑对计算单元的位移有贡献 (左) ; 细胞质心被拉向
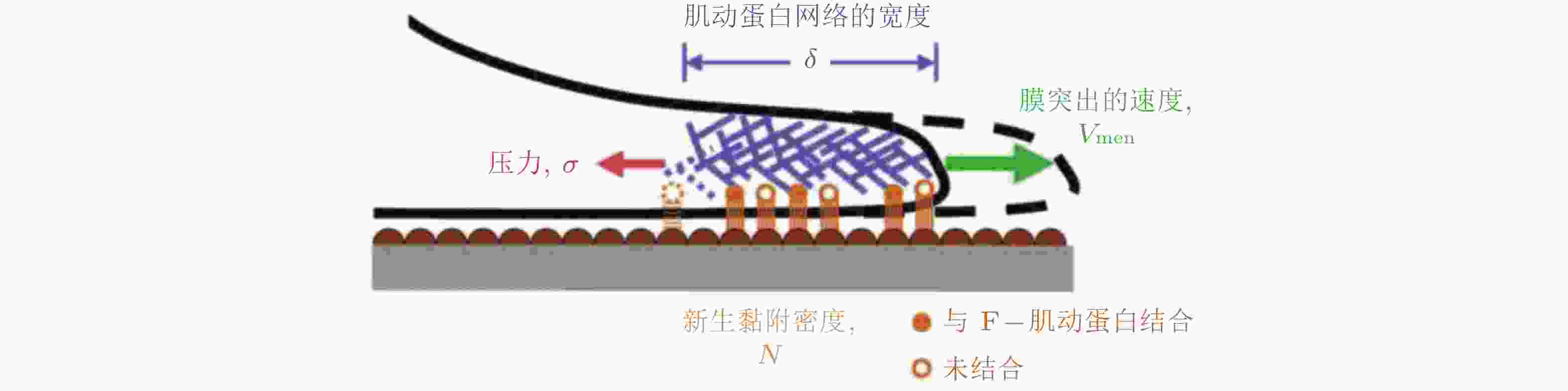
$ {\theta }_{\mathrm{M}} $ 方向, 对应于锚定在相关黏附点上的纤维的最大牵引力; 向量r表示细胞质心从初始位置 (深灰色) 到最终位置 (浅灰色) 的位移.图 21 细胞前缘突出动力学模型(Welf et al. 2013)
图 22 预测细胞集体趋硬性的广义Motor-Clutch模型(Sunyer et al. 2016). (a) 在模型中, 用连续的弹性体模拟单层相连的细胞, 并通过弹簧与基质连接, (b) (上)将每个黏着斑等效为“Clutch”以传递使基质变形的力; (下) 为保持力平衡, 基质中柔软一侧的变形更大(
$ {d}_{1} > {d}_{2} $ ), 使单层细胞整体表现为向较硬一侧的基质靠近 ($ {{d}_{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{M}}=d}_{1}-{d}_{2} $ )图 23 通过Motor-Clutch模型动态调控正/负向趋硬行为的示意图(Isomursu et al. 2022). 在没有黏附强化 (d) 的情况下, Motor-Clutch模型预测牵张力和基质刚度 (a-c) 之间的双相关系
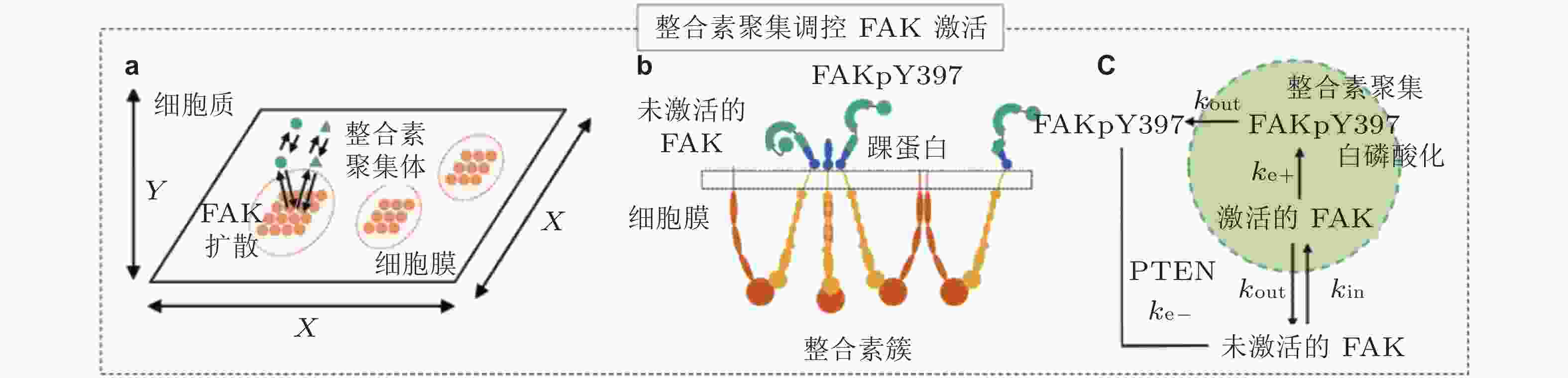
图 24 FAK磷酸化水平模型(Cheng et al. 2020). (a) 整合素和FAK分子的空间模拟示意图; FAK可在细胞质内自由扩散, 整合素聚集体固定在细胞膜上, (b) FAK可以被整合素聚集体中的整合素胞内结构域激活, (c) FAK与整合素簇的结合和分离分别由
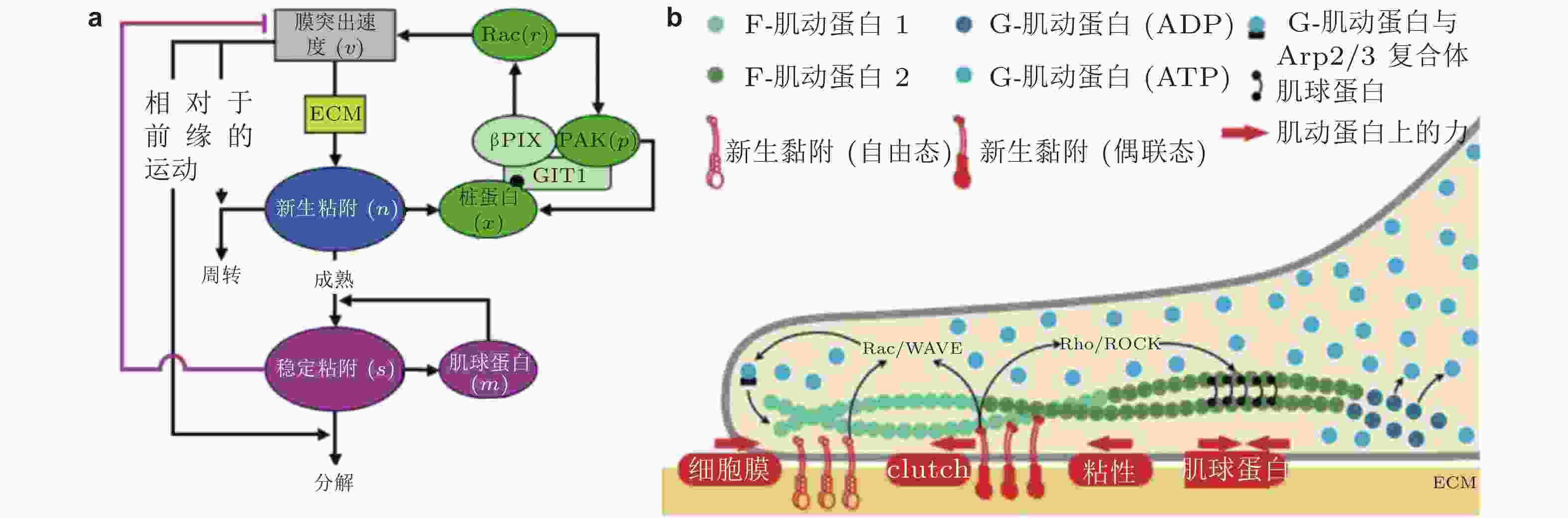
$ {k}_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $ (s−1) 和$ {k}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{t}} $ (s−1) 描述; 在整合素聚集体或细胞质中, FAK通过磷酸酶和张力素同源物 (PTEN) 的脱磷酸化而激活和失活, 分别用$ {k}_{\mathrm{e}+} $ (s−1) 和$ {k}_{\mathrm{e}-} $ (s−1) 来描述图 25 细胞前缘突出的力-化耦合模型. (a) 信号反馈回路新生黏附和周转的速率取决于膜突出的速度 (v) , 形成速率取决于ECM的密度, Rac的激活进一步促进膜突出; 新生黏附的稳定被肌球蛋白介导的反馈加强, 而稳定的黏附可拮抗膜突出(Cirit et al. 2010), (b) 基于正反馈信号回路的前缘运动模型(Chandra et al. 2022); 新生黏附被分子键稳定, 并介导下游信号通路以激活肌球蛋白和促进肌动蛋白聚合
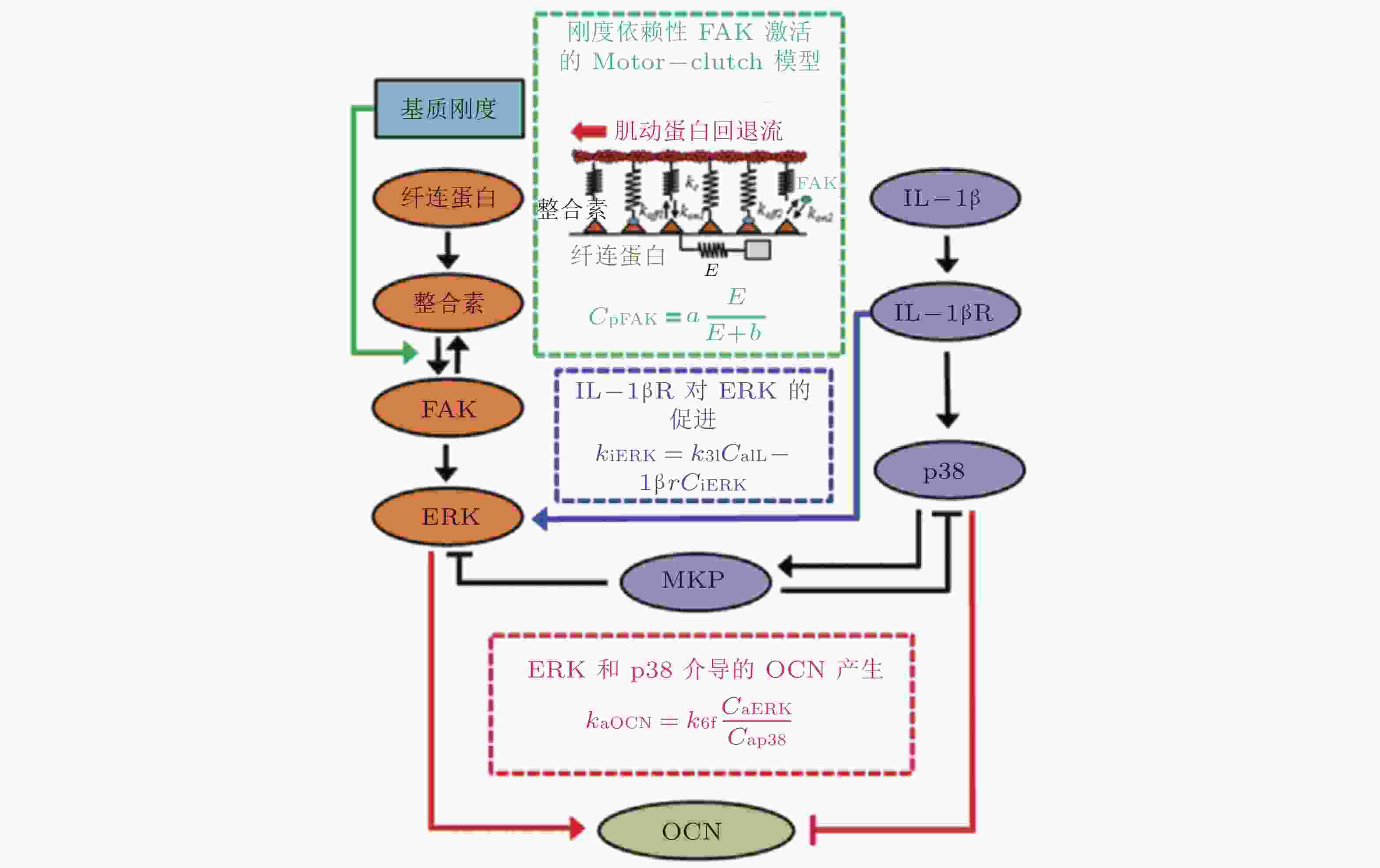
图 26 基质刚度和IL-1β介导的信号通路数学模型(Cheng et al. 2016)
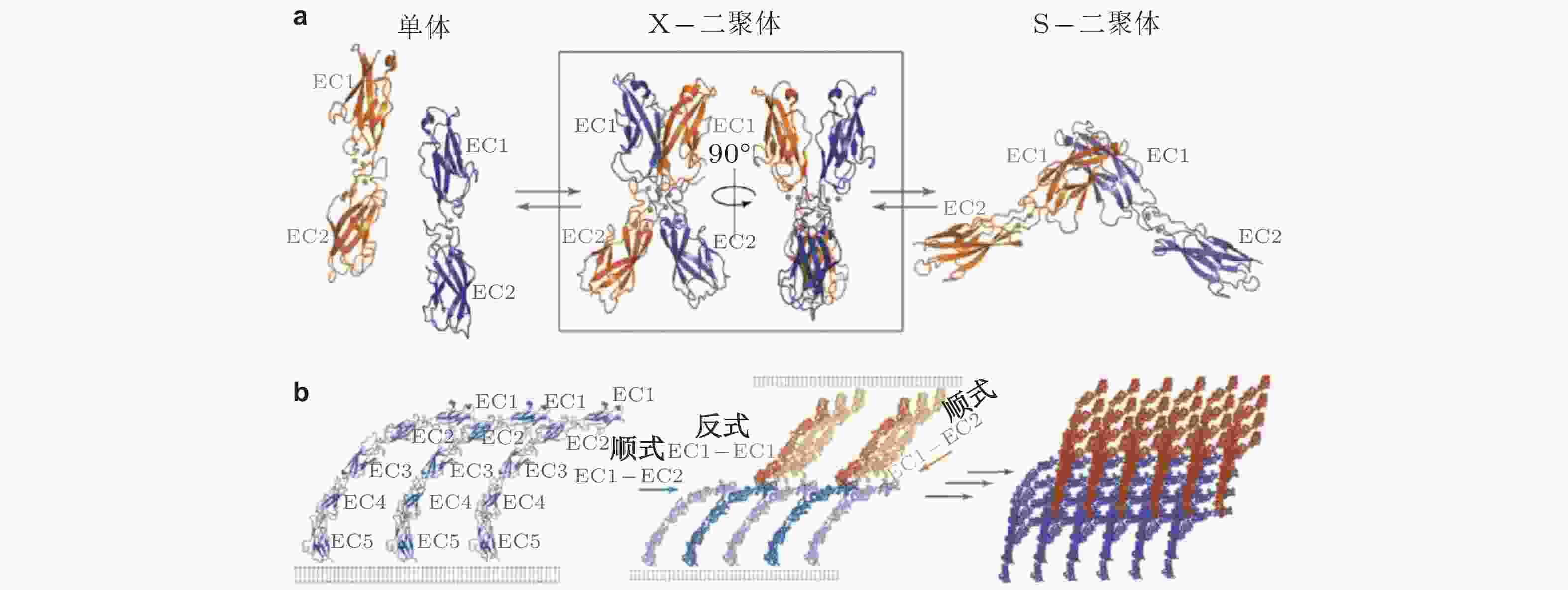
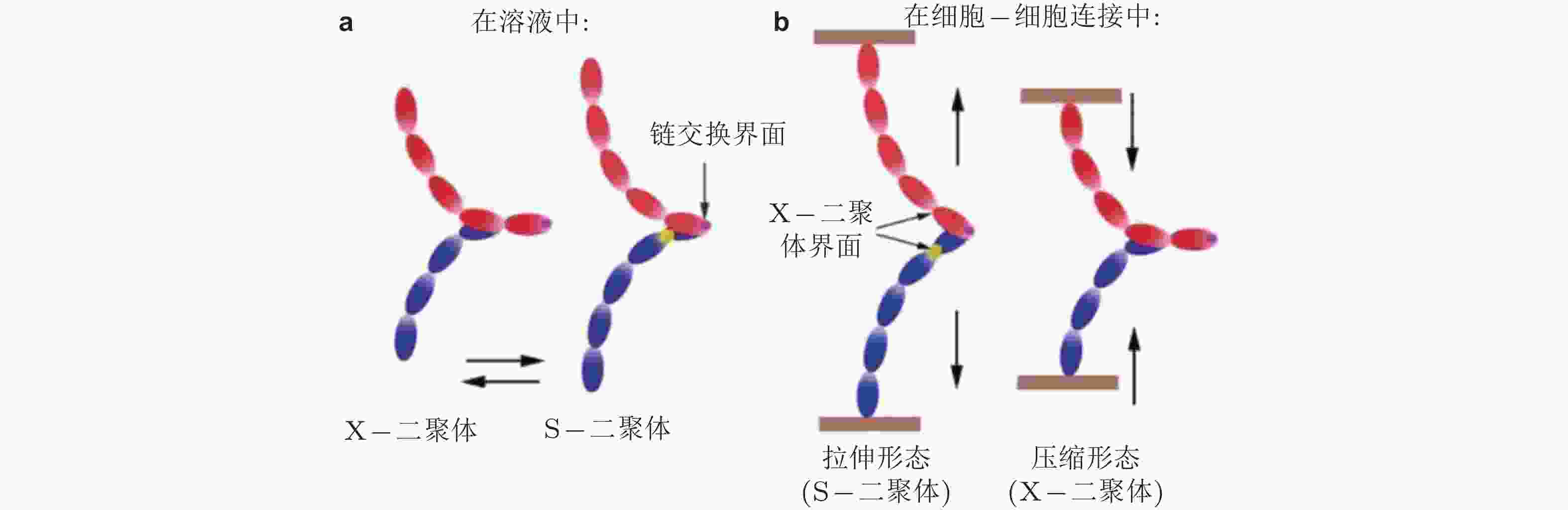
图 27 经典钙黏素反式与顺式相互作用的结构示意图(Brasch et al. 2012). (a) 经典钙黏素的单体及反式二聚体的构象转换 (单体中仅展示2个结构域) . 钙黏素单体相互作用形成X-二聚体后经链交换成熟为S-二聚体, 小球表示结合的Ca2+,(b) 胞外结构形成顺式和跨外结构域的的黏附连接. 左为同侧钙黏素分子的胞外结构域 (EC1-5) ; 相邻的S-二聚体分子的EC1和EC2形成顺式界面连接 (中) , 与反式相互作用方向大致垂直; 顺式和反式相互作用的结合使粘连蛋白外域形成有序的网络 (右) , 是钙黏素实现跨膜连接的基础
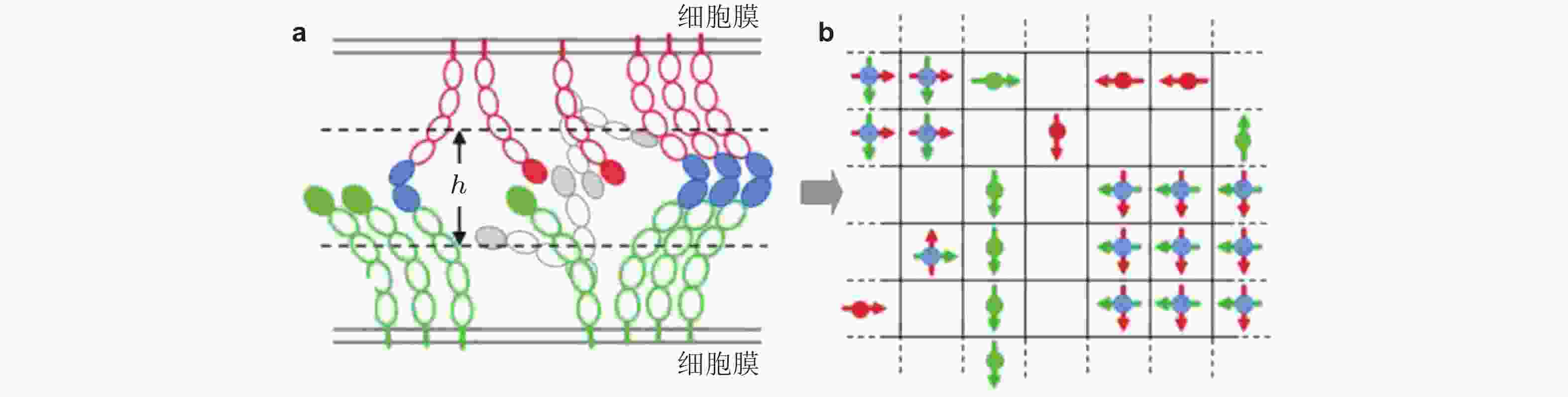
图 28 钙黏素二维晶格模型示意图(Wu et al. 2010). (a) 两种相互作用的钙黏素胞外区域结构示意图. 绿色为下层膜中的钙黏素分子, 红色为上层膜的钙黏素, EC1结构域由实心椭圆标记; 如果相邻的EC1结构域形成反式二聚体, 则标记为实蓝色. 空心椭圆表示EC2-EC5结构域, (b) 二维方格显示了所有EC1结构域 (偶极子/单体) 相互作用的俯视图.每个晶格只能容纳最多一个的上层膜单体(红色偶极子)或下层膜单体(绿色偶极子); 当格子被夹角为90°的两单体 (蓝色实心圆) 占据时, 代表反式二聚体形成
图 29 二维膜空间中钙黏素形成二聚体过程的示意图(Wu et al. 2011). (a) 分子只能在二维空间内自由扩散, 旋转运动受到限制. 钙黏素五个细胞外区域以椭球形表示, 反式二聚体(蓝色)由两个相邻细胞表面的两个钙黏素单体形成, (b) EC1域的转动自由度由三个欧拉角
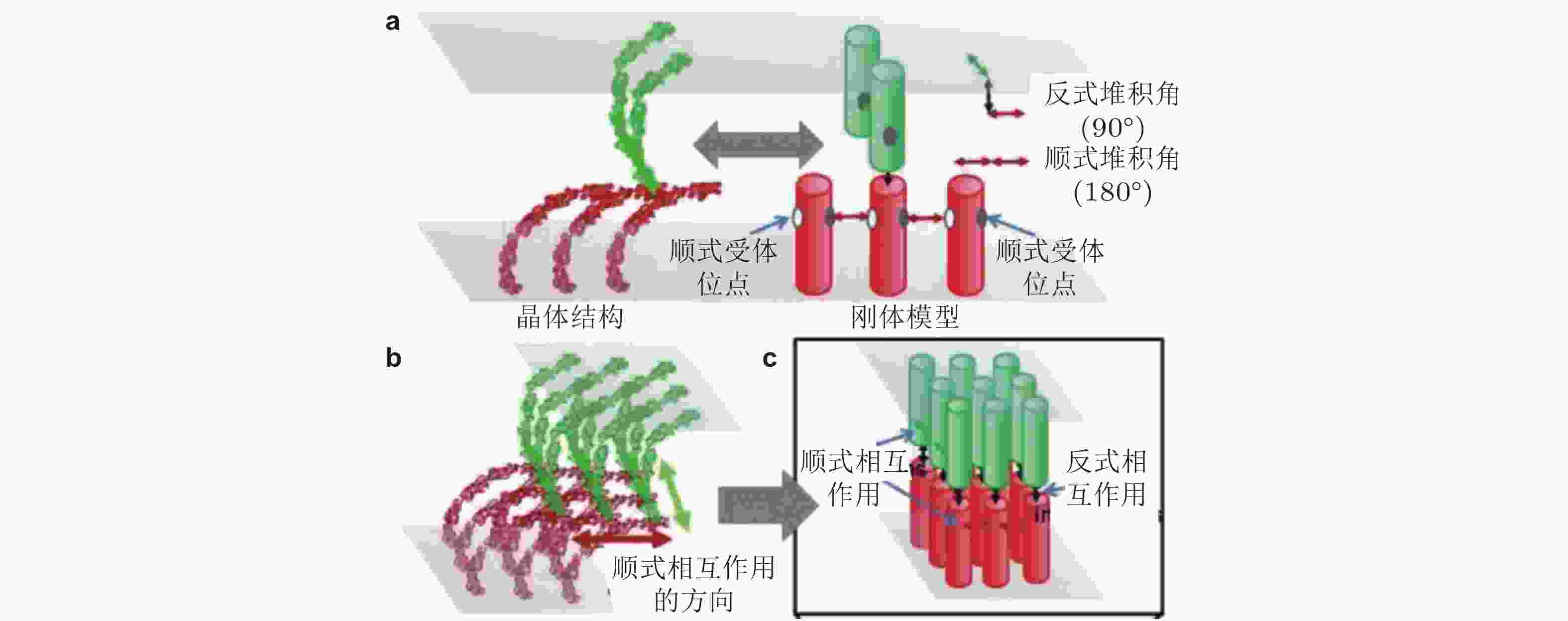
$\phi{(^\circ)}$ ,$\theta{(^\circ)}$ 和$\psi{(^\circ)}$ 表征图 30 基于RB方法(Xie et al. 2014)的钙黏素分子聚集模拟示意图(Chen et al. 2016). (a) 每个钙黏素都被简化为一个刚性圆柱. 细胞界面由2个相互重叠的平面表示. 每个圆柱的顶部有1个反式结合位点, 两侧有2个顺式结合位点, (b) 钙黏素反式和顺式二聚体的各向异性排列形成二维超分子结构簇, (c) 采用扩散-反应算法进行的空间动力学模拟
图 31 E-钙黏素分子状态转变的计算模型示意图(Chen et al. 2021). (a) 三维计算域示意图, 两个内表面代表相邻细胞的细胞膜, 两个外表面代表肌动球蛋白细胞骨架, (b) 参与状态转换计算的蛋白分子示意图, (c) E-钙黏素分子状态转换的动力学示意图
图 32 钙黏素二聚体状态的调控机制示意图(Hong et al. 2011). (a) 溶液中的钙黏素二聚体不受牵张力的调节, 在X-和链交换模式之间自由转转, (b) 已形成细胞-细胞黏附连接的二聚体不能在两种模式间自由转换
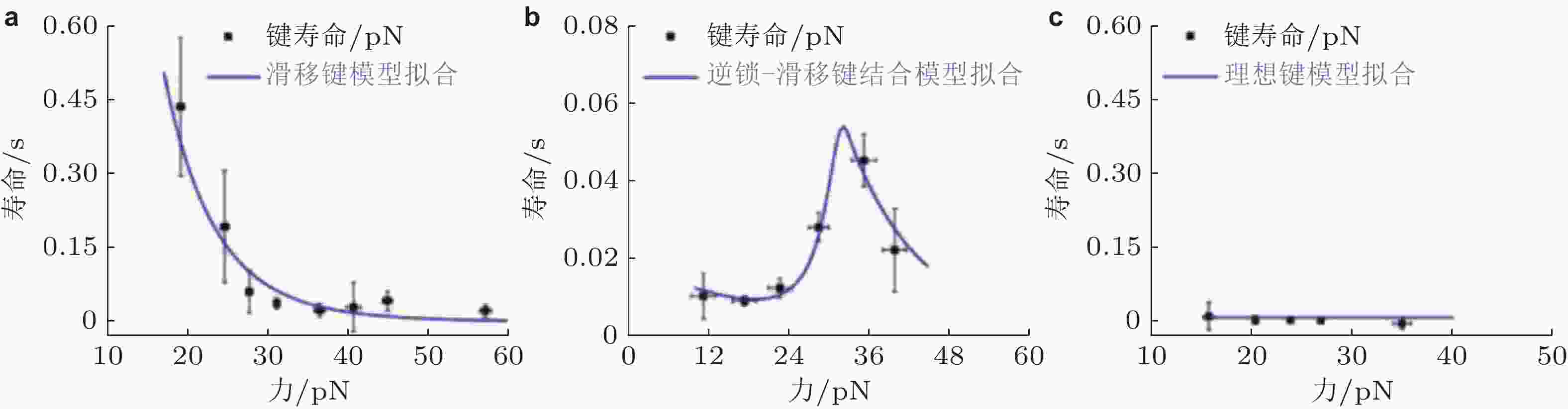
图 33 E-钙黏素突变体力依赖性的键寿命(Priest et al. 2017). (a) S-二聚体形成滑移键, 寿命随力的增加而迅速下降, (b) X-二聚体形成逆锁-滑移键, 在临界张力之前, 键寿命随力增加, (c) 野生型E-钙黏素形成与力无关的理想键
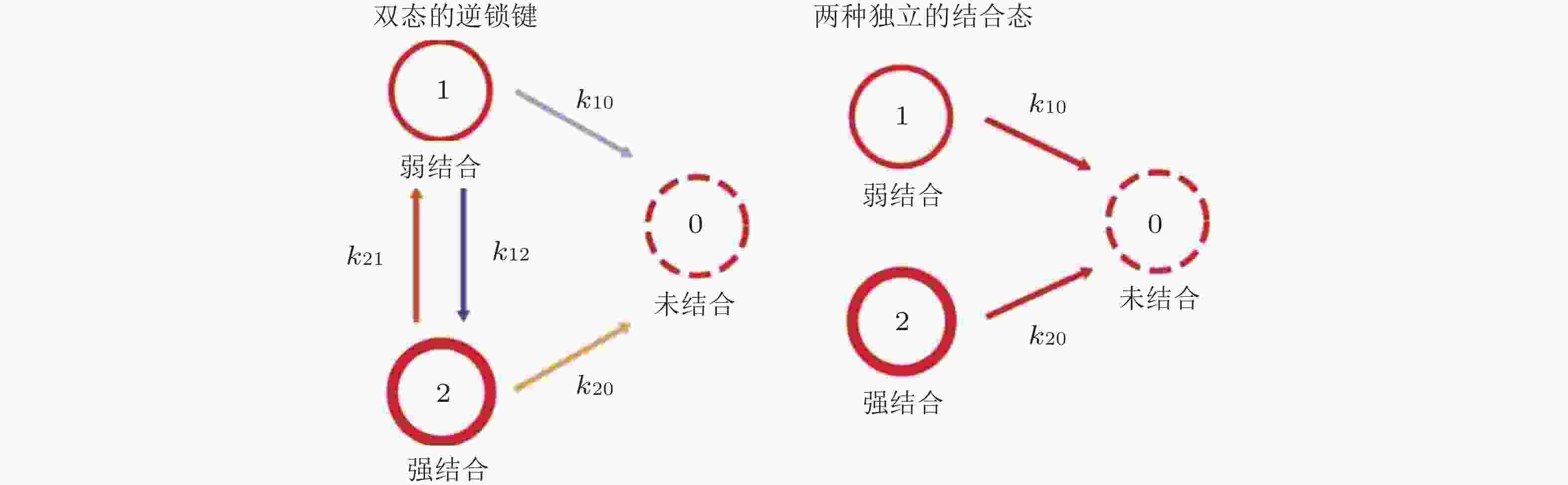
图 34 双态逆锁键动力学模型(Buckley et al. 2014). 状态1和状态2分别是弱结合态和强结合态, 状态0为未结合状态 (左) ; 状态1和状态2之间的转化以速率k12 (s−1) 和k21 (s−1) 发生, 这些转换不会发生在独立结合态模型中(右)
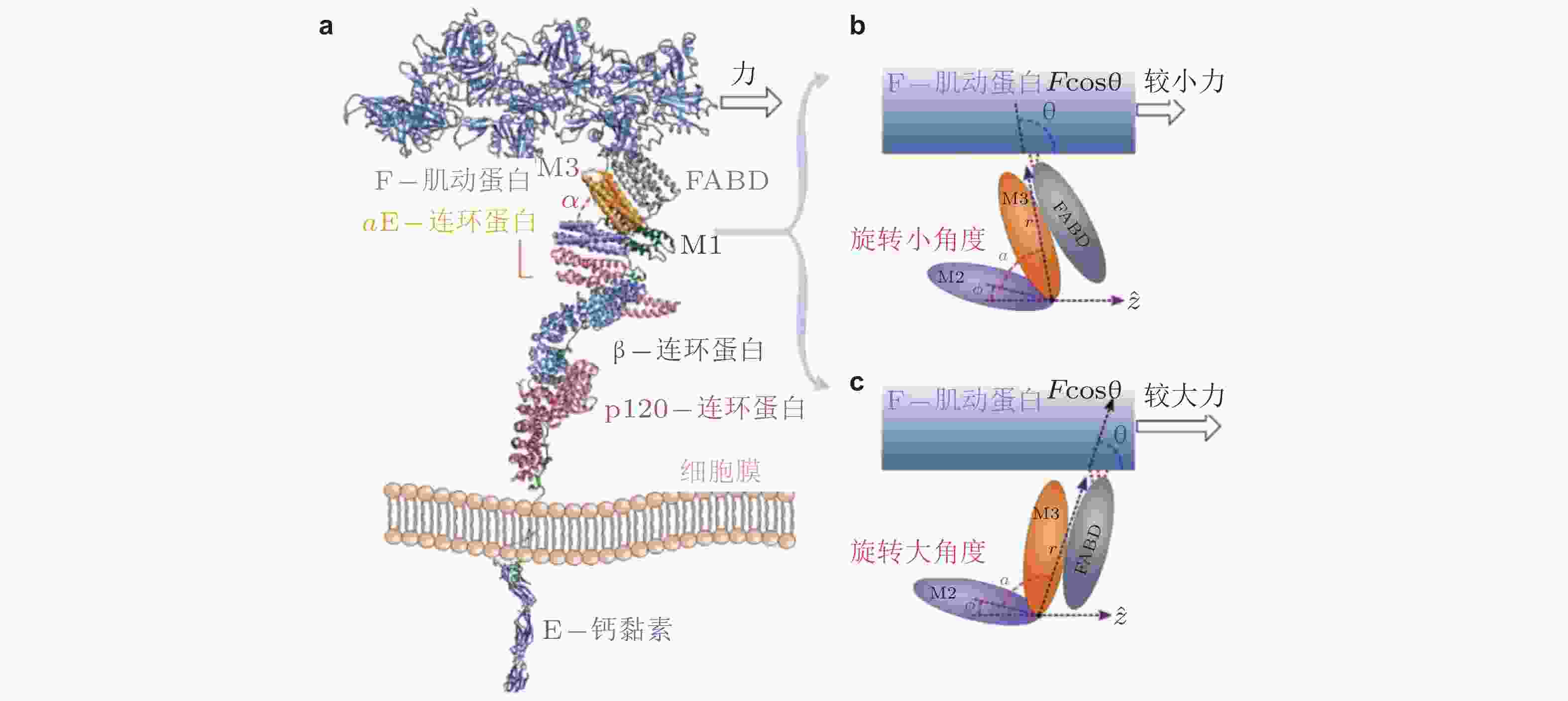
图 35 外力引起的钙黏素-连环蛋白-肌动蛋白复合物的构象变化(Adhikari et al. 2018). (a) 相关蛋白的晶体结构组合图, (b) αE-连环蛋白的M区域, 较小的力下有利于M2和M3区域之间呈现小角度α的构象, (c) 与b对应, 更大的力易于促成大角度的构象, 引起FABD-肌动蛋白相互作用的增强, 最终导致逆锁键行为
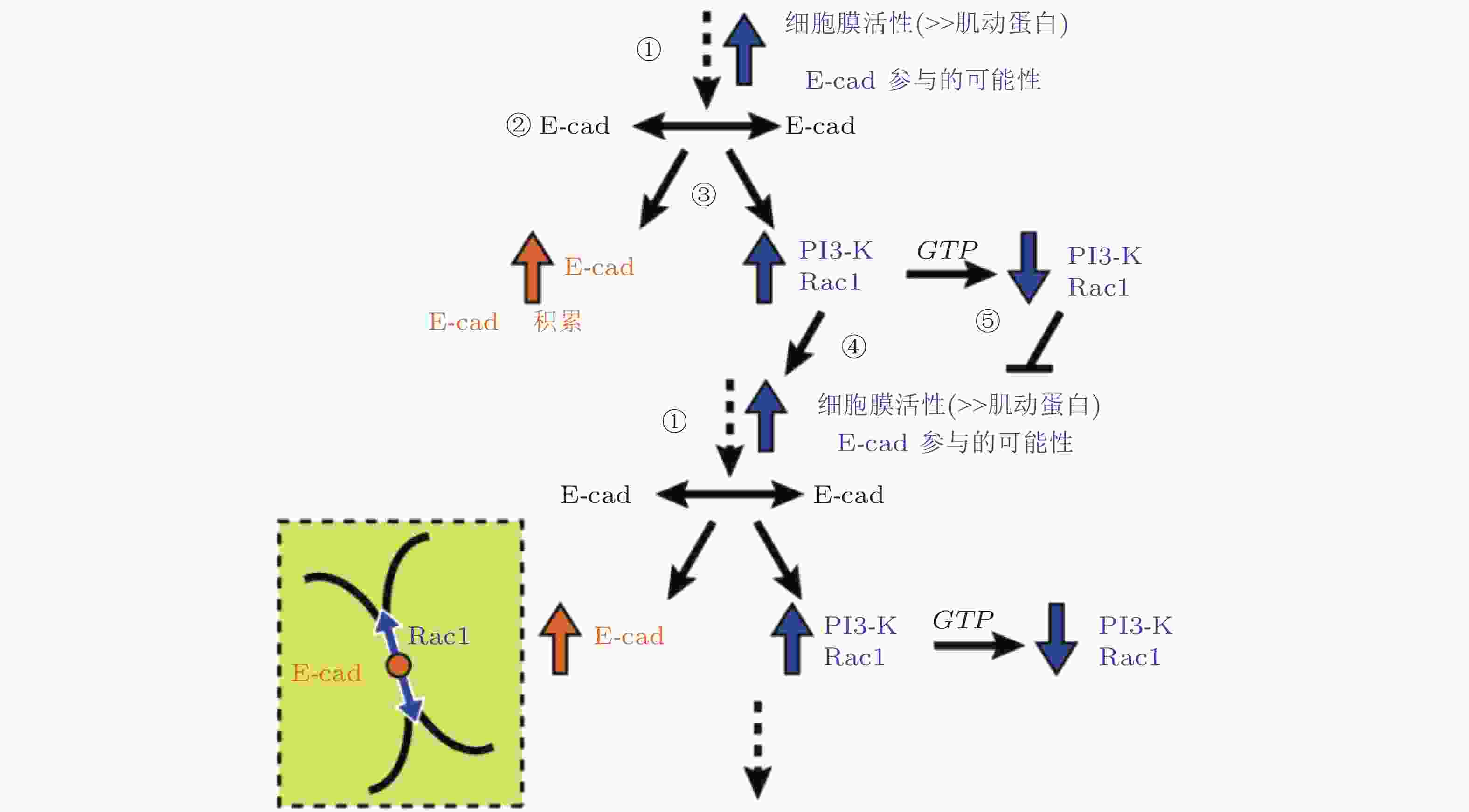
图 36 E-钙黏素介导的黏附初期信号回路模型(Perez et al. 2008)
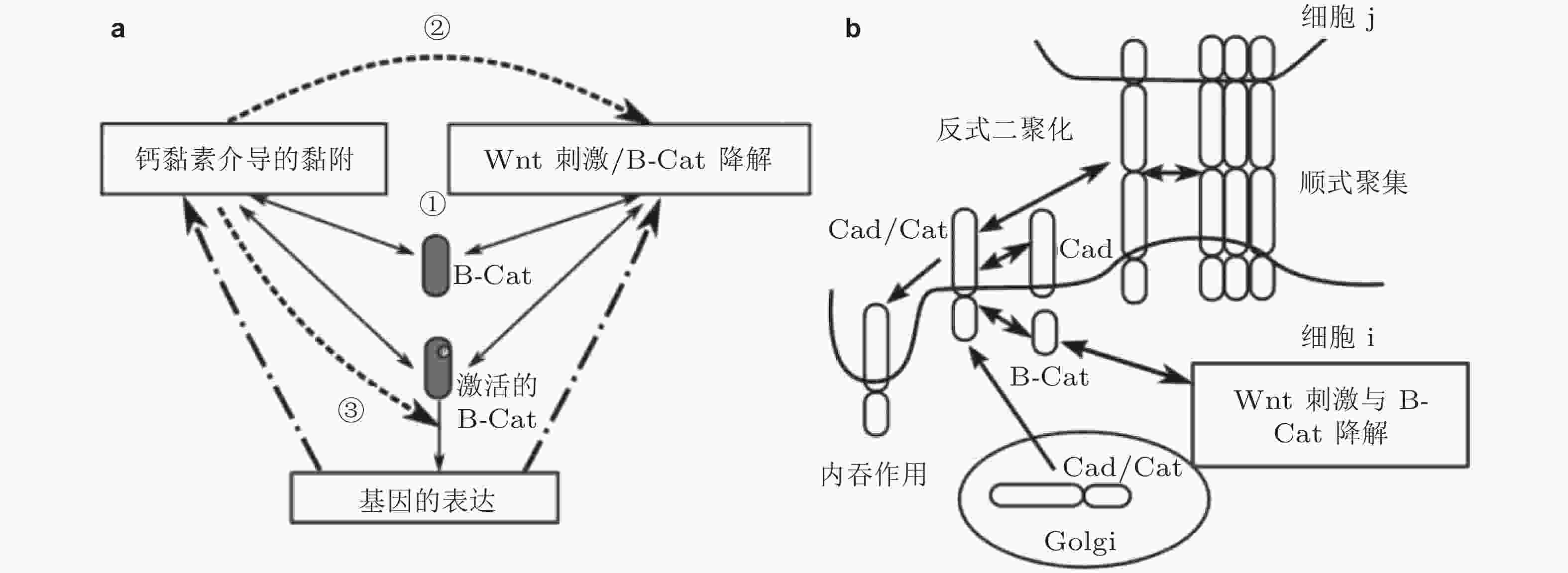
图 37 钙黏素黏附与Wnt信号通路相互作用(Chen et al. 2014). (a) 网络模型的整体示意图. 3个模块由正常和激活的β-连环蛋白连接 (仅后者可激活基因表达) , 数字表示Wnt信号与细胞黏附之间的串话, (b) Cad/Cat复合物通过多个步骤形成黏附连接
图 38 NMII-RhoA双稳态信号网络模型(Priya et al. 2015). (a) 上皮细胞黏附带的稳定的Rho区域示意图, (b) 双稳态信号网络模型的结构及结算结果; 图中信号分子处的箭头和T形接头代表连接招募的刺激和抑制
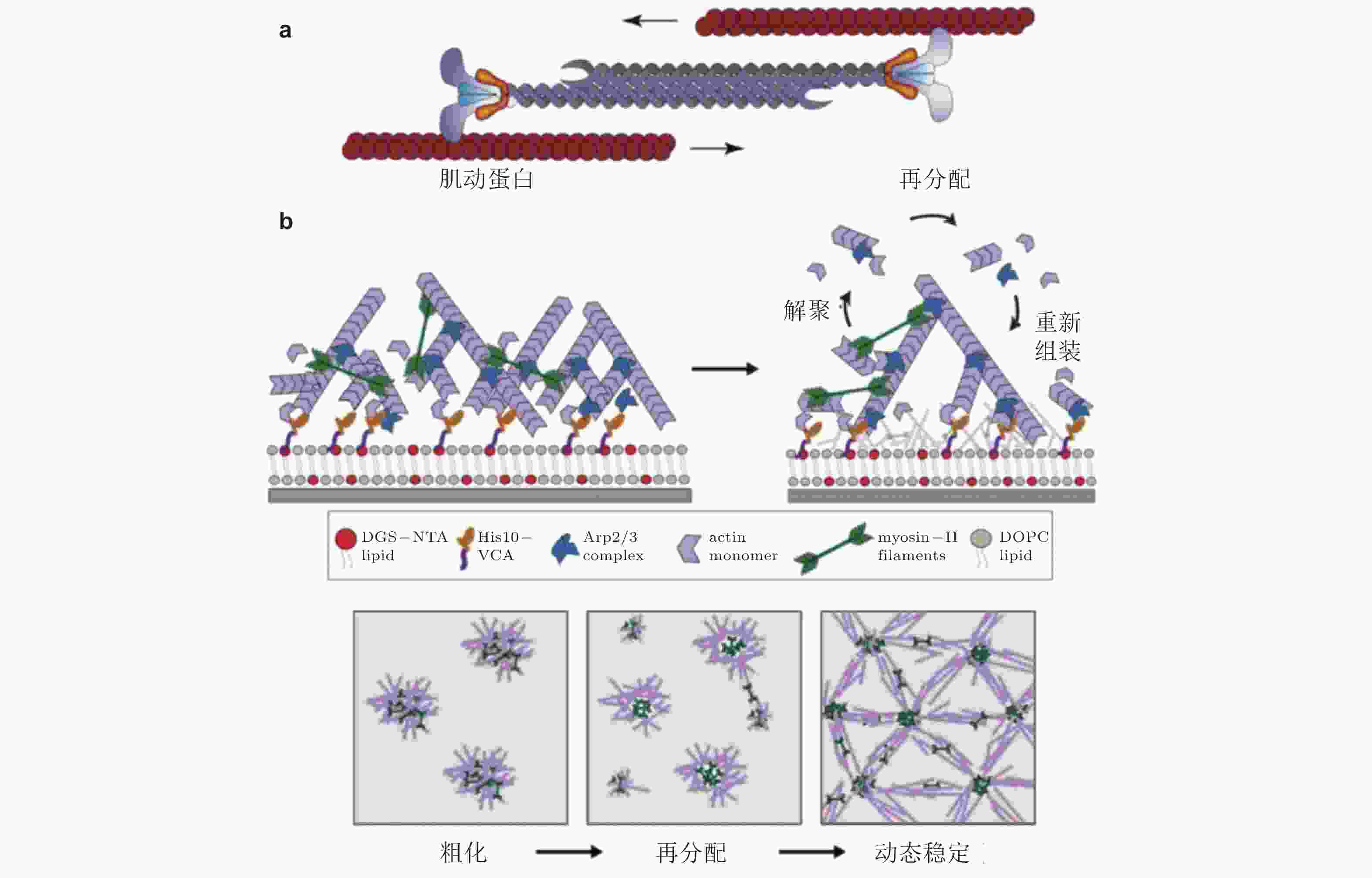
图 39 肌球蛋白驱动肌动蛋白的收缩、解聚和重组装示意图. (a) 肌动蛋白丝的运动驱动肌动蛋白网络的收缩(Clark et al. 2007), (b) 肌球蛋白Ⅱ会刺激肌动蛋白网络的解聚与重新组装(Sonal et al. 2018)
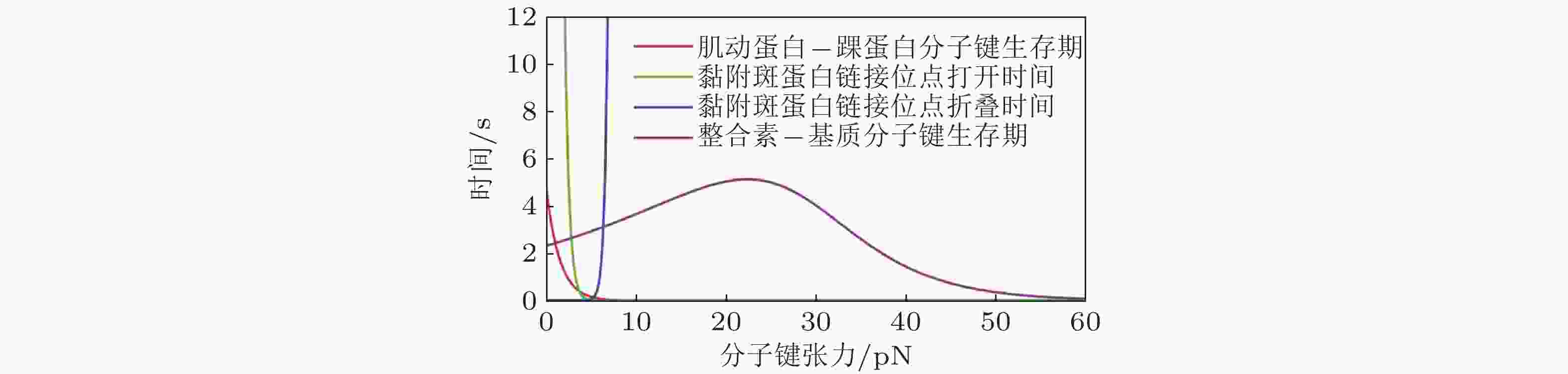
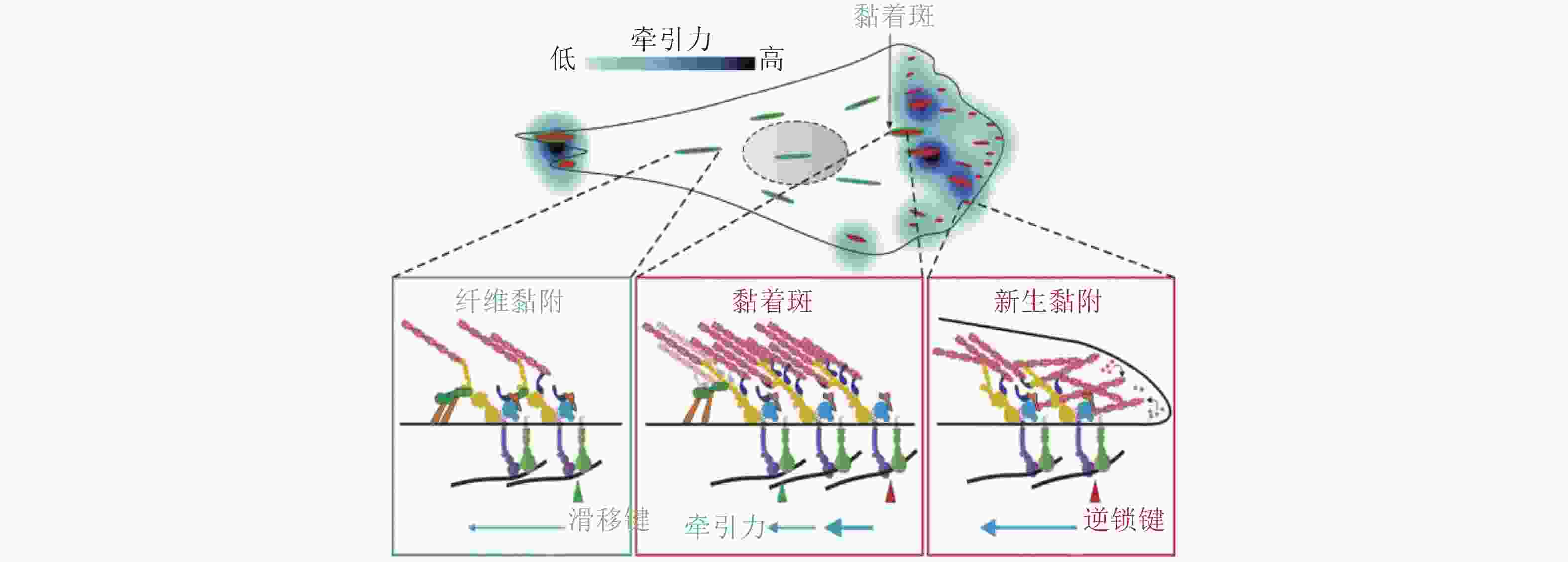
图 41 细胞-ECM界面分子键断裂动力学(Cheng et al. 2016)
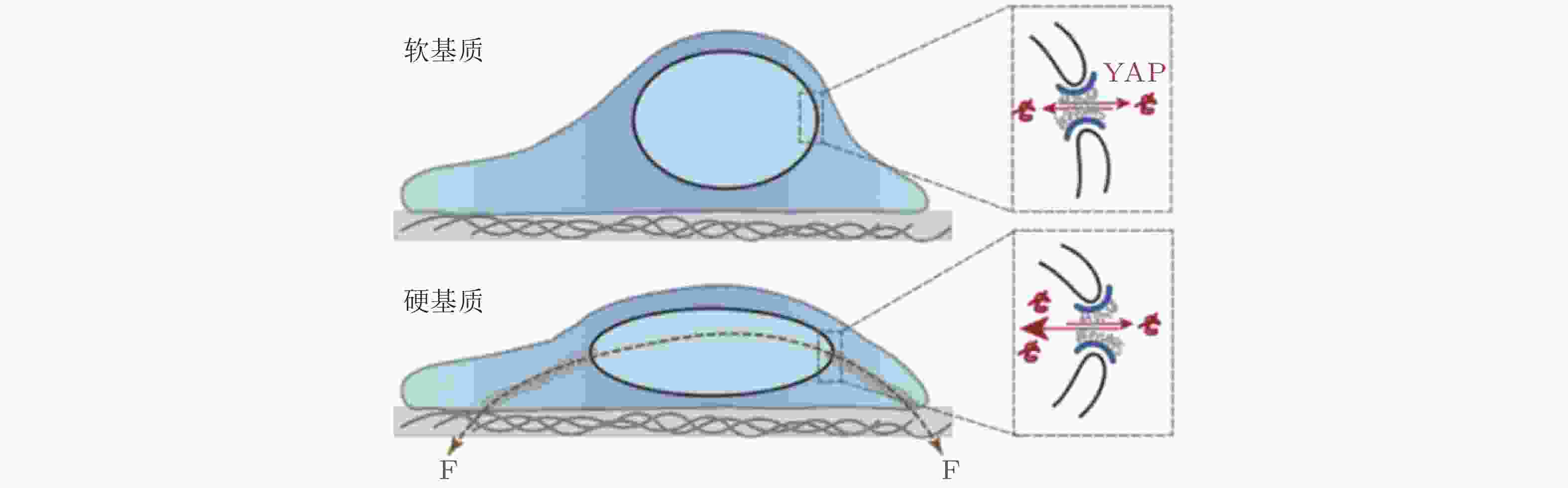
图 42 ECM-核机械耦合使 YAP 易位以响应基质刚度(Elosegui-Artola et al. 2017)
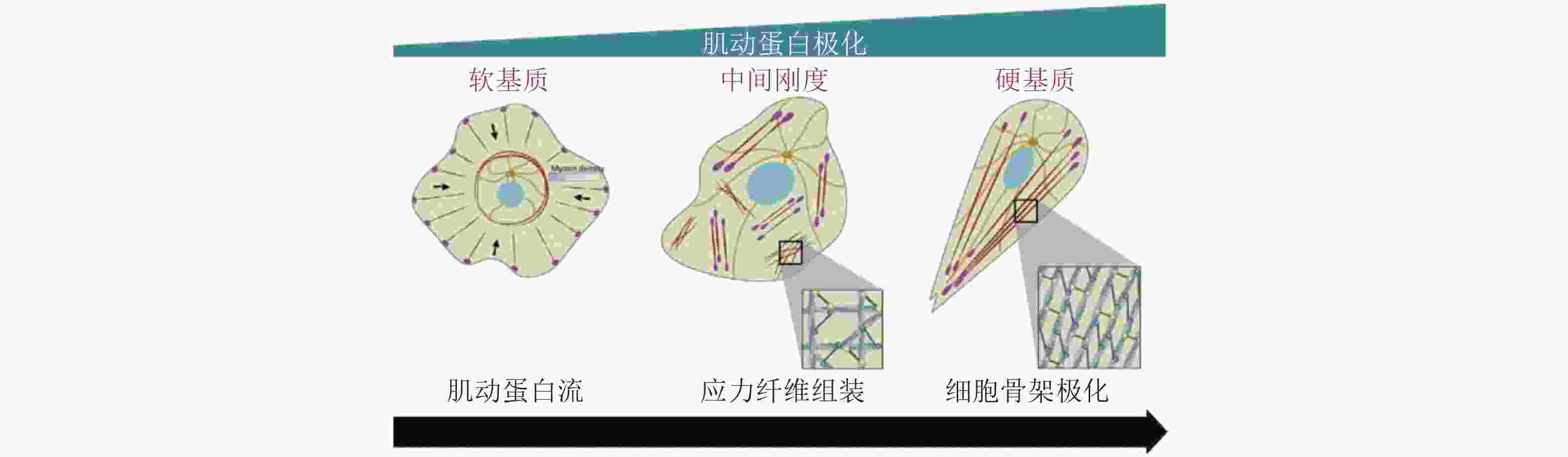
图 43 黏附介导的细胞极化(Ladoux et al. 2016)
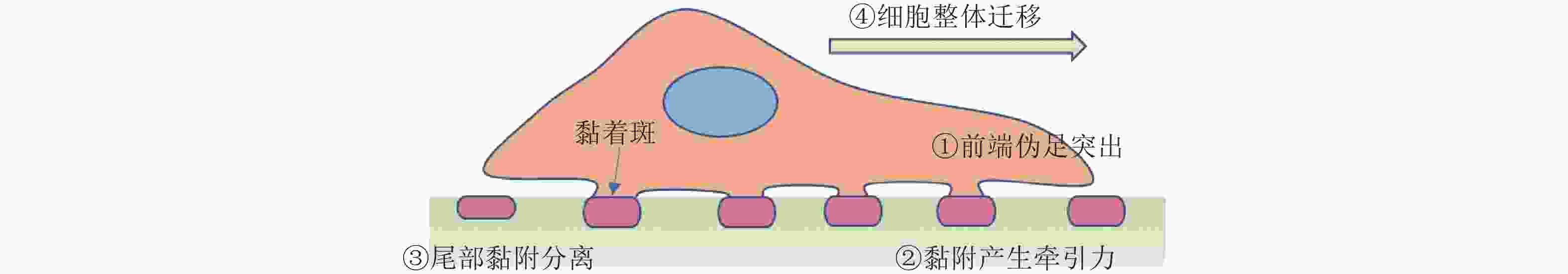
图 44 细胞迁移过程(Sun, Guo et al. 2016)
图 46 钙黏素介导的黏附调控细胞力学感知(Cosgrove et al. 2016)
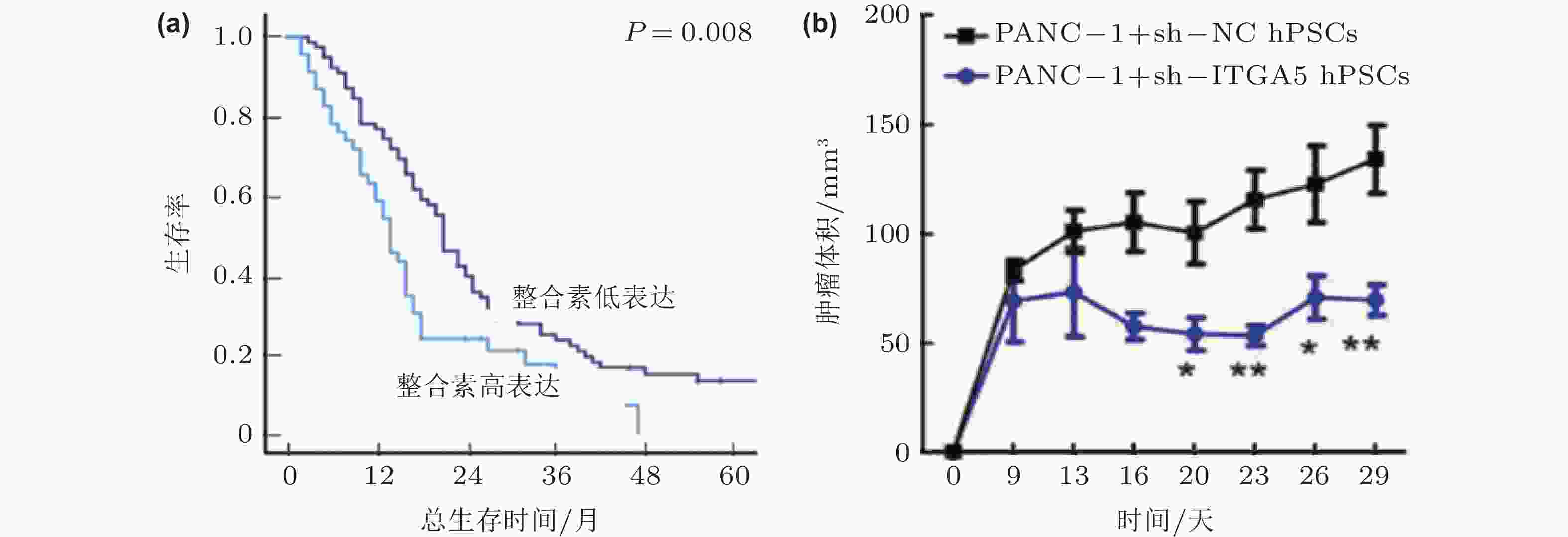
图 48 整合素α5β1的表达影响胰腺癌的进展(Kuninty et al. 2019). (a)胰腺癌组织中整合素α5β1的高表达与5年生存率下降相关; (b)整合素α5β1的敲除可以显著抑制胰腺星状细胞的功能, 抑制胰腺肿瘤体积的增长
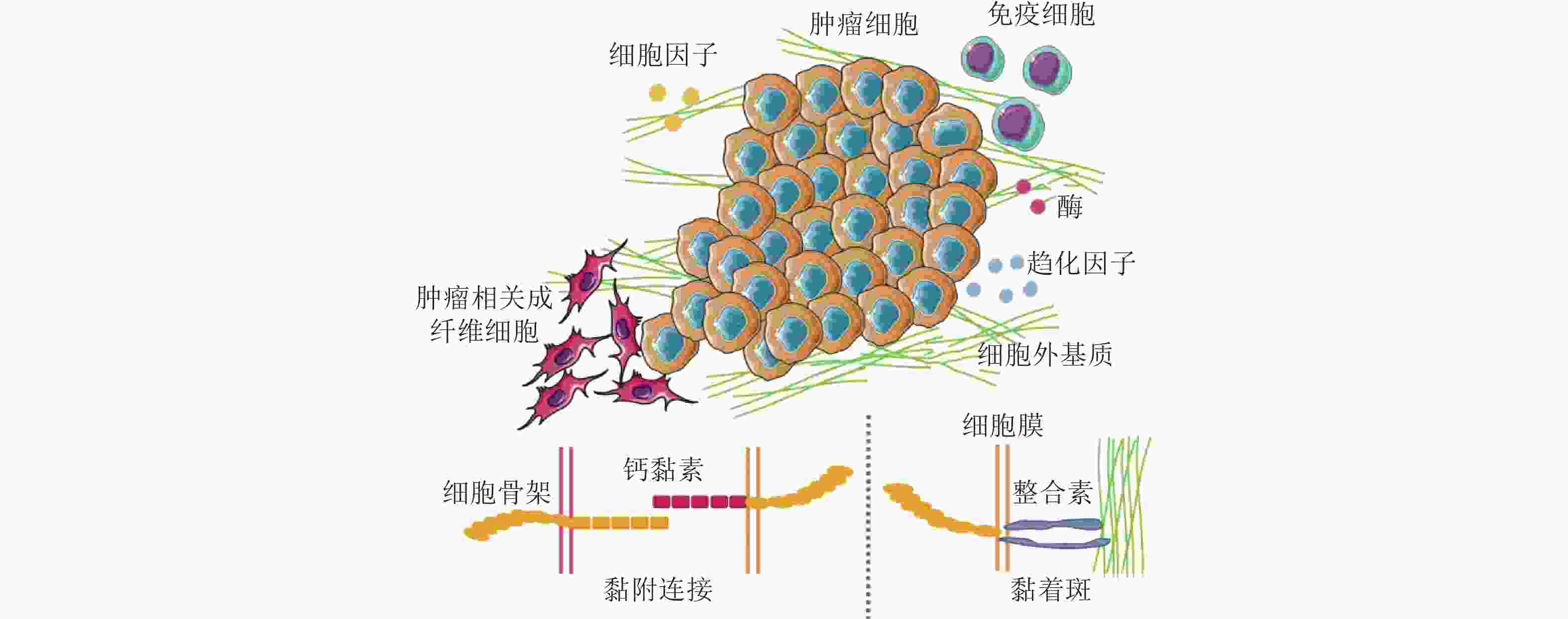
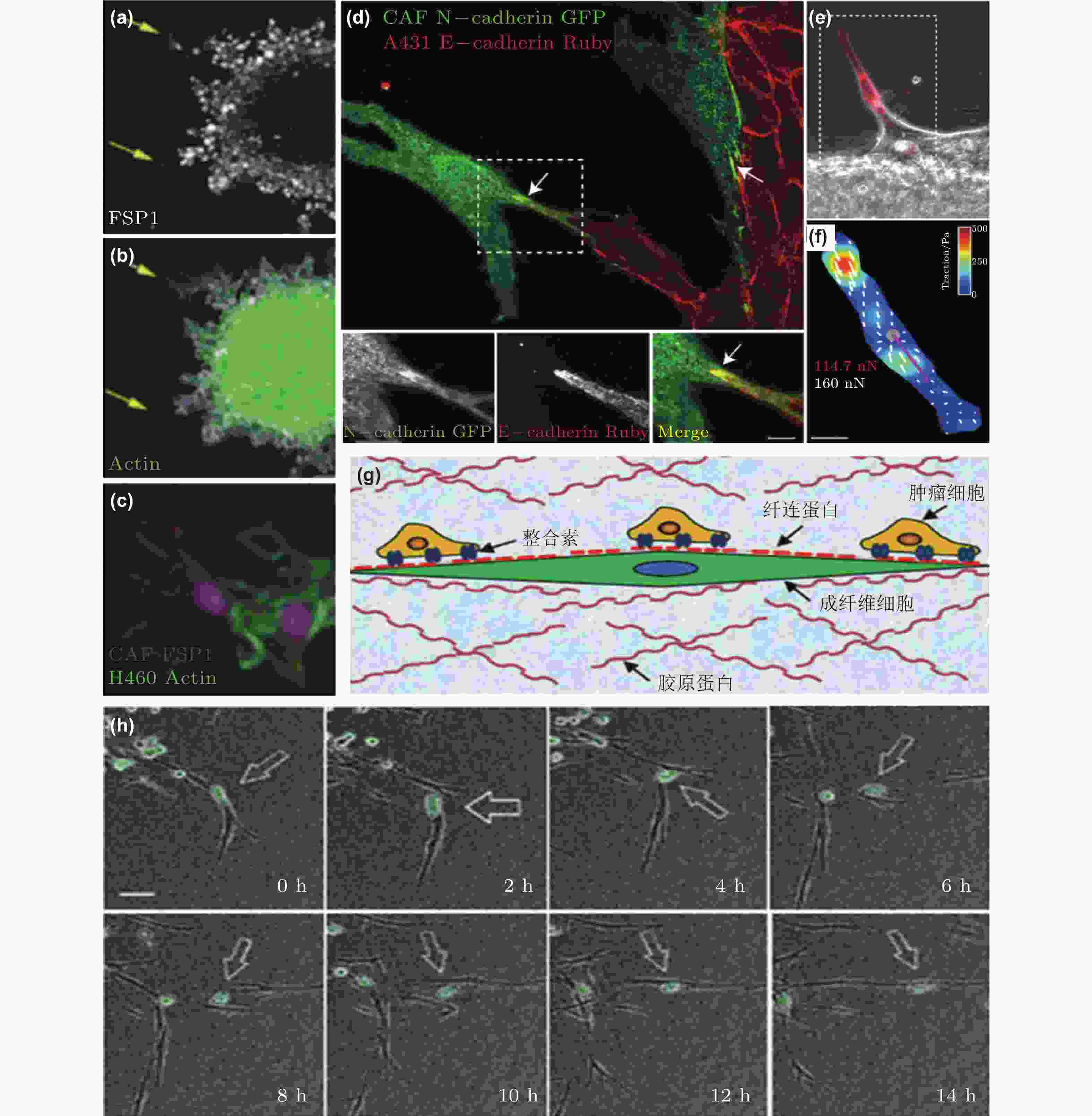
图 50 CAF通过和癌细胞间的黏附作用促进癌细胞迁移. (a-c) CAF和癌细胞共培养体系中标记蛋白染色结果(Richardson et al. 2018); (d-f) CAF和癌细胞之间存在黏附作用(Labernadie et al. 2017); (d) CAF表达的N-钙黏素和癌细胞表达的E-钙黏素直接作用的染色结果; (e-f) CAF产生的牵引力的表征(紫色线表示CAF作用于癌细胞的牵引力的大小和方向); (g) CAF与癌细胞通过整合素/纤连蛋白力传导进行迁移示意图(Miyazaki et al. 2019); (h) 癌细胞和CAF共培养的实时检测结果显示肺癌细胞沿着CAF突起迁移(Miyazaki et al. 2019)
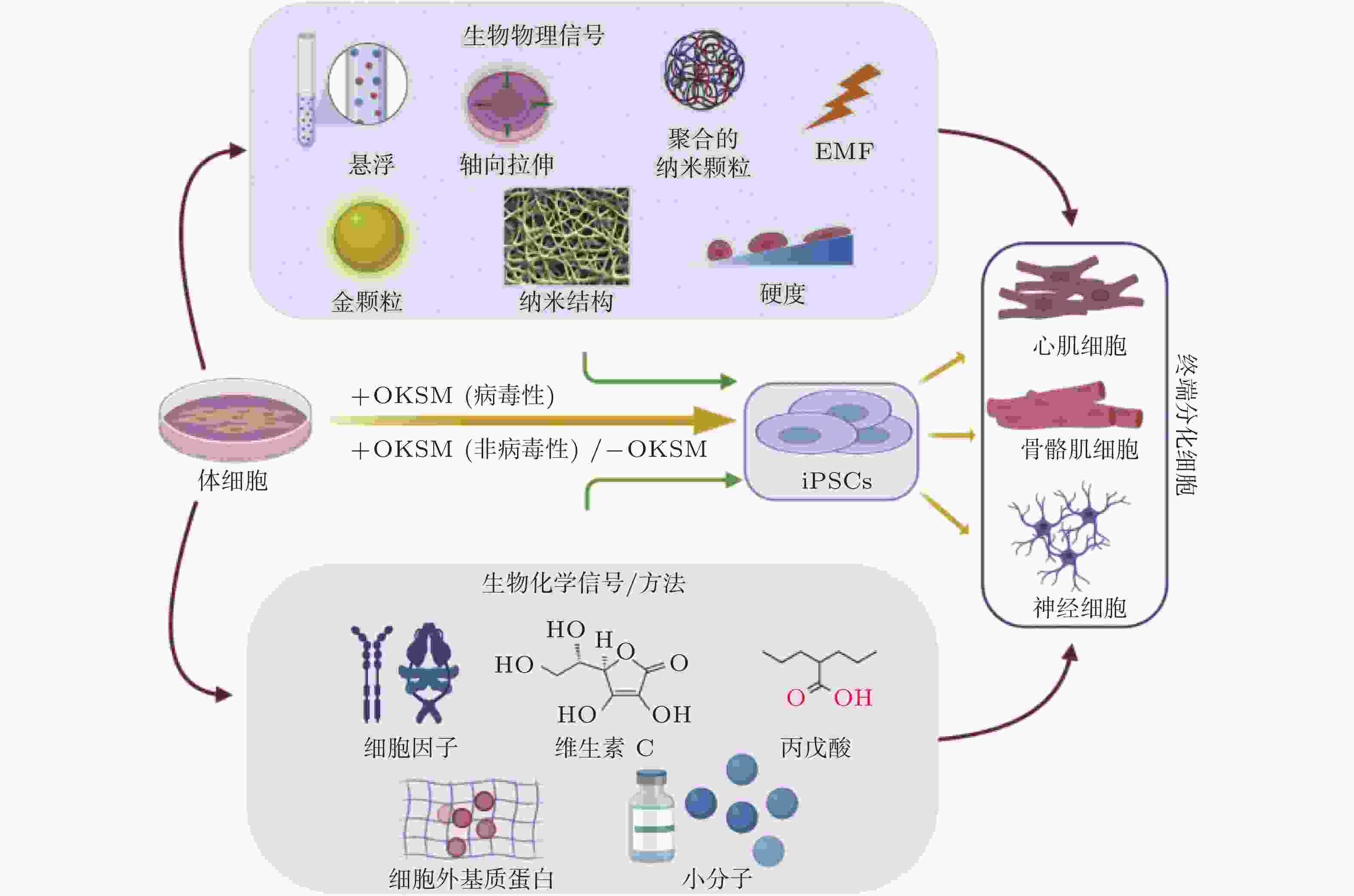
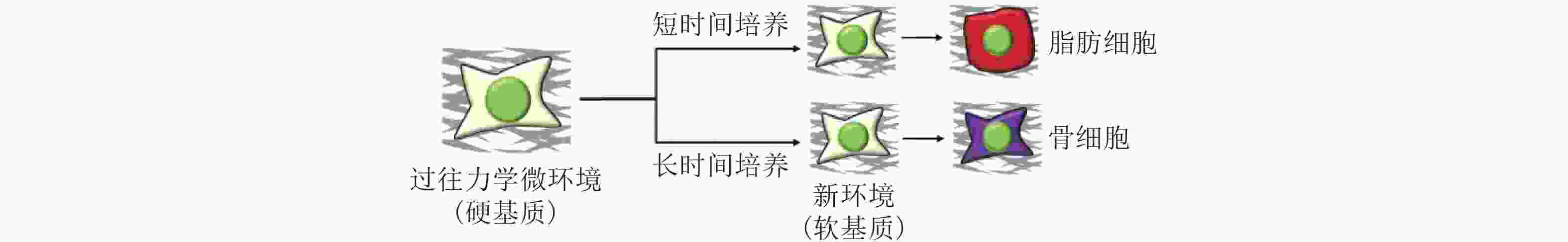
图 51 微环境中的各种生物力学因素诱导细胞命运(Romanazzo et al. 2020)
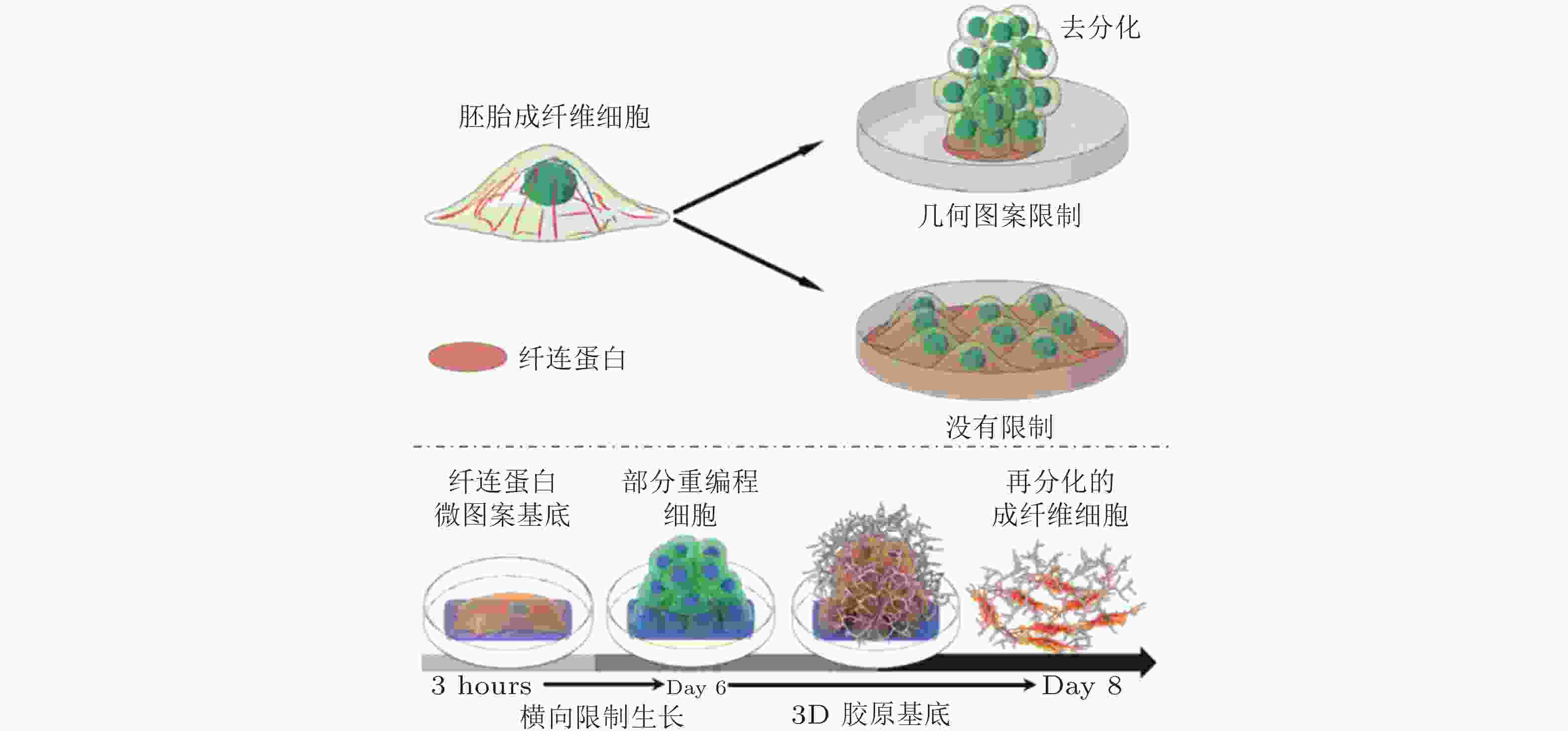
图 52 图案化的基质诱导细胞重编程示意图(Roy et al. 2018, Xu et al. 2014)
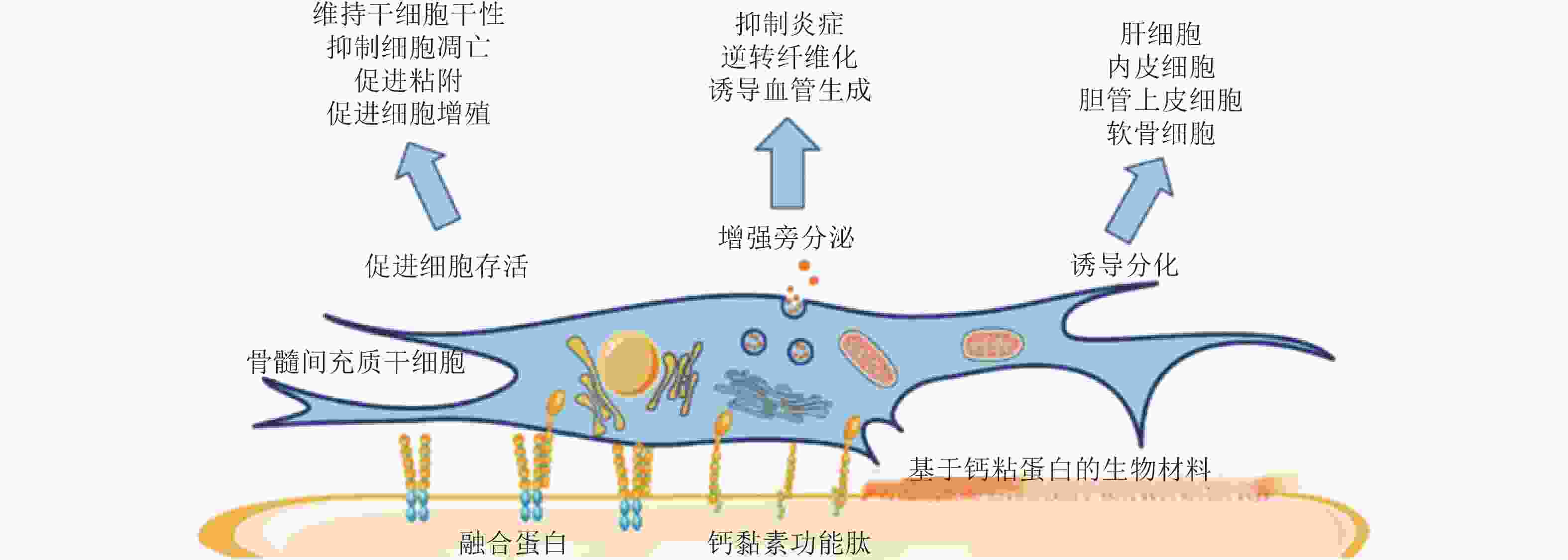
图 54 HAVDI与钙黏素受体重编程硬基质上已分化的间充质干细胞(Zhang et al. 2021)
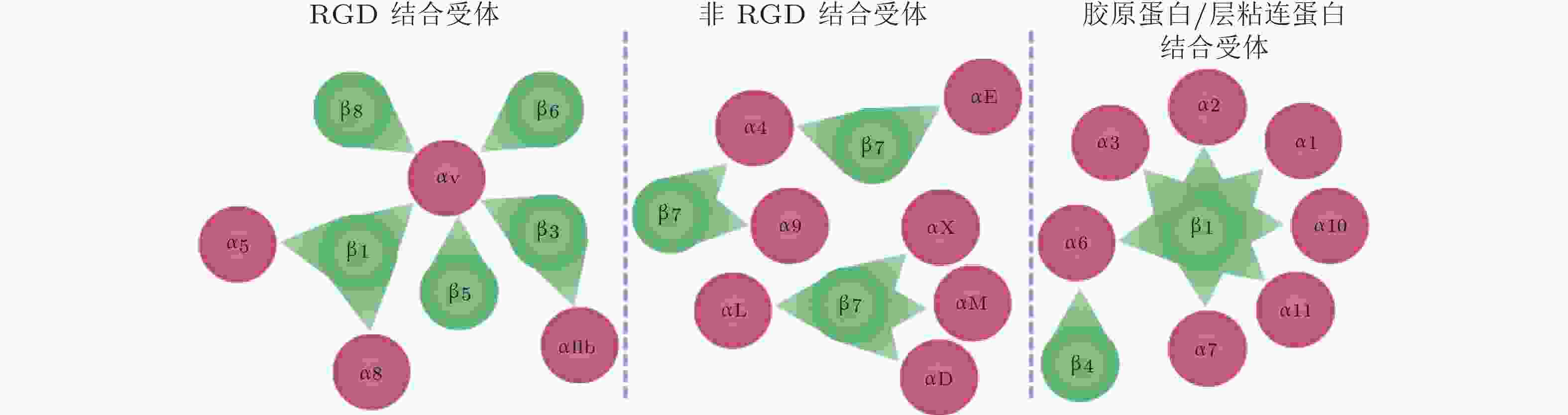
图 55 24种整合类型及其对应的配体类型(Slack et al. 2022)
图 56 基于钙黏素的生物材料调控MSC行为(Zhang et al. 2020)
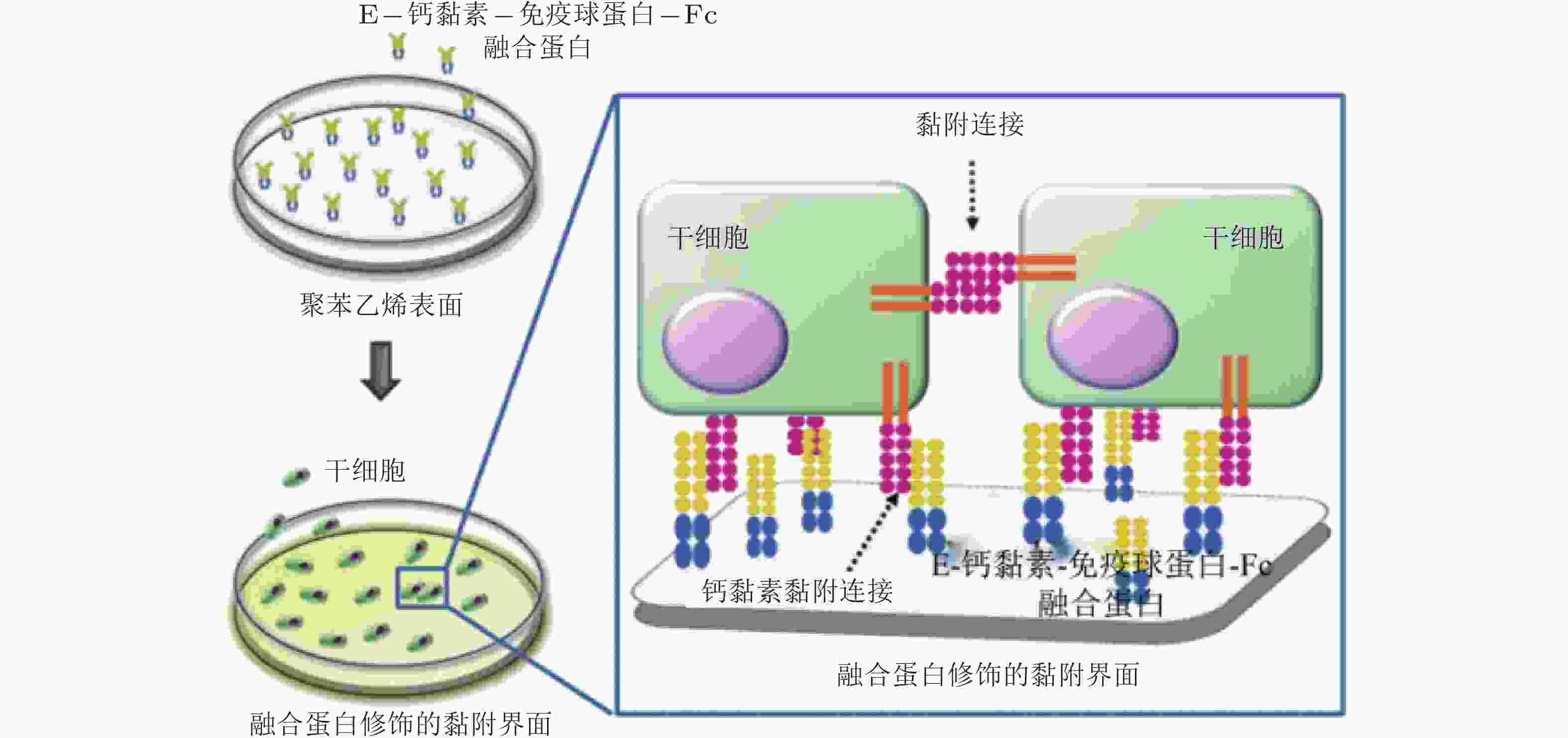
图 57 E-钙黏素表面修饰的材料用于间充质干细胞研究的示意图(Zhang et al. 2016)
图 58 RGD和HAVDI修饰的水凝胶黏附界面示意图(Zhang et al. 2021)
表 1 细胞-ECM界面的力敏感蛋白及功能
细胞-ECM 黏附界面的力敏感蛋白 结构 功能 整合素
(integrin)介导细胞与ECM相互作用, 可以识别、结合ECM中相应的配体, 为细胞黏附提供附着点; 调整细胞骨架结构, 调节蛋白的磷酸化水平和基因表达, 从而调控细胞的运动增殖和凋亡. 踝蛋白
(talin)通过与多种黏着斑蛋白、细胞骨架蛋白及肌动蛋白丝相结合并相互作用, 参与细胞的力-化学信号转导; 在细胞黏附、伸展、运动、增殖、存活等过程中起重要作用. 黏着斑蛋白
(vinculin)激活整合素; 作为细胞骨架肌动蛋白结合蛋白在膜蛋白与细胞骨架结构的偶联以及信号转导中起到了非常重要的作用. 肌动蛋白丝
(F-actin)与肌球蛋白一起作用, 使细胞产生和传导机械力, 并促进细胞运动; 细胞形态维持、细胞运动等细胞基本生物学行为的调控. 表 2 细胞-细胞界面的力敏感蛋白及功能
细胞-细胞黏附界面的
力敏感蛋白结构 功能 钙黏素
(cadherin)介导同型或异型细胞间的黏附相互作用; 与其他黏附蛋白共同形成黏附复合物, 与细胞骨架建立连接, 介导细胞-细胞力学信号转导, 进而调控细胞功能. β-连环蛋白
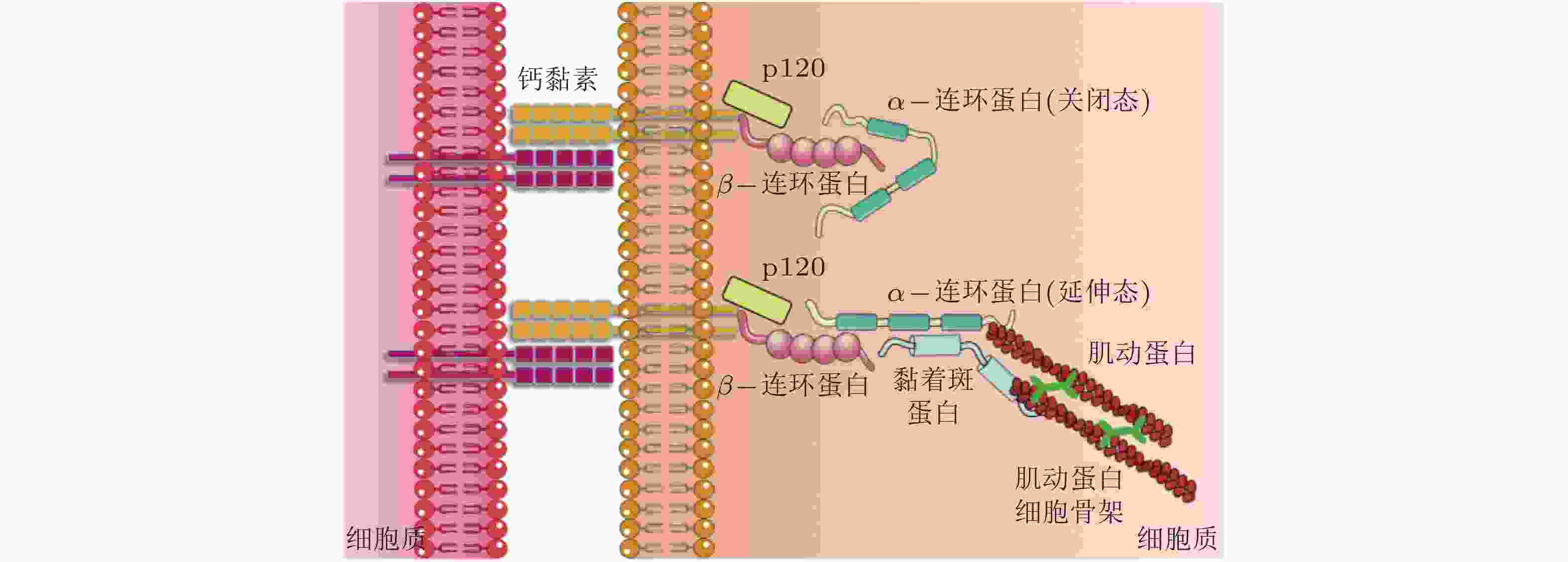
(β-catenin)作为黏附分子, 通过磷酸化调控与钙黏素结合形成功能复合体, 参与细胞间的黏附调节从而影响细胞的活动; 可以募集α-连环蛋白. α-连环蛋白
(α-catenin)作为力敏感蛋白, 受到力学刺激变为激活构型, 暴露出结合位点募集黏着斑蛋白, 进而激活下游信号分子; 调节钙黏素的功能, 其表达下调将影响细胞间黏附复合物的活性. -
[1] 程波, 徐峰. 2021. 考虑细胞外基质黏弹性行为的细胞黏附力学模型. 应用数学和力学, 42: 1074-1080 (Cheng B, Xu F. 2021. A molecular clutch model of cellular adhesion on viscoelastic substrate. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 42: 1074-1080 (in Chinese)).Cheng B, Xu F. A molecular clutch model of cellular adhesion on viscoelastic substrate Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42: 1074-1080 (in Chinese) [2] 姜宗来. 2017. 从生物力学到力学生物学的进展. 力学进展, 47: 309-332 (Jiang Z L. 2017. Advance from biomechanics to mechanobiology. Advances in Mechanics, 47: 309-332 (in Chinese)). doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-16-023(Z l JIANG. 2017. Advance from biomechanics to mechanobiology. Advances in Mechanics, 47: 309-332 (in Chinese)). doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-16-023 [3] 姜宗来. 2021. 发展生物力学 造福人类健康——“十四五”我国生物力学研究发展战略思考. 医用生物力学, 36: 671-675Jiang Z l. 2021. Develop biomechanics, benefit human health: pondering on the development strategy of biomechanical researches during the 14th five-year plan in china . Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 36: 671-675 (in Chinese) [4] 李洋, 洪莉. 2019. 整合素与细胞骨架生物学关系研究进展. 医学综述. 25: 44-48Li Y, Hong L. 2019. Research progress of biological relationship between integrin and cytoskeleton. Medical Recapitulate, 25: 44-48 (in Chinese) [5] 刘璐, 张云霞, 董欣, 刘虎, 曾强成. 2014. 力学环境下成纤维细胞生物学响应研究. 德州学院学报, 30: 23-29Liu L, Zhang Y X, Dong X, Liu H, Zeng Q C. 2014. Research of biological response of fibroblast under the mechanical environment. Journal of Dezhou University, 30: 23-29 (in Chinese) [6] 吕东媛, 周吕文, 龙勉. 2017. 干细胞的生物力学研究. 力学进展, 47: 534-585Lü D Y, Zhou L W, Long M. 2017. Biomechanics of stem cells. Advances in Mechanics, 47: 534-585 (in Chinese) [7] 齐颖新. 2022. 细胞核与应力信号转导. 医用生物力学, 37: 385-388Qi Y X. 2022. Nucleus in mechanotransduction. Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 37: 385-388 (in Chinese) [8] 施兴华, 张路姚, 李博, 冯西桥. 2018. 肿瘤及其微环境的力学问题. 力学进展, 48: 360-409Shi X H, Zhang L Y, Li B, Feng X Q. 2018. The mechanical problems in tumor and tumor microenvironment. Advances in Mechanics, 48: 360-409 (in Chinese) [9] 徐峰, 张晓慧, 鲍雪娇, 赵国旭, 刘付生等. 2018. 基于先进生物材料的心肌细胞力–电微环境体外构建. 力学进展, 48: 320-359Xu F, Zheng X H, Bao X J, Zhao G X, Liu F S, et al. 2018. Engineering mechanical-electrical cell microenvironment in myocardium using advanced biomaterials. Advances in Mechanics, 48: 320-359 (in Chinese) [10] Adhikari S, Moran J, Weddle C, Hinczewski M. 2018. Unraveling the mechanism of the cadherin-catenin-actin catch bond. PLoS Computational Biology, 14: e1006399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006399 [11] Alimperti S, Andreadis S T. 2015. CDH2 and CDH11 act as regulators of stem cell fate decisions. Stem Cell Research, 14: 270-282. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2015.02.002 [12] Alimperti S, You H, George T, Agarwal S K, Andreadis S T. 2014. Cadherin-11 regulates both mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into smooth muscle cells and the development of contractile function in vivo. Journal of Cell Science, 127: 2627-38. [13] Alisafaei F, Jokhun D S, Shivashankar G V, Shenoy V B. 2019. Regulation of nuclear architecture, mechanics, and nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of epigenetic factors by cell geometric constraints. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 116: 13200-13209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902035116 [14] Angulo-Urarte A, van der Wal T, Huveneers S. 2020. Cell-cell junctions as sensors and transducers of mechanical forces. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta:Biomembranes, 1862: 183316. [15] Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, et al. 2013. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through yap/taz regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell, 154: 1047-1059. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.042 [16] Aragona M, Sifrim A, Malfait M, Song Y, Van Herck J, et al. 2020. Mechanisms of stretch-mediated skin expansion at single-cell resolution. Nature, 584: 268-273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2555-7 [17] Aratyn-Schaus Y, Gardel M L. 2010. Transient frictional slip between integrin and the ECM in focal adhesions under myosin II tension. Current Biology, 20: 1145-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.05.049 [18] Ashurst W T, Hoover W G. 1976. Microscopic fracture studies in the two-dimensional triangular lattice. Physical Review B, 14: 1465-1473. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.14.1465 [19] Austen K, Ringer P, Mehlich A, Chrostek-Grashoff A, Kluger C, et al. 2015. Extracellular rigidity sensing by talin isoform-specific mechanical linkages. Nature Cell Biology, 17: 1597-1606. doi: 10.1038/ncb3268 [20] Bachir A I, Horwitz A R, Nelson W J, Bianchini J M. 2017. Actin-based adhesion modules mediate cell interactions with the extracellular matrix and neighboring cells. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 9: a023234. [21] Bajpai A, Tong J, Qian W, Peng Y, Chen W. 2019. The interplay between cell-cell and cell-matrix forces regulates cell migration dynamics. Biophysical Journal, 117: 1795-1804. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.10.015 [22] Balestrini J L, Chaudhry S, Sarrazy V, Koehler A, Hinz B. 2012. The mechanical memory of lung myofibroblasts. Integrative Biology, 4: 410-421. doi: 10.1039/c2ib00149g [23] Bangasser B L, Odde D J. 2013. Master equation-based analysis of a motor-clutch model for cell traction force. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering, 6: 449-459. doi: 10.1007/s12195-013-0296-5 [24] Bangasser B L, Shamsan G A, Chan C E, Opoku K N, Tüzel E, et al. 2017. Shifting the optimal stiffness for cell migration. Nature Communications, 8: 15313. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15313 [25] Bangasser B L, Rosenfeld S S, Odde D J. 2013. Determinants of maximal force transmission in a motor-clutch model of cell traction in a compliant microenvironment. Biophysical Journal, 105: 581-592. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.06.027 [26] Bao M, Xie J, Huck Wilhelm T S. 2018. Recent advances in engineering the stem cell microniche in 3D. Advanced Science, 5: 1800448. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800448 [27] Barbazan J, Matic Vignjevic D. 2019. Cancer associated fibroblasts: is the force the path to the dark side? Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 56: 71-79. [28] Barcelona-Estaje E, Dalby M J, Cantini M, Salmeron-Sanchez M. 2021. You talking to me? Cadherin and integrin crosstalk in biomaterial design. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 10: 2002048. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202002048 [29] Barthes J, Özçelik H, Hindié M, Ndreu-Halili A, Hasan A, Vrana N E. 2014. Cell microenvironment engineering and monitoring for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: the recent advances. BioMed Research International, 2014: 921905. [30] Bauer J, Emon M A B, Staudacher J J, Thomas A L, Zessner-Spitzenberg J, et al. 2020. Increased stiffness of the tumor microenvironment in colon cancer stimulates cancer associated fibroblast-mediated prometastatic activin A signaling. Scientific Reports, 10: 50-50. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55687-6 [31] Bazellières E, Conte V, Elosegui-Artola A, Serra-Picamal X, Bintanel-Morcillo M, et al. 2015. Control of cell-cell forces and collective cell dynamics by the intercellular adhesome. Nature Cell Biology, 17: 409-420. doi: 10.1038/ncb3135 [32] Belardi B, Son S, Felce J H, Dustin M L, Fletcher D A. 2020. Cell–cell interfaces as specialized compartments directing cell function. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 21: 750-764. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00298-7 [33] Bell G I, Dembo M, Bongrand P. 1984. Cell adhesion. Competition between nonspecific repulsion and specific bonding. Biophysical Journal, 45: 1051-64. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84252-6 [34] Bell G I. 1978. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science, 200: 618-27. doi: 10.1126/science.347575 [35] Bennett M, Cantini M, Reboud J, Cooper J M, Roca-Cusachs P, Salmeron-Sanchez M. 2018. Molecular clutch drives cell response to surface viscosity. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 115: 1192-1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710653115 [36] Bertocchi C, Wang Y, Ravasio A, Hara Y, Wu Y, et al. 2017. Nanoscale architecture of cadherin-based cell adhesions. Nature Cell Biology, 19: 28-37. doi: 10.1038/ncb3456 [37] Besser A, Safran S A. 2006. Force-induced adsorption and anisotropic growth of focal adhesions. Biophysical Journal, 90: 3469-84. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.074377 [38] Besser A, Schwarz U S. 2007. Coupling biochemistry and mechanics in cell adhesion: a model for inhomogeneous stress fiber contraction. New Journal of Physics, 9: 425-425. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/9/11/425 [39] Bian L, Guvendiren M, Mauck R L, Burdick J A. 2013. Hydrogels that mimic developmentally relevant matrix and N-cadherin interactions enhance MSC chondrogenesis. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 110: 10117-10122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214100110 [40] Biggs M J P, Fernandez M, Thomas D, Cooper R, Palma M, et al. 2017. The functional response of mesenchymal stem cells to electron-beam patterned elastomeric surfaces presenting micrometer to nanoscale heterogeneous rigidity. Advanced Materials, 29: 1702119. doi: 10.1002/adma.201702119 [41] Blaschuk O W. 2015. N-cadherin antagonists as oncology therapeutics. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences, 370: 20140039. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0039 [42] Boggon T J, Murray J, Chappuis-Flament S, Wong E, Gumbiner B M, Shapiro L. 2002. C-cadherin ectodomain structure and implications for cell adhesion mechanisms. Science, 296: 1308-13. doi: 10.1126/science.1071559 [43] Borghi N, Sorokina M, Shcherbakova O G, Weis W I, Pruitt B L, et al. 2012. E-cadherin is under constitutive actomyosin-generated tension that is increased at cell-cell contacts upon externally applied stretch. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 109: 12568-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204390109 [44] Boscher C, Zheng Y Z, Lakshminarayan R, Johannes L, Dennis J W, et al. 2012. Galectin-3 protein regulates mobility of N-cadherin and GM1 ganglioside at cell-cell junctions of mammary carcinoma cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287: 32940-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.353334 [45] Brasch J, Harrison O J, Honig B, Shapiro L. 2012. Thinking outside the cell: how cadherins drive adhesion. Trends in Cell Biology, 22: 299-310. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.03.004 [46] Breckenridge M T, Desai R A, Yang M T, Fu J, Chen C S. 2014. Substrates with engineered step changes in rigidity induce traction force polarity and durotaxis. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering, 7: 26-34. doi: 10.1007/s12195-013-0307-6 [47] Bretscher M S. 2008. On the shape of migrating cells — a `front-to-back' model. Journal of Cell Science, 121: 2625-2628. doi: 10.1242/jcs.031120 [48] Buckley C D, Tan J, Anderson K L, Hanein D, Volkmann N, et al. 2014. Cell adhesion. The minimal cadherin-catenin complex binds to actin filaments under force. Science, 346: 1254211. doi: 10.1126/science.1254211 [49] Camper L, Hellman U, Lundgren-Akerlund E. 1998. Isolation, cloning, and sequence analysis of the integrin subunit alpha10, a beta1-associated collagen binding integrin expressed on chondrocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273: 20383. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.32.20383 [50] Canel M, Serrels A, Frame M C, Brunton V G. 2013. E-cadherin-integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and metastasis. Journal of Cell Science, 126: 393-401. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100115 [51] Cao X, Lin Y, Driscoll T P, Franco-Barraza J, Cukierman E, et al. 2015. A chemomechanical model of matrix and nuclear rigidity regulation of focal adhesion size. Biophysical Journal, 109: 1807-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.08.048 [52] Caputo K E, Hammer D A. 2005. Effect of microvillus deformability on leukocyte adhesion explored using adhesive dynamics simulations. Biophysical Journal, 89: 187-200. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.054171 [53] Case L B, Waterman C M. 2015. Integration of actin dynamics and cell adhesion by a three-dimensional, mechanosensitive molecular clutch. Nature Cell Biology, 17: 955-963. doi: 10.1038/ncb3191 [54] Caswell P T, Norman J C. 2006. Integrin trafficking and the control of cell migration. Traffic, 7: 14-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00362.x [55] Cavalcanti-Adam E A, Micoulet A, Blummel J, Auernheimer J, Kessler H, Spatz J P. 2006. Lateral spacing of integrin ligands influences cell spreading and focal adhesion assembly. European Journal of Cell Biology, 85: 219-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2005.09.011 [56] Cavallaro U, Christofori G. 2004. Cell adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 4: 118-32. doi: 10.1038/nrc1276 [57] Chan C E, Odde D J. 2008. Traction dynamics of filopodia on compliant substrates. Science, 322: 1687-1691. doi: 10.1126/science.1163595 [58] Chan W-L, Silberstein J, Hai C-M. 2000. Mechanical strain memory in airway smooth muscle. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 278: C895-C904. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2000.278.5.C895 [59] Chandra A, Butler M T, Bear J E, Haugh J M. 2022. Modeling cell protrusion predicts how myosin II and actin turnover affect adhesion-based signaling. Biophysical Journal, 121: 102-118. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.11.2889 [60] Chang B, Svoboda K K H, Liu X. 2019. Cell polarization: from epithelial cells to odontoblasts. European Journal of Cell Biology, 98: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2018.11.003 [61] Changede R, Sheetz M. 2017. Integrin and cadherin clusters: A robust way to organize adhesions for cell mechanics. Bioessays, 39: 1-12. doi: 10.1002/bies.201670013 [62] Changede R, Xu X, Margadant F, Sheetz M P. 2015. Nascent integrin adhesions form on all matrix rigidities after integrin activation. Developmental Cell, 35: 614-621. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.11.001 [63] Charras G, Yap A S. 2018. Tensile forces and mechanotransduction at cell-cell junctions. Current Biology, 28: R445-R457. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.003 [64] Chaudhuri O, Cooper-White J, Janmey P A, Mooney D J, Shenoy V B. 2020. Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour. Nature, 584: 535-546. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2612-2 [65] Chaudhuri O, Gu L, Darnell M, Klumpers D, Bencherif S A, et al. 2015a. Substrate stress relaxation regulates cell spreading. Nature Communications, 6: 6364. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7364 [66] Chaudhuri O, Gu L, Klumpers D, Darnell M, Bencherif S A, et al. 2015b. Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity. Nature Materials, 15: 326-334. [67] Chaudhuri P K, Low B C, Lim C T. 2018. Mechanobiology of tumor growth. Chemical Reviews, 118: 6499-6515. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00042 [68] Chen B, Ji B, Gao H. 2015. Modeling active mechanosensing in cell-matrix interactions. Annual Review of Biophysics, 44: 1-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-051013-023102 [69] Chen C S. 2008. Mechanotransduction - a field pulling together? Journal of Cell Science, 121: 3285-92. [70] Chen D, Hu S, Liu J, Li S. 2019. E-cadherin regulates biological behaviors of neural stem cells and promotes motor function recovery following spinal cord injury. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 17: 2061-2070. [71] Chen J, Newhall J, Xie Z R, Leckband D, Wu Y. 2016. A computational model for kinetic studies of cadherin binding and clustering. Biophysical Journal, 111: 1507-1518. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.08.038 [72] Chen J, Xie Z R, Wu Y. 2014. Computational modeling of the interplay between cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and Wnt signaling pathway. PLoS One, 9: e100702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100702 [73] Chen T, Yuan D, Wei B, Jiang J, Kang J, et al. 2010. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell contact is critical for induced pluripotent stem cell generation. Stem Cells, 28: 1315-25. doi: 10.1002/stem.456 [74] Chen Y, Brasch J, Harrison O J, Bidone T C. 2021. Computational model of E-cadherin clustering under force. Biophysical Journal, 120: 4944-4954. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.10.018 [75] Cheng B, Lin M, Huang G, Li Y, Ji B, et al. 2017. Cellular mechanosensing of the biophysical microenvironment: A review of mathematical models of biophysical regulation of cell responses. Physics of Life Reviews, 22-23: 88-119. doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2017.06.016 [76] Cheng B, Lin M, Li Y, Huang G, Yang H, et al. 2016. An integrated stochastic model of matrix-stiffness-dependent filopodial dynamics. Biophysical Journal, 111: 2051-2061. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.09.026 [77] Cheng B, Wan W T, Huang G, Li Y, Genin G M, et al. 2020. Nanoscale integrin cluster dynamics controls cellular mechanosensing via FAKY397 phosphorylation. Science Advances, 6: eaax1909. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax1909 [78] Choi C K, Xu Y J, Wang B, Zhu M, Zhang L, Bian L. 2015. Substrate coupling strength of integrin-binding ligands modulates adhesion, spreading, and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nano Letters, 15: 6592-600. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02323 [79] Choquet D, Felsenfeld D P, Sheetz M P. 1997. Extracellular matrix rigidity causes strengthening of integrin–cytoskeleton linkages. Cell, 88: 39-48. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81856-5 [80] Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M, Burridge K. 1996. Rho-stimulated contractility drives the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions. Journal of Cell Biology, 133: 1403-15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1403 [81] Cirit M, Krajcovic M, Choi C K, Welf E S, Horwitz A F, Haugh J M. 2010. Stochastic model of integrin-mediated signaling and adhesion dynamics at the leading edges of migrating cells. PLoS Computational Biology, 6: e1000688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000688 [82] Clark K, Langeslag M, Figdor C G, van Leeuwen F N. 2007. Myosin II and mechanotransduction: a balancing act. Trends in Cell Biology, 17: 178-86. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.02.002 [83] Clevers H, Nusse R. 2012. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell, 149: 1192-205. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.012 [84] Cohen D J, Nelson W J. 2018. Secret handshakes: cell–cell interactions and cellular mimics. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 50: 14-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2018.01.001 [85] Cohen M, Klein E, Geiger B, Addadi L. 2003. Organization and adhesive properties of the hyaluronan pericellular coat of chondrocytes and epithelial cells. Biophysical Journal, 85: 1996-2005. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74627-X [86] Collins C, Denisin A K, Pruitt B L, Nelson W J. 2017. Changes in E-cadherin rigidity sensing regulate cell adhesion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114: E5835. [87] Constantina B, Cohen D M, Bankston L A, Bobkov A A, Cadwell G W, et al. 2004. Structural basis for vinculin activation at sites of cell adhesion. Nature, 430: 583. doi: 10.1038/nature02610 [88] Copos C A, Walcott S, Del Álamo J C, Bastounis E, Mogilner A, Guy R D. 2017. Mechanosensitive adhesion explains stepping motility in amoeboid cells. Biophysical Journal, 112: 2672-2682. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.04.033 [89] Corallino S, Malabarba M G, Zobel M, Di Fiore P P, Scita G. 2015. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal plasticity harnesses endocytic circuitries. Frontiers in Oncology, 5: 45. [90] Cosgrove B D, Mui K L, Driscoll T P, Caliari S R, Mehta K D, et al. 2016. N-cadherin adhesive interactions modulate matrix mechanosensing and fate commitment of mesenchymal stem cells. Nature Materials, 15: 1297-1306. doi: 10.1038/nmat4725 [91] Craig E M, Stricker J, Gardel M, Mogilner A. 2015. Model for adhesion clutch explains biphasic relationship between actin flow and traction at the cell leading edge. Physical Biology, 12: 035002. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/12/3/035002 [92] Dalby M J, Gadegaard N, Oreffo R O. 2014. Harnessing nanotopography and integrin-matrix interactions to influence stem cell fate. Nature Materials, 13: 558-69. doi: 10.1038/nmat3980 [93] D'Arcangelo E, Wu N C, Cadavid J L, McGuigan A P. 2020. The life cycle of cancer-associated fibroblasts within the tumour stroma and its importance in disease outcome. British Journal of Cancer, 122: 931-942. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0705-1 [94] Das R K, Gocheva V, Hammink R, Zouani O F, Rowan A E. 2015. Stress-stiffening-mediated Stem-Cell Commitment Switch in Soft Responsive Hydrogels. Nature Materials, 15: 318. [95] de Beco S, Amblard F, Coscoy S. 2012. New insights into the regulation of e-cadherin distribution by endocytosis. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, 295: 63-108. [96] De R, Zemel A, Safran S A. 2010. Theoretical concepts and models of cellular mechanosensing. Methods in Cell Biology, 98: 143-175. [97] de Rooij J. 2014. Cadherin adhesion controlled by cortical actin dynamics. Nature Cell Biology, 16: 508-510. doi: 10.1038/ncb2980 [98] Dembo M, Torney D C, Saxman K, Hammer D. 1988. The reaction-limited kinetics of membrane-to-surface adhesion and detachment. Proceedings of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences, 234: 55-83. [99] Deng Z, Yan W, Dai X, Chen M, Qu Q, et al. 2021. N-cadherin regulates the odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via β-catenin activity. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 9: 661116. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.661116 [100] Dingal P C D P, Bradshaw A M, Cho S, Raab M, Buxboim A, et al. 2015. Fractal heterogeneity in minimal matrix models of scars modulates stiff-niche stem-cell responses via nuclear exit of a mechanorepressor. Nature Materials, 14: 951-960. doi: 10.1038/nmat4350 [101] Douezan S, Dumond J, Brochard-Wyart F. 2012. Wetting transitions of cellular aggregates induced by substrate rigidity. Soft Matter, 8: 4578-4583. doi: 10.1039/c2sm07418d [102] Du V, Luciani N, Richard S, Mary G, Gay C, et al. 2017. A 3D magnetic tissue stretcher for remote mechanical control of embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature Communications, 8: 400. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00543-2 [103] Dumbauld D W, Lee T T, Singh A, Scrimgeour J, Gersbach C A, et al. 2013. How vinculin regulates force transmission. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 110: 9788-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216209110 [104] Dumortier Julien G, Le Verge-Serandour M, Tortorelli Anna F, Mielke A, de Plater L, et al. 2019. Hydraulic fracturing and active coarsening position the lumen of the mouse blastocyst. Science, 365: 465-468. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw7709 [105] Elbediwy A, Vincent-Mistiaen Z I, Spencer-Dene B, Stone R K, Boeing S, et al. 2016. Integrin signalling regulates YAP and TAZ to control skin homeostasis. Development, 143: 1674-87. [106] Elosegui-Artola A, Andreu I, Beedle A E M, Lezamiz A, Uroz M, et al. 2017. Force triggers yap nuclear entry by regulating transport across nuclear pores. Cell, 171: 1397-1410 e14. [107] Elosegui-Artola A, Bazellières E, Allen M D, Andreu I, Oria R, S et al. 2014. Rigidity sensing and adaptation through regulation of integrin types. Nature Materials, 13: 631-637. doi: 10.1038/nmat3960 [108] Elosegui-Artola A, Oria R, Chen Y, Kosmalska A, Pérez-González C, et al. 2016. Mechanical regulation of a molecular clutch defines force transmission and transduction in response to matrix rigidity. Nature Cell Biology, 18: 540. doi: 10.1038/ncb3336 [109] Elosegui-Artola A, Trepat X, Roca-Cusachs P. 2018. Control of mechanotransduction by molecular clutch dynamics. Trends in Cell Biology, 28: 356-367. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.01.008 [110] Engler A J, Sen S, Sweeney H L, Discher D E. 2006. Matrix Elasticity Directs Stem Cell Lineage Specification. Cell, 126: 677-689. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044 [111] Engler A, Bacakova L, Newman C, Hategan A, Griffin M, Discher D. 2004. Substrate compliance versus ligand density in cell on gel responses. Biophysical Journal, 86: 617-628. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74140-5 [112] Espina J A, Marchant C L, Barriga E H. 2021. Durotaxis: the mechanical control of directed cell migration. FEBS Journal, 289: 2736-2754. [113] Even-Ram S, Artym V, Yamada K M. 2006. Matrix control of stem cell fate. Cell, 126: 645-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.008 [114] Fang J, Hsueh Y Y, Soto J, Sun W, Wang J, et al. 2020. Engineering biomaterials with micro/nanotechnologies for cell reprogramming. ACS Nano, 14: 1296-1318. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b04837 [115] Feng Q, Gao H, Wen H, Huang H, Li Q, et al. 2020. Engineering the cellular mechanical microenvironment to regulate stem cell chondrogenesis: Insights from a microgel model. Acta Biomater, 113: 393-406. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.06.046 [116] Fillingham I, Gingras A, Papagrigoriou E, Patel B, Emsley J, et al. 2005. A vinculin binding domain from the talin rod unfolds to form a complex with the vinculin head. Structure, 13: 65-74. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.11.006 [117] Fiore V F, Krajnc M, Quiroz F G, Levorse J, Pasolli H A, et al. 2020. Mechanics of a multilayer epithelium instruct tumour architecture and function. Nature, 585: 433-439. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2695-9 [118] Foster C T, Gualdrini F, Treisman R. 2017. Mutual dependence of the MRTF-SRF and YAP-TEAD pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts is indirect and mediated by cytoskeletal dynamics. Genes and Development, 31: 2361-2375. doi: 10.1101/gad.304501.117 [119] Francesco R, Antonio G, Manlio B, Alfonso B. 2010. From cell-ECM interactions to tissue engineering. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 199: 174-180. [120] Friedl P, Gilmour D. 2009. Collective cell migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 10: 445-457. doi: 10.1038/nrm2720 [121] Friedl P, Mayor R. 2017. Tuning collective cell migration by cell-cell junction regulation. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 9: a029199. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029199 [122] Friedland J C, Lee M H, Boettiger D. 2009. Mechanically activated integrin switch controls α5β1 function. Science, 323: 642. doi: 10.1126/science.1168441 [123] Frisch T, Thoumine O. 2002. Predicting the kinetics of cell spreading. Journal of Biomechanics, 35: 1137-1141. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9290(02)00075-1 [124] Gaggioli C, Hooper S, Hidalgo-Carcedo C, Grosse R, Marshall J F, et al. 2007. Fibroblast-led collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nature Cell Biology, 9: 1392-1400. doi: 10.1038/ncb1658 [125] Garcia M A, Nelson W J, Chavez N. 2018. Cell-cell junctions organize structural and signaling networks. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 10. [126] Gardel M L, Sabass B, Ji L, Danuser G, Schwarz U S, Waterman C M. 2008. Traction stress in focal adhesions correlates biphasically with actin retrograde flow speed. Journal of Cell Biology, 183: 999-1005. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200810060 [127] Gauthier N C, Roca-Cusachs P. 2018. Mechanosensing at integrin-mediated cell-matrix adhesions: from molecular to integrated mechanisms. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 50: 20-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.12.014 [128] Geiger B, Spatz J P, Bershadsky A D. 2009. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 10: 21-33. doi: 10.1038/nrm2593 [129] Ghassemi S, Meacci G, Liu S, Gondarenko A A, Mathur A, et al. 2012. Cells test substrate rigidity by local contractions on submicrometer pillars. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 109: 5328-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119886109 [130] Ghibaudo M, Saez A, Trichet L, Xayaphoummine A, Browaeys J, et al. 2008. Traction forces and rigidity sensing regulate cell functions. Soft Matter, 4: 1836-1843. doi: 10.1039/b804103b [131] Giannone G. 2015. Super-resolution links vinculin localization to function in focal adhesions. Nature Cell Biology, 17: 845-847. doi: 10.1038/ncb3196 [132] Gkretsi V, Stylianopoulos T. 2018. Cell adhesion and matrix stiffness: coordinating cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Frontiers in Oncology, 8: 145-145. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00145 [133] Gong Z, Szczesny S E, Caliari S R, Charrier E E, Chaudhuri O, et al. 2018. Matching material and cellular timescales maximizes cell spreading on viscoelastic substrates. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 115: E2686-E2695. [134] Gooding J M, Yap K L, Ikura M. 2004. The cadherin–catenin complex as a focal point of cell adhesion and signalling: new insights from three‐dimensional structures. Bioessays, 26: 497-511. doi: 10.1002/bies.20033 [135] Gough R E, Goult B T. 2018. The tale of two talins - two isoforms to fine-tune integrin signalling. Febs Letters, 592: 2108-2125. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13081 [136] Grolman J M, Weinand P, Mooney D J. 2020. Extracellular matrix plasticity as a driver of cell spreading. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 117: 25999-26007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008801117 [137] Guan X. 2015. Cancer metastases: challenges and opportunities. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 5: 402-418. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.005 [138] Guilluy C, Swaminathan V, Garcia-Mata R, Timothy O’Brien E, Superfine R, Burridge K. 2011. The Rho GEFs LARG and GEF-H1 regulate the mechanical response to force on integrins. Nature Cell Biology, 13: 722-727. doi: 10.1038/ncb2254 [139] Gul I S, Hulpiau P, Saeys Y, van Roy F. 2017. Evolution and diversity of cadherins and catenins. Experimental cell research, 358: 3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.03.001 [140] Hadden W J, Young J L, Holle A W, McFetridge M L, Kim D Y, et al. 2017. Stem cell migration and mechanotransduction on linear stiffness gradient hydrogels. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 114: 5647-5652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618239114 [141] Haining A W, Lieberthal T J, Del Río Hernández A. 2016. Talin: a mechanosensitive molecule in health and disease. FASEB Journal, 30: 2073-85. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500080R [142] Hamidi H, Ivaska J. 2018. Every step of the way: integrins in cancer progression and metastasis. Nature Reviews Cancer, 18: 533-548. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0038-z [143] Han S-B, Kim J-K, Lee G, Kim D-H. 2020. Mechanical properties of materials for stem cell differentiation. Advanced Biosystems, 4: 2000247. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202000247 [144] Harland B, Walcott S, Sun S X. 2011. Adhesion dynamics and durotaxis in migrating cells. Physical Biology, 8: 015011-015011. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/8/1/015011 [145] Harrison O J, Bahna F, Katsamba P S, Jin X, Brasch J, et al. 2010. Two-step adhesive binding by classical cadherins. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 17: 348-57. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1784 [146] Hoffman B D, Grashoff C, Schwartz M A. 2011. Dynamic molecular processes mediate cellular mechanotransduction. Nature, 475: 316-23. doi: 10.1038/nature10316 [147] Holmes W R, Edelstein-Keshet L. 2012. A comparison of computational models for eukaryotic cell shape and motility. PLoS Computational Biology, 8: e1002793. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002793 [148] Hong S, Troyanovsky R B, Troyanovsky S M. 2011. Cadherin exits the junction by switching its adhesive bond. Journal of Cell Biology, 192: 1073-83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201006113 [149] Hou Y, Yu L, Xie W, Camacho L C, Zhang M, Chu Z, et al. 2020. Surface roughness and substrate stiffness synergize to drive cellular mechanoresponse. Nano Lettersers, 20: 748-757. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b04761 [150] Houk A R, Jilkine A, Mejean C O, Boltyanskiy R, Dufresne E R, et al. 2012. Membrane tension maintains cell polarity by confining signals to the leading edge during neutrophil migration. Cell, 148: 175-88. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.050 [151] Hu S, Chen T-H, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Lam R H W. 2018. Protein–substrate adhesion in microcontact printing regulates cell behavior. Langmuir, 34: 1750-1759. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02935 [152] Huang C, Akaishi S, Ogawa R. 2012. Mechanosignaling pathways in cutaneous scarring. Archives of Dermatological Research, 304: 589-597. doi: 10.1007/s00403-012-1278-5 [153] Huang G, Li F, Zhao X, Ma Y, Li Y, et al. 2017. Functional and biomimetic materials for engineering of the three-dimensional cell microenvironment. Chemical Reviews, 117: 12764-12850. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00094 [154] Huang J, Peng X, Xiong C, Fang J. 2011. Influence of substrate stiffness on cell-substrate interfacial adhesion and spreading: a mechano-chemical coupling model. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 355: 503-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.12.055 [155] Huber A H, Weis W I. 2001. The structure of the β-catenin/e-cadherin complex and the molecular basis of diverse ligand recognition by β-catenin. Cell, 105: 391-402. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00330-0 [156] Humphries J D, Pengbo W, Charles S, Benny G, Humphries M J, Christoph B. 2007. Vinculin controls focal adhesion formation by direct interactions with talin and actin. Journal of Cell Biology, 179: 1043-1057. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200703036 [157] Hynes R O. 2002. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell, 110: 673-687. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00971-6 [158] Isomursu A, Park K-Y, Hou J, Cheng B, Shamsan G, et al. 2022. Negative durotaxis: cell movement toward softer environments. Nature Materials. [159] Jannie K M, Ellerbroek S M, Zhou D W, Sophia C, Crompton D J, et al. 2015. Vinculin-dependent actin bundling regulates cell migration and traction forces. Biophysical Journal, 465: 383-93. [160] Jansen K A, Atherton P, Ballestrem C. 2017. Mechanotransduction at the cell-matrix interface. Seminars in Cell and Developmental Biology, 71: 75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.07.027 [161] Jiang H, Qian J, Lin Y, Ni Y, He L. 2015. Aggregation dynamics of molecular bonds between compliant materials. Soft Matter, 11: 2812-20. doi: 10.1039/C4SM02903H [162] Jin J-K, Tien P-C, Cheng C-J, Song J H, Huang C, et al. 2015. Talin1 phosphorylation activates β1 integrins: a novel mechanism to promote prostate cancer bone metastasis. Oncogene, 34: 1811-1821. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.116 [163] Judokusumo E, Tabdanov E, Kumari S, Dustin M L, Kam L C. 2012. Mechanosensing in T lymphocyte activation. Biophysical Journal, 102: L5-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.12.011 [164] Kaunas R, Usami S, Chien S. 2006. Regulation of stretch-induced JNK activation by stress fiber orientation. Cellular Signalling, 18: 1924-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.02.008 [165] Kechagia J Z, Ivaska J, Roca-Cusachs P. 2019. Integrins as biomechanical sensors of the microenvironment. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 20: 457-473. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0134-2 [166] Khalil A A, Friedl P. 2010. Determinants of leader cells in collective cell migration. Integrative Biology (Camb) , 2: 568-74. doi: 10.1039/c0ib00052c [167] Killaars A R, Grim J C, Walker C J, Hushka E A, Brown T E, Anseth K S. 2019. Extended exposure to stiff microenvironments leads to persistent chromatin remodeling in human mesenchymal stem cells. Advanced Science, 6: 1801483. doi: 10.1002/advs.201801483 [168] Kim D-H, Khatau S B, Feng Y, Walcott S, Sun S X, et al. 2012. Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing. Scientific Reports, 2: 555. doi: 10.1038/srep00555 [169] Kim J-K, Louhghalam A, Lee G, Schafer B W, Wirtz D, Kim D-H. 2017. Nuclear lamin A/C harnesses the perinuclear apical actin cables to protect nuclear morphology. Nature Communications, 8: 2123. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02217-5 [170] Kong D, Ji B, Dai L. 2010. Stabilizing to disruptive transition of focal adhesion response to mechanical forces. Journal of Biomechanics, 43: 2524-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.05.019 [171] Kourtidis A, Ngok S P, Anastasiadis P Z. 2013. Chapter eighteen - p120 catenin: an essential regulator of cadherin stability, adhesion-induced signaling, and cancer progression. Progress in molecular biology and translational science, 116: 409-432. [172] Krasik E F, Caputo K E, Hammer D A. 2008. Adhesive dynamics simulation of neutrophil arrest with stochastic activation. Biophysical Journal, 95: 1716-28. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.119677 [173] Kumar S, Parekh S H. 2021. Molecular control of the interfacial fibronectin structure on graphene oxide steers cell fate. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 13: 2346-2359. [174] Kuninty P R, Bansal R, De Geus S W L, Mardhian D F, Schnittert J, et al. 2019. ITGA5 inhibition in pancreatic stellate cells attenuates desmoplasia and potentiates efficacy of chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Science Advances, 5: eaax2770. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax2770 [175] Kuo C H, Xian J, Brenton J D, Franze K, Sivaniah E. 2012. Complex stiffness gradient substrates for studying mechanotactic cell migration. Advanced Materials, 24: 6059-64. doi: 10.1002/adma.201202520 [176] Kwa M Q, Herum K M, Brakebusch C. 2019. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: how do they contribute to metastasis? Clinical & Experimental Metastasi, 36: 71-86. [177] Kwon M Y, Vega S L, Gramlich W M, Kim M, Mauck R L, Burdick J A. 2018. Dose and timing of n-cadherin mimetic peptides regulate msc chondrogenesis within hydrogels. Advanced healthcare materials, 7: e1701199. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201701199 [178] Labernadie A, Kato T, Brugues A, Serra-Picamal X, Derzsi S, et al. 2017. A mechanically active heterotypic E-cadherin/N-cadherin adhesion enables fibroblasts to drive cancer cell invasion. Nature Cell Biology, 19: 224-237. doi: 10.1038/ncb3478 [179] Lachowski D, Cortes E, Robinson B, Rice A, Rombouts K, Del Río Hernández A E. 2018. FAK controls the mechanical activation of YAP, a transcriptional regulator required for durotaxis. FASEB Journal, 32: 1099-1107. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700721R [180] Ladoux B, Mege R M. 2017. Mechanobiology of collective cell behaviours. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 18: 743-757. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.98 [181] Ladoux B, Anon E, Lambert M, Rabodzey A, Hersen P, et al. 2010. Strength Dependence of Cadherin-Mediated Adhesions. Biophysical Journal, 98: 534-542. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.10.044 [182] Ladoux B, Mège R-M, Trepat X. 2016. Front–rear polarization by mechanical cues: from single cells to tissues. Trends in Cell Biology, 26: 420-433. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.02.002 [183] Ladoux B, Nelson W J, Yan J, Mège R M. 2015. The mechanotransduction machinery at work at adherens junctions. Integrative Biology (Camb) , 7: 1109-19. doi: 10.1039/c5ib00070j [184] le Duc Q, Shi Q, Blonk I, Sonnenberg A, Wang N, et al. 2010. Vinculin potentiates E-cadherin mechanosensing and is recruited to actin-anchored sites within adherens junctions in a myosin II-dependent manner. Journal of Cell Biology, 189: 1107-15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201001149 [185] Leckband D E, Rooij J D. 2014. Cadherin adhesion and mechanotransduction. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 30: 291-315. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100913-013212 [186] Leckband D E, Duc Q L, Ning W, Rooij J D. 2011. Mechanotransduction at cadherin-mediated adhesions. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 23: 523-530. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.08.003 [187] Lee H-p, Stowers R, Chaudhuri O. 2019. Volume expansion and trpv4 activation regulate stem cell fate in three-dimensional microenvironments. Nature Communications, 10: 529. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08465-x [188] Lee J W, An H, Lee K Y. 2017. Introduction of N-cadherin-binding motif to alginate hydrogels for controlled stem cell differentiation. Colloids and Surfaces, B:Biointerfaces, 155: 229-237. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.04.014 [189] Legate K R, Wickström S A, Fässler R. 2009. Genetic and cell biological analysis of integrin outside-in signaling. Genes & Development, 23: 397-418. [190] Lei K, Kurum A, Tang L. 2020. Mechanical immunoengineering of t cells for therapeutic applications. Accounts of Chemical Research, 53: 2777-2790. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00486 [191] Leiphart R J, Chen D, Peredo A P, Loneker A E, Janmey P A. 2019. Mechanosensing at cellular interfaces. Langmuir, 35: 7509-7519. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02841 [192] Levental K R, Yu H, Kass L, Lakins J N, Egeblad M, et al. 2009. Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing integrin signaling. Cell, 139: 891-906. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.027 [193] Li C X, Talele N P, Boo S, Koehler A, Knee-Walden E, et al. 2016. Microrna-21 preserves the fibrotic mechanical memory of mesenchymal stem cells. Nature Materials, 16: 379. [194] Li J, Di Russo J, Hua X, Chu Z, Spatz J P, Wei Q. 2019. Surface immobilized e-cadherin mimetic peptide regulates the adhesion and clustering of epithelial cells. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 8: 1801384. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201801384 [195] Li J, Li X, Zhang J, Kawazoe N, Chen G. 2017. Induction of chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by biomimetic gold nanoparticles with tunable rgd density. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 6. 28489328 [196] Li L, Bennett S A L, Wang L. 2012. Role of E-cadherin and other cell adhesion molecules in survival and differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Adhesion & Migration, 6: 59-70. [197] Li R, Xu J, Wong D S H, Li J, Zhao P, Bian L. 2017. Self-assembled N-cadherin mimetic peptide hydrogels promote the chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells through inhibition of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biomaterials, 145: 33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.08.031 [198] Li S, Wang X, Cao B, Ye K, Li Z, Ding J. 2015. Effects of nanoscale spatial arrangement of arginine-glycine-aspartate peptides on dedifferentiation of chondrocytes. Nano Letters, 15: 7755-65. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04043 [199] Li Y, Kilian K A. 2015. Bridging the gap: from 2d cell culture to 3d microengineered extracellular matrices. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 4: 2780-2796. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201500427 [200] Li Y, Altorelli N L, Bahna F, Honig B, Shapiro L, Palmer A G. 2013. Mechanism of E-cadherin dimerization probed by NMR relaxation dispersion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110: 16462-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314303110 [201] Li Y, Mao A S, Seo B R, Zhao X, Gupta S K, et al. 2020. Compression-induced dedifferentiation of adipocytes promotes tumor progression. Science Advances, 6: eaax5611. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax5611 [202] Li Z, Shen D, Hu S, Su T, Huang K, et al. 2018. Pretargeting and bioorthogonal click chemistry-mediated endogenous stem cell homing for heart repair. ACS Nano, 12: 12193-12200. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05892 [203] Lin S Z, Li B, Lan G, Feng X Q. 2017. Activation and synchronization of the oscillatory morphodynamics in multicellular monolayer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114: 8157-8162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705492114 [204] Ling K, Doughman R L, Firestone A J, Bunce M W, Anderson R A. 2002. Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase targets and regulates focal adhesions. Nature, 420: 89-93. doi: 10.1038/nature01082 [205] Ling K, Doughman R L, Iyer V V, Firestone A J, Bairstow S F, et al. 2003. Tyrosine phosphorylation of type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase by Src regulates an integrin–talin switch. Journal of Cell Biology, 163: 1339-1349. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200310067 [206] Liu J, Tan Y, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Xu P, et al. 2012. Soft fibrin gels promote selection and growth of tumorigenic cells. Nature materials, 11: 734-741. doi: 10.1038/nmat3361 [207] Liu L, Zhang S X, Liao W, Farhoodi H P, Wong C W, et al. 2017. Mechanoresponsive stem cells to target cancer metastases through biophysical cues. Science Translational Medicine, 9: eaan2966. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aan2966 [208] Liu Y A, Liang B Y, Guan Y, You J, Zhu L, et al. 2015. Loss of N-cadherin is associated with loss of E-cadherin expression and poor outcomes of liver resection in hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Surgical Research, 194: 167-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.09.031 [209] Liu Z, Tan J L, Cohen D M, Yang M T, Sniadecki N J, et al. 2010. Mechanical tugging force regulates the size of cell—cell junctions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107: 9944-9949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914547107 [210] Lo C-M, Wang H-B, Dembo M, Wang Y-l. 2000. Cell movement is guided by the rigidity of the substrate. Biophysical Journal, 79: 144-152. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76279-5 [211] Lou J, Yago T, Klopocki A G, Mehta P, Chen W, et al. 2006. Flow-enhanced adhesion regulated by a selectin interdomain hinge. Journal of Cell Biology, 174: 1107-17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200606056 [212] Lyons A J, Jones J. 2007. Cell adhesion molecules, the extracellular matrix and oral squamous carcinoma. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, 36: 671-679. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2007.04.002 [213] Ma R, Kellner A V, Ma V P, Su H, Deal B R, et al. 2019. DNA probes that store mechanical information reveal transient piconewton forces applied by T cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116: 16949-16954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904034116 [214] Ma Y, Lin M, Huang G, Li Y, Wang S, et al. 2018. 3D spatiotemporal mechanical microenvironment: a hydrogel-based platform for guiding stem cell fate. Advanced Materials, 30: 1705911. doi: 10.1002/adma.201705911 [215] Madl C M, LeSavage B L, Dewi R E, Dinh C B, Stowers R S, et al. 2017. Maintenance of neural progenitor cell stemness in 3d hydrogels requires matrix remodelling. Nature Materials, 16: 1233-1242. doi: 10.1038/nmat5020 [216] Madl C M, LeSavage B L, Dewi R E, Lampe K J, Heilshorn S C. 2019. Matrix remodeling enhances the differentiation capacity of neural progenitor cells in 3D hydrogels. Advanced Materials, 6: 1801716. [217] Manibog K, Li H, Rakshit S, Sivasankar S. 2014. Resolving the molecular mechanism of cadherin catch bond formation. Nature Communications, 5: 3941. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4941 [218] Manibog K, Sankar K, Kim S A, Zhang Y, Jernigan R L, Sivasankar S. 2016. Molecular determinants of cadherin ideal bond formation: Conformation-dependent unbinding on a multidimensional landscape. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113: E5711-20. [219] Mao C Y, Wang Y G, Zhang X, Zheng X Y, Tang T T, Lu E Y. 2016. Double-edged-sword effect of IL-1β on the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells via crosstalk between the NF-κB, MAPK and BMP/Smad signaling pathways. Cell Death & Disease, 7: e2296. [220] Martino F, Perestrelo A R, Vinarsky V, Pagliari S, Forte G. 2018. Cellular mechanotransduction: from tension to function. Frontiers in Physiology, 9: 824. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00824 [221] Maruthamuthu V, Aratyn-Schaus Y and Gardel M L. 2010. Conserved F-actin dynamics and force transmission at cell adhesions. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 22: 583-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.07.010 [222] Maruthamuthu V, Sabass B, Schwarz U S, Gardel M L, Chien S. 2011. Cell-ECM traction force modulates endogenous tension at cell-cell contacts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108: 4708-4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011123108 [223] Mayor R, Etienne-Manneville S. 2016. The front and rear of collective cell migration. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 17: 97-109. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.14 [224] Mège R M, Gavard J, Lambert M. 2006. Regulation of cell–cell junctions by the cytoskeleton. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 18: 541-548. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.08.004 [225] Miller K D, Nogueira L, Mariotto A B, Rowland J H, Yabroff K R, et al. 2019. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics. CA:A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 69: 363-385. doi: 10.3322/caac.21565 [226] Mitchison T, Kirschner M. 1988. Cytoskeletal dynamics and nerve growth. Neuron, 1: 761-72. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90124-9 [227] Mitra S K, Schlaepfer D D. 2006. Integrin-regulated FAK–Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 18: 516-523. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.08.011 [228] Miyazaki K, Oyanagi J, Hoshino D, Togo S, Kumagai H, Miyagi Y. 2019. Cancer cell migration on elongate protrusions of fibroblasts in collagen matrix. Scientific Reports, 9: 292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36646-z [229] Mongera A, Rowghanian P, Gustafson H J, Shelton E, Kealhofer D A, et al. 2018. A fluid-to-solid jamming transition underlies vertebrate body axis elongation. Nature, 561: 401-405. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0479-2 [230] Muhamed I, Wu J, Sehgal P, Kong X, Tajik A, et al. 2016. E-cadherin-mediated force transduction signals regulate global cell mechanics. Journal of Cell Science, 129: 1843-54. [231] Mui K L, Chen C S, Assoian R K. 2016. The mechanical regulation of integrin-cadherin crosstalk organizes cells, signaling and forces. Journal of Cell Science, 129: 1093-1100. [232] Najafi M, Farhood B, Mortezaee K. 2019. Extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness and degradation as cancer drivers. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120: 2782-2790. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27681 [233] Nasrollahi S, Walter C, Loza A J, Schimizzi G V, Longmore G D, Pathak A. 2017. Past matrix stiffness primes epithelial cells and regulates their future collective migration through a mechanical memory. Biomaterials, 146: 146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.09.012 [234] Nemec S, Kilian K A. 2021. Materials control of the epigenetics underlying cell plasticity. Nature Reviews Materials, 6: 69-83. doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-00238-z [235] Ng M R, Besser A, Danuser G, Brugge J S. 2012. Substrate stiffness regulates cadherin-dependent collective migration through myosin-II contractility. Journal of Cell Biology, 199: 545-563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201207148 [236] Nia H T, Munn L L, Jain R K. 2020. Physical traits of cancer. Science, 370: eaaz0868. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz0868 [237] Nickaeen M, Novak I L, Pulford S, Rumack A, Brandon J, et al. 2017. A free-boundary model of a motile cell explains turning behavior. PLoS Computational Biology, 13: e1005862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005862 [238] Nicolas A, Safran S A. 2006. Limitation of cell adhesion by the elasticity of the extracellular matrix. Biophysical Journal, 91: 61-73. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.077115 [239] Nicolas A, Besser A, Safran S A. 2008. Dynamics of cellular focal adhesions on deformable substrates: consequences for cell force microscopy. Biophysical Journal, 95: 527-39. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.127399 [240] Nicolas A, Geiger B, Safran S A. 2004. Cell mechanosensitivity controls the anisotropy of focal adhesions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101: 12520-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403539101 [241] Nolan J, Mahdi A F, Dunne C P, Kiely P A. 2020. Collagen and fibronectin promote an aggressive cancer phenotype in breast cancer cells but drive autonomous gene expression patterns. Gene, 761. [242] O'Connor R S, Hao X, Shen K, Bashour K, Akimova T, et al. 2012. Substrate rigidity regulates human T cell activation and proliferation. Journal of Immunology, 189: 1330-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102757 [243] Onder T T, Gupta P B, Mani S A, Yang J, Lander E S, Weinberg R A. 2008. Loss of e-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Research, 68: 3645. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2938 [244] Oria R, Wiegand T, Escribano J, Elosegui-Artola A, Uriarte J J, et al. 2017. Force loading explains spatial sensing of ligands by cells. Nature, 552: 219-224. doi: 10.1038/nature24662 [245] Owen L M, Adhikari A S, Patel M, Grimmer P, Leijnse N, et al. 2017. A cytoskeletal clutch mediates cellular force transmission in a soft, three-dimensional extracellular matrix. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 28: 1959-1974. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e17-02-0102 [246] Pannekoek W, de Rooij J, Gloerich M. 2019. Force transduction by cadherin adhesions in morphogenesis. F1000Research, 8. [247] Papusheva E, Heisenberg C-P. 2010. Spatial organization of adhesion: force-dependent regulation and function in tissue morphogenesis. EMBO Journal, 29: 2753-2768. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.182 [248] Parsons J T, Horwitz A R, Schwartz M A. Cell adhesion: integrating cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular tension. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 11: 633-643. [249] Paszek M J, Boettiger D, Weaver V M, Hammer D A. 2009. Integrin clustering is driven by mechanical resistance from the glycocalyx and the substrate. PLoS Computational Biology, 5: e1000604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000604 [250] Paszek M J, DuFort C C, Rossier O, Bainer R, Mouw J K, et al. 2014. The cancer glycocalyx mechanically primes integrin-mediated growth and survival. Nature, 511: 319-25. doi: 10.1038/nature13535 [251] Peng X, Huang J, Xiong C, Fang J. 2012. Cell adhesion nucleation regulated by substrate stiffness: a Monte Carlo study. Journal of Biomechanics, 45: 116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2011.09.013 [252] Peng Y, Chen Z, Chen Y, Li S, Jiang Y, et al. 2019. ROCK isoforms differentially modulate cancer cell motility by mechanosensing the substrate stiffness. Acta Biomaterialia, 88: 86-101. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.02.015 [253] Peng Y, Chen Z, He Y, Li P, Chen Y, et al. 2022. Non-muscle myosin II isoforms orchestrate substrate stiffness sensing to promote cancer cell contractility and migration. Cancer Letters, 524: 245-258. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.030 [254] Perez T D, Tamada M, Sheetz M P, Nelson W J. 2008. Immediate-early signaling induced by E-cadherin engagement and adhesion. Journal of Biomechanics, 283: 5014-22. [255] Petrie R J, Doyle A D, Yamada K M. 2009. Random versus directionally persistent cell migration. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 10: 538-49. doi: 10.1038/nrm2729 [256] Picaut L, Trichet L, Helary C, Ducourthial G, Bonnin M-A, et al. 2021. Core-shell pure collagen threads extruded from highly concentrated solutions promote colonization and differentiation of C3H10T1/2 cells. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 7: 626-635. [257] Piersma B, Bank R A, Boersema M. 2015. Signaling in fibrosis: TGF-β, WNT, and YAP/TAZ converge. Frontiers in Medicine (Lausanne) , 2: 59. [258] Plotnikov S V, Waterman C M. 2013. Guiding cell migration by tugging. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 25: 619-626. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.06.003 [259] Plotnikov S V, Pasapera A M, Sabass B, Waterman C M. 2012. Force fluctuations within focal adhesions mediate ECM-rigidity sensing to guide directed cell migration. Cell, 151: 1513-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.034 [260] Pollard T D, Borisy G G. 2003. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell, 112: 453-465. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00120-X [261] Priest A V, Shafraz O, Sivasankar S. 2017. Biophysical basis of cadherin mediated cell-cell adhesion. Experimental Cell Research, 358: 10-13. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.03.015 [262] Priya R, Gomez G A, Budnar S, Verma S, Cox H L, et al. 2015. Feedback regulation through myosin II confers robustness on RhoA signalling at E-cadherin junctions. Nature Cell Biology, 17: 1282-93. doi: 10.1038/ncb3239 [263] Priya R, Yap A S, Gomez G A. 2013. E-cadherin supports steady-state Rho signaling at the epithelial zonula adherens. Differentiation, 86: 133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2013.01.002 [264] Qi L, Jafari N, Li X, Chen Z, Li L, et al. 2016. Talin2-mediated traction force drives matrix degradation and cell invasion. Journal of Cell Science, 129: 3661-3674. doi: 10.1242/jcs.185959 [265] Qi Y X, Yao Q P, Huang K, Shi Q, Zhang P, et al. 2016. Nuclear envelope proteins modulate proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells during cyclic stretch application. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113: 5293-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604569113 [266] Qi Y-X, Jiang J, Jiang X-H, Wang X-D, Ji S-Y, et al. 2011. PDGF-BB and TGF-β1 on cross-talk between endothelial and smooth muscle cells in vascular remodeling induced by low shear stress. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108: 1908-1913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019219108 [267] Qian J, Liu H, Lin Y, Chen W, Gao H. 2013. A mechanochemical model of cell reorientation on substrates under cyclic stretch. PLoS One, 8: e65864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065864 [268] Qian J, Wang J, Gao H. 2008. Lifetime and strength of adhesive molecular bond clusters between elastic media. Langmuir, 24: 1262-70. doi: 10.1021/la702401b [269] Qian J, Wang J, Lin Y, Gao H. 2009. Lifetime and strength of periodic bond clusters between elastic media under inclined loading. Biophysical Journal, 97: 2438-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.08.027 [270] Qian L, Saltzman W M. 2004. Improving the expansion and neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through culture surface modification. Biomaterials, 25: 1331-1337. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.08.013 [271] Qin X, Park B O, Liu J, Chen B, Choesmel-Cadamuro V, et al. 2017. Cell-matrix adhesion and cell-cell adhesion differentially control basal myosin oscillation and Drosophila egg chamber elongation. Nature Communications, 8: 14708. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14708 [272] Qin X, Zhang Y, He Y, Chen K, Zhang Y, et al. 2021. Shear stress triggered circular dorsal ruffles formation to facilitate cancer cell migration. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 709: 108967. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2021.108967 [273] Raghupathy R, Anilkumar Anupama A, Polley A, Singh Parvinder P, Yadav M, et al. 2015. Transbilayer lipid interactions mediate nanoclustering of lipid-anchored proteins. Cell, 161: 581-594. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.048 [274] Rakshit S, Zhang Y, Manibog K, Shafraz O, Sivasankar S. 2012. Ideal, catch, and slip bonds in cadherin adhesion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109: 18815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208349109 [275] Ramaswamy G, Bidez M W, Misch C E. 2015. Chapter 6 – Bone response to mechanical loads//Dental Implant Prosthetics, 2nd edn. Netgherlands: Elsevier. [276] Ratnikov B I, Partridge AWGinsberg M H. 2005. Integrin activation by talin. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 3: 1783-1790. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01362.x [277] Redmer T, Diecke S, Grigoryan T, Quiroga-Negreira A, Birchmeier W, Besser D. 2011. E-cadherin is crucial for embryonic stem cell pluripotency and can replace OCT4 during somatic cell reprogramming. EMBO Reports, 12: 720-726. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.88 [278] Rees D J G, Ades S E, Singer S J, Hynes R O. 1990. Sequence and domain structure of talin. Nature, 347: 685-689. doi: 10.1038/347685a0 [279] Rens E G, Merks R M H. 2020. Cell Shape and Durotaxis Explained from Cell-Extracellular Matrix Forces and Focal Adhesion Dynamics. iScience, 23: 101488. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101488 [280] Richardson A M, Havel L S, Koyen A E, Konen J M, Shupe J, et al. 2018. Vimentin is required for lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via heterotypic tumor cell-cancer-associated fibroblast interactions during collective invasion. Clinical Cancer Research, 24: 420-432. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1776 [281] Ridley A J. 2006. Rho GTPases and actin dynamics in membrane protrusions and vesicle trafficking. Trends in Cell Biology, 16: 522-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.08.006 [282] Roca-Cusachs P, Iskratsch T, Sheetz M. 2012. Finding the weakest link: Exploring integrin-mediated mechanical molecular pathways. Journal of Cell Science, 125: 3025-38. [283] Romanazzo S, Lin K, Srivastava P, Kilian K A. 2020. Targeting cell plasticity for regeneration: From in vitro to in vivo reprogramming. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 161-162: 124-144. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.08.007 [284] Ronen Z B, Benjamin G. 2010. The switchable integrin adhesome. Journal of Cell Science, 123: 1385-1388. doi: 10.1242/jcs.066183 [285] Roy B, Venkatachalapathy S, Ratna P, Wang Y, Jokhun D S, et al. 2018. Laterally confined growth of cells induces nuclear reprogramming in the absence of exogenous biochemical factors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115: E4741. [286] Roy B, Yuan L, Lee Y, Bharti A, Mitra A, Shivashankar G V. 2020. Fibroblast rejuvenation by mechanical reprogramming and redifferentiation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117: 10131-10141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911497117 [287] Ruggiero F, Comte J, Cabañas C, Garrone R. 1996. Structural requirements for alpha 1 beta 1 and alpha 2 beta 1 integrin mediated cell adhesion to collagen V. Journal of Cell Science, 109 ( Pt 7): 1865-1874. [288] Saenz-de-Santa-Maria I, Celada L, Chiara M D. 2020. The leader position of mesenchymal cells expressing n-cadherin in the collective migration of epithelial cancer. Cells, 9: 731. doi: 10.3390/cells9030731 [289] Saunders R M, Holt M R, Jennings L, Sutton D H, Barsukov I L, et al. 2006. Role of vinculin in regulating focal adhesion turnover. European Journal of Cell Biology, 85: 487-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.014 [290] Schiller H B, Hermann M R, Polleux J, Vignaud T, Zanivan S, et al. 2013. Beta1- and alphav-class integrins cooperate to regulate myosin II during rigidity sensing of fibronectin-based microenvironments. Nature Cell Biology, 15: 625-36. doi: 10.1038/ncb2747 [291] Schnittert J, Bansal R, Storm G, Prakash J. 2018. Integrins in wound healing, fibrosis and tumor stroma: High potential targets for therapeutics and drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 129: 37-53. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.01.020 [292] Schroeder M E, Gonzalez Rodriguez A, Speckl K F, Walker C J, Midekssa F S, et al. 2021. Collagen networks within 3D PEG hydrogels support valvular interstitial cell matrix mineralization. Acta Biomaterialia, 119: 197-210. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.11.012 [293] Segel M, Neumann B, Hill M F E, Weber I P, Viscomi C, et al. 2019. Niche stiffness underlies the ageing of central nervous system progenitor cells. Nature, 573: 130-134. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1484-9 [294] Seong J, Tajik A, Sun J, Guan J-L, Humphries M J, et al. 2013. Distinct biophysical mechanisms of focal adhesion kinase mechanoactivation by different extracellular matrix proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110: 19372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307405110 [295] Shapiro L, Weis W I. 2009. Structure and biochemistry of cadherins and catenins. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 1: a003053. [296] Shapiro L, Fannon A M, Kwong P D, Thompson A, Lehmann M S, et al. 1995. Structural basis of cell-cell adhesion by cadherins. Nature, 374: 327-37. doi: 10.1038/374327a0 [297] Shellard A, Mayor R. 2020. All Roads Lead to Directional Cell Migration. Trends in Cell Biology, 30: 852-868. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.08.002 [298] Shibata A C E, Fujiwara T K, Chen L, Suzuki K G N, Ishikawa Y, et al. 2012. Archipelago architecture of the focal adhesion: Membrane molecules freely enter and exit from the focal adhesion zone. Cytoskeleton, 69: 380-392. doi: 10.1002/cm.21032 [299] Shih Y R, Tseng K F, Lai H Y, Lin C H, Lee O K. 2011. Matrix stiffness regulation of integrin-mediated mechanotransduction during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 26: 730-8. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.278 [300] Shiu J-Y, Aires L, Lin Z, Vogel V. 2018. Nanopillar force measurements reveal actin-cap-mediated YAP mechanotransduction. Nature Cell Biology, 20: 262-271. doi: 10.1038/s41556-017-0030-y [301] Shivashankar G V. 2019. Mechanical regulation of genome architecture and cell-fate decisions. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 56: 115-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2018.12.001 [302] Silva C S, Pinto R D, Amorim S, Pires R A, Correia-Neves M, et al. 2020. Fibronectin-functionalized fibrous meshes as a substrate to support cultures of thymic epithelial cells. Biomacromolecules, 21: 4771-4780. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00933 [303] Sivasankar S. 2013. Tuning the kinetics of cadherin adhesion. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 133: 2318-2323. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.229 [304] Slack R J, Macdonald S J F, Roper J A, Jenkins R G, Hatley R J D. 2022. Emerging therapeutic opportunities for integrin inhibitors. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 21: 60-78. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00284-4 [305] Slováková J, Sikora M, Arslan F N, Caballero-Mancebo S, Krens S F G, et al. 2022. Tension-dependent stabilization of E-cadherin limits cell–cell contact expansion in zebrafish germ-layer progenitor cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119: e2122030119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2122030119 [306] Smith M A, Hoffman L M, Beckerle M C. 2014. LIM proteins in actin cytoskeleton mechanoresponse. Trends in Cell Biology, 24: 575-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.04.009 [307] Smith Q, Chan X Y, Carmo A M, Trempel M, Saunders M, Gerecht S. 2017. Compliant substratum guides endothelial commitment from human pluripotent stem cells. Science Advances, 3: e1602883. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1602883 [308] Smutny M, Cox H L, Leerberg J M, Kovacs E M, Conti M A, et al. 2010. Myosin II isoforms identify distinct functional modules that support integrity of the epithelial zonula adherens. Nature Cell Biology, 12: 696-702. doi: 10.1038/ncb2072 [309] S Sonal, Ganzinger K A, Vogel S K, Mücksch J, Blumhardt P, Schwille P. 2018. Myosin-II activity generates a dynamic steady state with continuous actin turnover in a minimal actin cortex. Journal of Cell Science, 132: JCS219899. [310] Spoerri P M, Strohmeyer N, Sun Z, Fässler R, Müller D J. 2020. Protease-activated receptor signalling initiates α(5)β(1)-integrin-mediated adhesion in non-haematopoietic cells. Nature Materials, 19: 218-226. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0580-4 [311] Srichai M B, Zent R. 2010. Integrin Structure and Function//Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions in Cancer. New York: Springer [312] Stephanou A, Mylona E, Chaplain M, Tracqui P. 2008. A computational model of cell migration coupling the growth of focal adhesions with oscillatory cell protrusions. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 253: 701-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.04.035 [313] Strohmeyer N, Bharadwaj M, Costell M, Fässler R, Müller D J. 2017. Fibronectin-bound α5β1 integrins sense load and signal to reinforce adhesion in less than a second. Nature Materials, 16: 1262-1270. doi: 10.1038/nmat5023 [314] Stutchbury B, Atherton P, Tsang R, Wang D Y, Ballestrem C. 2017. Distinct focal adhesion protein modules control different aspects of mechanotransduction. Journal of Cell Science, 130: 1612-1624. [315] Sun M, Spill F, Zaman Muhammad H. 2016. A Computational Model of YAP/TAZ Mechanosensing. Biophysical Journal, 110: 2540-2550. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.04.040 [316] Sun Z, Costell M, Faessler R. 2019. Integrin activation by talin, kindlin and mechanical forces. Nature Cell Biology, 21: 25-31. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0234-9 [317] Sun Z, Guo S S, Fässler R. 2016. Integrin-mediated mechanotransduction. Journal of Cell Biology, 215: 445-456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201609037 [318] Sun Z, Tseng H Y, Tan S, Senger F, Kurzawa L, et al. 2016. Kank2 activates talin, reduces force transduction across integrins and induces central adhesion formation. Nature Cell Biology, 18: 941-53. doi: 10.1038/ncb3402 [319] Sung Haeng L, Roberto D. 2010. Regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics in cells. Molecules & Cells, 29: 311-325. [320] Sunyer R, Conte V, Escribano J, Elosegui-Artola A, Labernadie A, et al. 2016. Collective cell durotaxis emerges from long-range intercellular force transmission. Science, 353: 1157-1161. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf7119 [321] Tadokoro S, Shattil S J, Eto K, Tai V, Liddington R C, et al. 2003. Talin binding to integrin β tails: a final common step in integrin activation. Science, 302: 103-106. doi: 10.1126/science.1086652 [322] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. 2006. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell, 126: 663-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024 [323] Takeichi M. 1991. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science, 251: 1451-1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419 [324] Takeichi M. 2014. Dynamic contacts: rearranging adherens junctions to drive epithelial remodelling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 15: 397-410. doi: 10.1038/nrm3802 [325] Tam R Y, Smith L J, Shoichet M S. 2017. Engineering cellular microenvironments with photo- and enzymatically responsive hydrogels: toward biomimetic 3d cell culture models. Accounts of Chemical Research, 50: 703-713. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00543 [326] Tang K, Xin Y, Li K, Chen X, Tan Y. 2021. Cell cytoskeleton and stiffness are mechanical indicators of organotropism in breast cancer. Biology, 10: 259. doi: 10.3390/biology10040259 [327] Tang S, Ma H, Tu H-C, Wang H-R, Lin P-C, Anseth K S. 2018. Adaptable fast relaxing boronate-based hydrogels for probing cell–matrix interactions. Advanced Science, 5: 1800638. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800638 [328] Tang Y, Feinberg T, Keller E T, Li X-Y, Weiss S J. 2016. Snail/slug binding interactions with yap/taz control skeletal stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Nature Cell Biology, 18: 917-929. doi: 10.1038/ncb3394 [329] Tao J, Li Y, Vig D K, Sun S X. 2017. Cell mechanics: a dialogue. Reports on Progress in Physics, 80: 036601. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/aa5282 [330] Tashiro K, Monji A, I, Hayashi Y, Matsuda K, Tashiro N, Mitsuyama Y. 1999. An IKLLI-containing peptide derived from the laminin alpha1 chain mediating heparin-binding, cell adhesion, neurite outgrowth and proliferation, represents a binding site for integrin alpha3beta1 and heparan sulphate proteoglycan. Biochemical Journal, 340: 119-126. doi: 10.1042/bj3400119 [331] Terekhova K, Pokutta S, Kee Y S, Li J, Tajkhorshid E, et al. 2019. Binding partner- and force-promoted changes in αE-catenin conformation probed by native cysteine labeling. Scientific Reports, 9: 15375. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51816-3 [332] Tomakidi P, Schulz S, Proksch S, Weber W, Steinberg T. 2014. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) perspectives in mechanobiology: implications for cell behaviour. Cell and Tissue Research, 357: 515-26. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1945-2 [333] Totaro A, Castellan M, Battilana G, Zanconato F, Azzolin L, et al. 2017. YAP/TAZ link cell mechanics to notch signalling to control epidermal stem cell fate. Nature Communications, 8: 15206. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15206 [334] Trujillo S, Vega S L, Song K H, San Felix A, Dalby M J, et al. 2020. Engineered full-length fibronectin-hyaluronic acid hydrogels for stem cell engineering. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 9: e2000989. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202000989 [335] van der Flier A, Sonnenberg A. 2001. Function and interactions of integrins. Cell and Tissue Research, 305: 285-98. doi: 10.1007/s004410100417 [336] Vazquez-Hidalgo E, Farris C M, Rowat A C, Katira P. 2022. Chemo-mechanical factors that limit cellular force generation. Frontiers in Physics, 10: 831776. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2022.831776 [337] Velling T, Kusche-Gullberg M, Sejersen T, Gullberg D. 1999. cDNA cloning and chromosomal localization of human alpha(11) integrin. A collagen-binding, I domain-containing, beta(1)-associated integrin alpha-chain present in muscle tissues. Journal of Biomechanics, 274: 25735-25742. [338] Venhuizen J-H, Zegers M M. 2017. Making heads or tails of it: cell-cell adhesion in cellular and supracellular polarity in collective migration. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 9: a027854. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027854 [339] Vining K H, Mooney D J. 2017. Mechanical forces direct stem cell behaviour in development and regeneration. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 18: 728. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.108 [340] Wahl A, Dinet C, Dillard P, Nassereddine A, Puech P H, et al. 2019. Biphasic mechanosensitivity of T cell receptor-mediated spreading of lymphocytes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116: 5908-5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811516116 [341] Walcott S, Kim D H, Wirtz D, Sun S X. 2011. Nucleation and decay initiation are the stiffness-sensitive phases of focal adhesion maturation. Biophysical Journal, 101: 2919-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.11.010 [342] Wan W, Cheng B, Zhang C, Ma Y, Li A, et al. 2019. Synergistic effect of matrix stiffness and inflammatory factors on osteogenic differentiation of msc. Biophysical Journal, 117: 129-142. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.05.019 [343] Wang J, Gao H. 2008. Clustering instability in adhesive contact between elastic solids via diffusive molecular bonds. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 56: 251-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2007.05.011 [344] Wang X, Li S, Yan C, Liu P, Ding J. 2015. Fabrication of RGD micro/nanopattern and corresponding study of stem cell differentiation. Nano Letters, 15: 1457-67. doi: 10.1021/nl5049862 [345] Wang Y-K, Chen C S. 2013. Cell adhesion and mechanical stimulation in the regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 17: 823-832. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12061 [346] Wehrle-Haller B. 2007. Analysis of Integrin Dynamics by Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching. Methods in Molecular Biology, 370: 173-202. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-353-0_13 [347] Welf E S, Johnson H E, Haugh J M. 2013. Bidirectional coupling between integrin-mediated signaling and actomyosin mechanics explains matrix-dependent intermittency of leading-edge motility. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 24: 3945-55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e13-06-0311 [348] Wells R G. 2008. The role of matrix stiffness in regulating cell behavior. Hepatology, 47: 1394-1400. doi: 10.1002/hep.22193 [349] Winograd-Katz S E, Fässler R, Geiger B, Legate K R. 2014. The integrin adhesome: from genes and proteins to human disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 15: 273-288. doi: 10.1038/nrm3769 [350] Wolfenson H, Yang B, Sheetz M P. 2019. Steps in Mechanotransduction Pathways that Control Cell Morphology. Annual Review of Physiology, 81: 585-605. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021317-121245 [351] Wu Y, Honig B, Ben-Shaul A. 2013. Theory and simulations of adhesion receptor dimerization on membrane surfaces. Biophysical Journal, 104: 1221-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.02.009 [352] Wu Y, Jin X, Harrison O, Shapiro L, Honig B H, Ben-Shaul A. 2010. Cooperativity between trans and cis interactions in cadherin-mediated junction formation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107: 17592-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011247107 [353] Wu Y, Vendome J, Shapiro L, Ben-Shaul A, Honig B. 2011. Transforming binding affinities from three dimensions to two with application to cadherin clustering. Nature, 475: 510-3. doi: 10.1038/nature10183 [354] Xia S, Kanchanawong P. 2017. Nanoscale mechanobiology of cell adhesions. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 71: 53-67. [355] Xia Y, Pfeifer C R, Cho S, Discher D E, Irianto J. 2018. Nuclear mechanosensing. Emerging Topics in Life Sciences, 2: 713-725. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20180051 [356] Xiao P, Cuff L E, Lawton C D, Demali K A. 2010. Vinculin regulates cell-surface E-cadherin expression by binding to beta-catenin. Journal of Cell Science, 123: 567-577. doi: 10.1242/jcs.056432 [357] Xie Z R, Chen J, Wu Y. 2014. A coarse-grained model for the simulations of biomolecular interactions in cellular environments. Journal of Chemical Physics, 140: 054112. doi: 10.1063/1.4863992 [358] Xu K, Shuai Q, Li X, Zhang Y, Gao C, et al. 2016. Human VE-Cadherin Fusion Protein as an Artificial Extracellular Matrix Enhancing the Proliferation and Differentiation Functions of Endothelial Cell. Biomacromolecules, 17: 756-766. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01467 [359] Xu L, Gutbrod S R, Bonifas A P, Su Y, Sulkin M S, et al. 2014. 3D multifunctional integumentary membranes for spatiotemporal cardiac measurements and stimulation across the entire epicardium. Nature Communications, 5: 3329. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4329 [360] Yamauchi M, Barker T H, Gibbons D L, Kurie J M. 2018. The fibrotic tumor stroma. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 128: 16-25. doi: 10.1172/JCI93554 [361] Yang C, DelRio F W, Ma H, Killaars A R, Basta L P, et al. 2016. Spatially patterned matrix elasticity directs stem cell fate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113: E4439-45. [362] Yang C, Tibbitt M W, Basta L, Anseth K S. 2014. Mechanical memory and dosing influence stem cell fate. Nature Materials, 13: 645-652. doi: 10.1038/nmat3889 [363] Yang Y, Jiang H. 2017. Shape and Dynamics of Adhesive Cells: Mechanical Response of Open Systems. Physical Review Letters, 118: 208102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.208102 [364] Yang Y, Jiang H. 2018. Cellular volume regulation and substrate stiffness modulate the detachment dynamics of adherent cells. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 112: 594-618. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2017.10.009 [365] Ye K, Wang X, Cao L, Li S, Li Z, et al. 2015. Matrix stiffness and nanoscale spatial organization of cell-adhesive ligands direct stem cell fate. Nano Letters, 15: 4720-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01619 [366] Yeung T, Georges P C, Flanagan L A, Marg B, Ortiz M, et al. 2005. Effects of substrate stiffness on cell morphology, cytoskeletal structure, and adhesion. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton, 60: 24-34. doi: 10.1002/cm.20041 [367] Yi B, Xu Q, Liu W. 2021. An overview of substrate stiffness guided cellular response and its applications in tissue regeneration. Bioactive Materials, 15: 82-102. [368] Yonemura S, Wada Y T, Nagafuchi A, Shibata M. 2010. alpha-Catenin as a tension transducer that induces adherens junction development. Nature Cell Biology, 12: 533-542. doi: 10.1038/ncb2055 [369] Yu J, Huang J, Jansen J A, Xiong C, Walboomers X F. 2017. Mechanochemical mechanism of integrin clustering modulated by nanoscale ligand spacing and rigidity of extracellular substrates. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 72: 29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.04.018 [370] Yue X-S, Murakami Y, Tamai T, Nagaoka M, Cho C-S, et al. 2010. A fusion protein N-cadherin-Fc as an artificial extracellular matrix surface for maintenance of stem cell features. Biomaterials, 31: 5287-5296. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.035 [371] Yuka M, Naoko I, Koji N, Nagatoki K, Hiroshi H, Shigenobu Y. 2006. Actomyosin tension is required for correct recruitment of adherens junction components and zonula occludens formation. Experimental Cell Research, 312: 1637-1650. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.01.031 [372] Zamir E, Katz M, Posen Y, Erez N, Yamada K M, et al. 2000. Dynamics and segregation of cell-matrix adhesions in cultured fibroblasts. Nature Cell Biology, 2: 191-6. doi: 10.1038/35008607 [373] Zeeshan R, Mutahir Z. 2017. Cancer metastasis - tricks of the trade. Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 17: 172-182. [374] Zhang C, Zhu H, Ren X, Gao B, Cheng B, et al. 2021. Mechanics-driven nuclear localization of YAP can be reversed by N-cadherin ligation in mesenchymal stem cells. Nature Communications, 12: 6229. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26454-x [375] Zhang G, Ma L, Bai L, Li M, Guo T, et al. 2021. Inflammatory microenvironment-targeted nanotherapies. Journal of Controlled Release, 334: 114-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.04.018 [376] Zhang S, Teng X, Toyama Y, Saunders T E. 2020. Periodic oscillations of myosin-ii mechanically proofread cell-cell connections to ensure robust formation of the cardiac vessel. Current Biology, 30: 3364-3377.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.06.041 [377] Zhang Y, Mao H, Qian M, Hu F, Cao L, et al. 2016. Surface modification with E-cadherin fusion protein for mesenchymal stem cell culture. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 4: 4267-4277. doi: 10.1039/C6TB00765A [378] Zhang Y, Qin Z, Qu Z, Ge M, Yang J. 2020. Cadherin-based biomaterials: Inducing stem cell fate towards tissue construction and therapeutics. Progress in Natural Science:Materials International, 30: 597-608. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2020.09.001 [379] Zheng C, Chen J, Liu S, Jin Y. 2019. Stem cell-based bone and dental regeneration: a view of microenvironmental modulation. International Journal of Oral Science, 11: 23. doi: 10.1038/s41368-019-0060-3 [380] Zhong C, Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M, Brown J, Shaub A, Belkin A M, Burridge K. 1998. Rho-mediated contractility exposes a cryptic site in fibronectin and induces fibronectin matrix assembly. Journal of Cell Biology, 141: 539-51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.2.539 [381] Zhou J, Lee P L, Tsai C S, Lee C I, Yang T L, et al. 2012. Force-specific activation of Smad1/5 regulates vascular endothelial cell cycle progression in response to disturbed flow. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109: 7770-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205476109 [382] Zhou J, Wang K-C, Wu W, Subramaniam S, Shyy J Y J, et al. 2011. MicroRNA-21 targets peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-alpha in an autoregulatory loop to modulate flow-induced endothelial inflammation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108: 10355-10360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107052108 [383] Zhu M, Lin S, Sun Y, Feng Q, Li G, Bian L. 2016. Hydrogels functionalized with N-cadherin mimetic peptide enhance osteogenesis of hMSCs by emulating the osteogenic niche. Biomaterials, 77: 44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.10.072 [384] Zuidema A, Wang W, Sonnenberg A. 2020. Crosstalk between Cell Adhesion Complexes in Regulation of Mechanotransduction. Bioessays, 42: 2000119. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000119 -




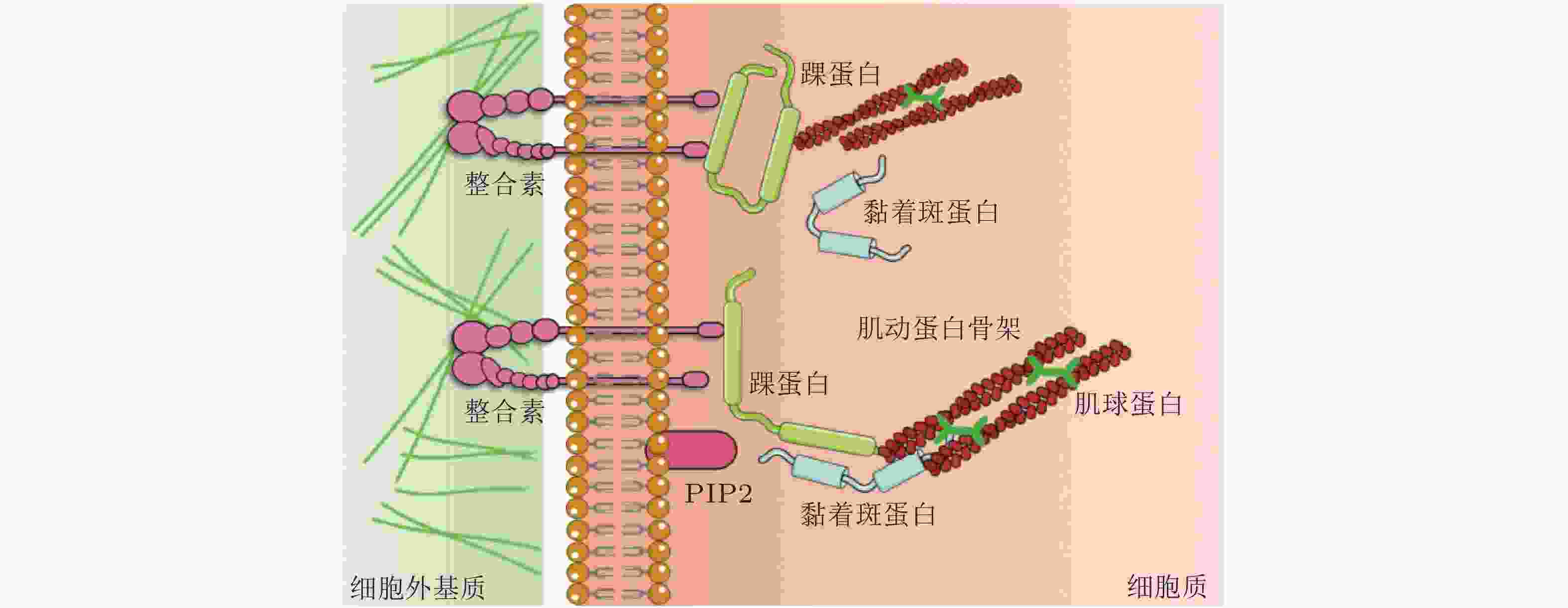
 下载:
下载: